| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-HSP70 monoclonal antibody (ZR152) 6217
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to HSP70
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:Rabbit IgG
- Control: Hepatocellular carcinoma
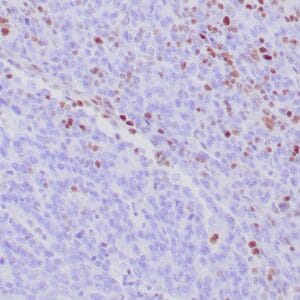
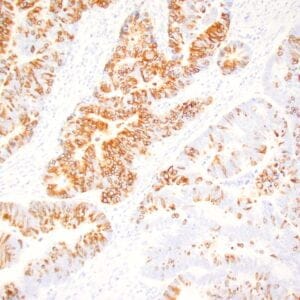
- Visualization: Nuclear and cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-HSP70 monoclonal antibody ZR152 6217
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein (EC 3.6.4.10) (Heat shock 70 kDa protein 8) (Heat shock protein family A member 8) (Lipopolysaccharide-associated protein 1) (LAP-1) (LPS-associated protein 1) |
| Gene names HSPA8,HSPA8 HSC70 HSP73 HSPA10 |
| Protein family Heat shock protein 70 family |
| Mass 70898Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Molecular chaperone implicated in a wide variety of cellular processes, including protection of the proteome from stress, folding and transport of newly synthesized polypeptides, chaperone-mediated autophagy, activation of proteolysis of misfolded proteins, formation and dissociation of protein complexes, and antigen presentation. Plays a pivotal role in the protein quality control system, ensuring the correct folding of proteins, the re-folding of misfolded proteins and controlling the targeting of proteins for subsequent degradation (PubMed:21148293, PubMed:21150129, PubMed:23018488, PubMed:24732912, PubMed:27916661, PubMed:2799391, PubMed:36586411). This is achieved through cycles of ATP binding, ATP hydrolysis and ADP release, mediated by co-chaperones (PubMed:12526792, PubMed:21148293, PubMed:21150129, PubMed:23018488, PubMed:24732912, PubMed:27916661). The co-chaperones have been shown to not only regulate different steps of the ATPase cycle of HSP70, but they also have an individual specificity such that one co-chaperone may promote folding of a substrate while another may promote degradation (PubMed:12526792, PubMed:21148293, PubMed:21150129, PubMed:23018488, PubMed:24732912, PubMed:27916661). The affinity of HSP70 for polypeptides is regulated by its nucleotide bound state. In the ATP-bound form, it has a low affinity for substrate proteins. However, upon hydrolysis of the ATP to ADP, it undergoes a conformational change that increases its affinity for substrate proteins. HSP70 goes through repeated cycles of ATP hydrolysis and nucleotide exchange, which permits cycles of substrate binding and release. The HSP70-associated co-chaperones are of three types: J-domain co-chaperones HSP40s (stimulate ATPase hydrolysis by HSP70), the nucleotide exchange factors (NEF) such as BAG1/2/3 (facilitate conversion of HSP70 from the ADP-bound to the ATP-bound state thereby promoting substrate release), and the TPR domain chaperones such as HOPX and STUB1 (PubMed:24121476, PubMed:24318877, PubMed:26865365, PubMed:27474739). Plays a critical role in mitochondrial import, delivers preproteins to the mitochondrial import receptor TOMM70 (PubMed:12526792). Acts as a repressor of transcriptional activation. Inhibits the transcriptional coactivator activity of CITED1 on Smad-mediated transcription. Component of the PRP19-CDC5L complex that forms an integral part of the spliceosome and is required for activating pre-mRNA splicing. May have a scaffolding role in the spliceosome assembly as it contacts all other components of the core complex. Binds bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and mediates LPS-induced inflammatory response, including TNF secretion by monocytes (PubMed:10722728, PubMed:11276205). Substrate recognition component in chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), a selective protein degradation process that mediates degradation of proteins with a -KFERQ motif: HSPA8/HSC70 specifically recognizes and binds cytosolic proteins bearing a -KFERQ motif and promotes their recruitment to the surface of the lysosome where they bind to lysosomal protein LAMP2 (PubMed:11559757, PubMed:2799391, PubMed:36586411). KFERQ motif-containing proteins are eventually transported into the lysosomal lumen where they are degraded (PubMed:11559757, PubMed:2799391, PubMed:36586411). In conjunction with LAMP2, facilitates MHC class II presentation of cytoplasmic antigens by guiding antigens to the lysosomal membrane for interaction with LAMP2 which then elicits MHC class II presentation of peptides to the cell membrane (PubMed:15894275). Participates in the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) quality control pathway in conjunction with J domain-containing co-chaperones and the E3 ligase STUB1 (PubMed:23990462). It is recruited to clathrin-coated vesicles through its interaction with DNAJC6 leading to activation of HSPA8/HSC70 ATPase activity and therefore uncoating of clathrin-coated vesicles (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P19120, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10722728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11276205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11559757, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12526792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15894275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21148293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21150129, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23018488, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23990462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24318877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24732912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27474739, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27916661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2799391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36586411, ECO:0000303|PubMed:24121476, ECO:0000303|PubMed:26865365}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:13065, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:43474, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=3.6.4.10; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:12526792}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17289661}. Melanosome {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17081065}. Nucleus, nucleolus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1586970}. Cell membrane. Lysosome membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11559757}; Peripheral membrane protein {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11559757}; Cytoplasmic side {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11559757}. Note=Localized in cytoplasmic mRNP granules containing untranslated mRNAs (PubMed:17289661). Translocates rapidly from the cytoplasm to the nuclei, and especially to the nucleoli, upon heat shock (PubMed:1586970). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1586970, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17289661}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Ubiquitous. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11276205}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Identified in a IGF2BP1-dependent mRNP granule complex containing untranslated mRNAs. Interacts with PACRG. Interacts with HSPH1/HSP105. Interacts with IRAK1BP1 and BAG1. Interacts with DNAJC7. Interacts with DNAJB12 (via J domain) (PubMed:21148293, PubMed:21150129, PubMed:24732912, PubMed:27916661). Interacts with DNAJB14 (via J domain) (PubMed:23018488, PubMed:24732912, PubMed:27916661). Interacts (via C-terminus) with the E3 ligase CHIP forming a 210 kDa complex of one CHIP and two HSPA8 molecules. Interacts with CITED1 (via N-terminus); the interaction suppresses the association of CITED1 to p300/CBP and Smad-mediated transcription transactivation. Component of the PRP19-CDC5L splicing complex composed of a core complex comprising a homotetramer of PRPF19, CDC5L, PLRG1 and BCAS2, and at least three less stably associated proteins CTNNBL1, CWC15 and HSPA8. Interacts with TRIM5. Part of a complex composed at least of ASH2L, EMSY, HCFC1, HSPA8, CCAR2, MATR3, MKI67, RBBP5, TUBB2A, WDR5 and ZNF335; this complex may have a histone H3-specific methyltransferase activity. Interacts with METTL21A. Following LPS binding, may form a complex with CXCR4, GDF5 and HSP90AA1. Interacts with PRKN. Interacts with FOXP3. Interacts with DNAJC9 (via J domain) (PubMed:17182002). Interacts with MLLT11 (PubMed:24880125). Interacts with RNF207 (PubMed:25281747). Interacts with DNAJC21 (PubMed:27346687). Interacts with DNAJB2 (PubMed:15936278). Interacts with TTC1 (via TPR repeats) (PubMed:15708368). Interacts with SGTA (via TPR repeats) (By similarity). Interacts with HSF1 (via transactivation domain) (PubMed:9499401). Interacts with HOPX, HSP40 and HSP90 (PubMed:27708256). Interacts with STUB1 (PubMed:27708256). Interacts with BAG2 (PubMed:