| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-MLH-1 monoclonal antibody (ZR347) 6258
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
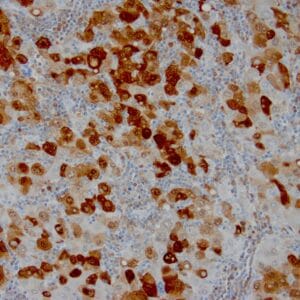
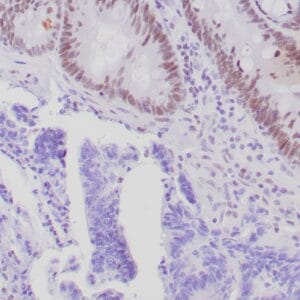
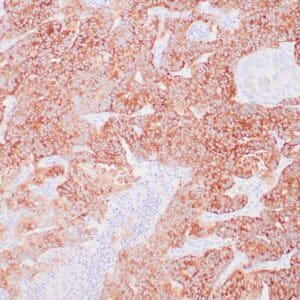
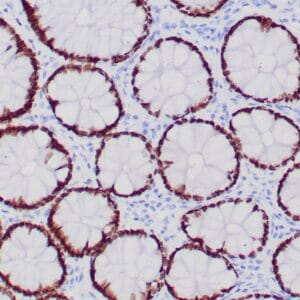
- Rabbit monoclonal to MLH-1
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
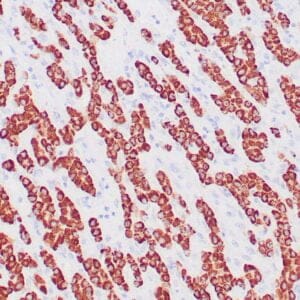
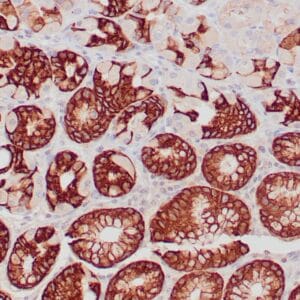
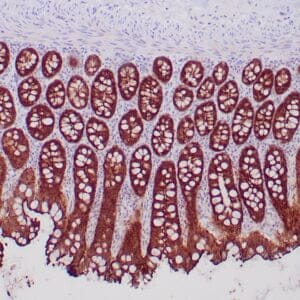
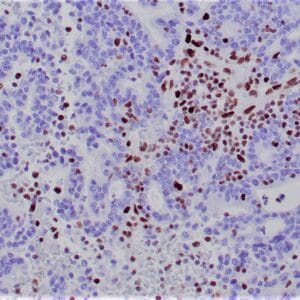
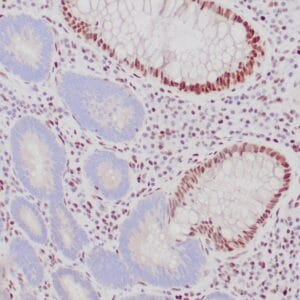
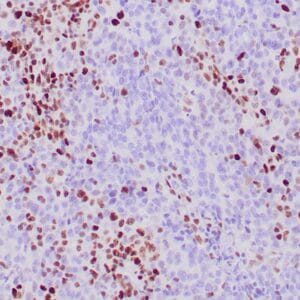
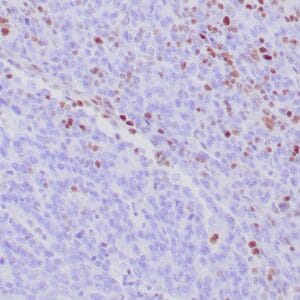
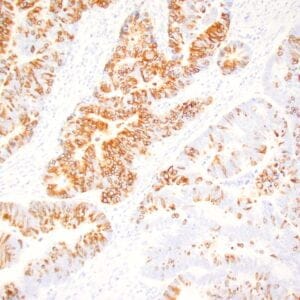
- Control: Colon carcinoma
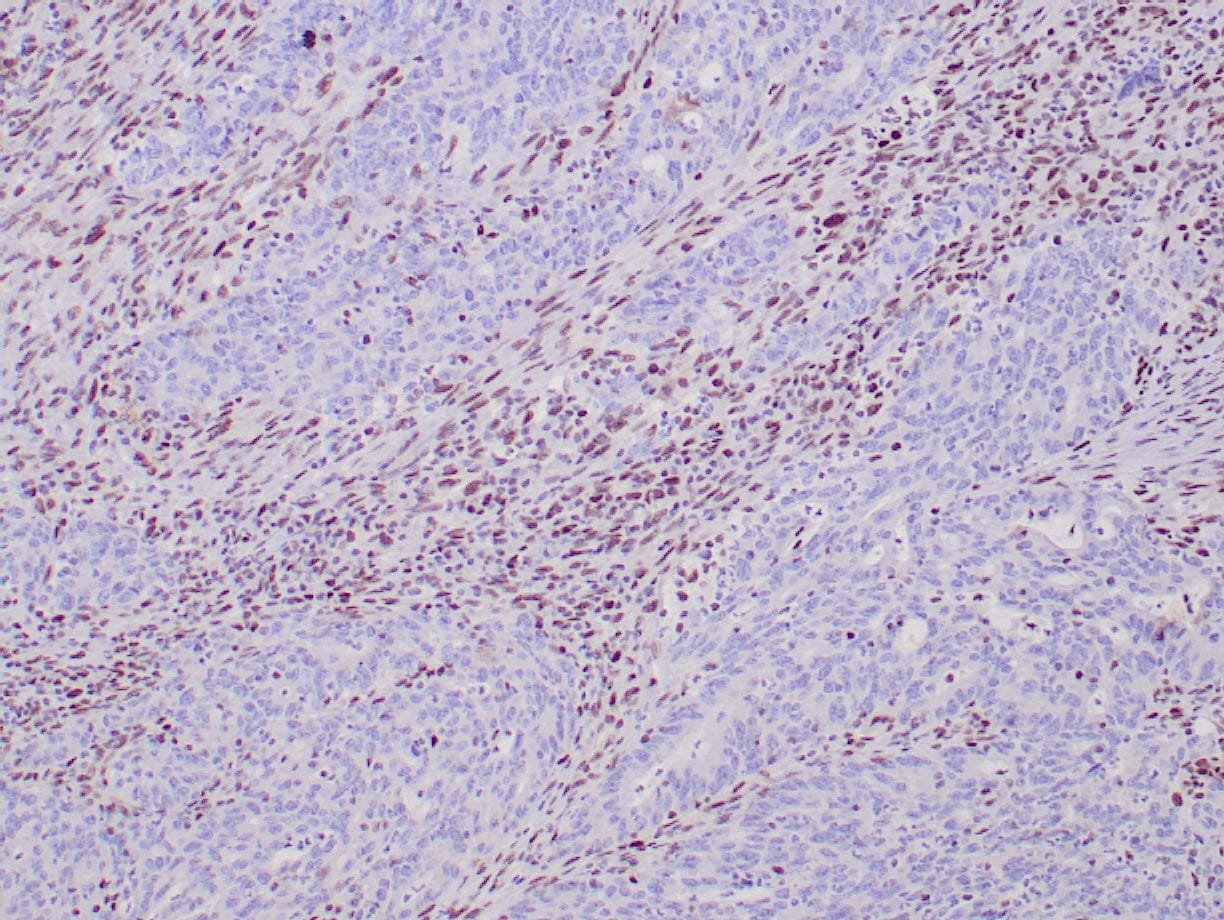
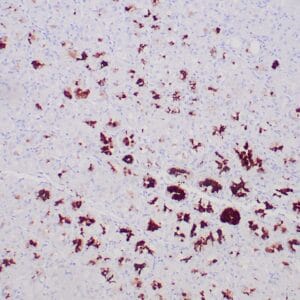
- Visualization: Nuclear
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-MLH-1 monoclonal antibody ZR347 6258
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh1 (MutL protein homolog 1) |
| Gene names MLH1,MLH1 COCA2 |
| Mass 84601Da |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.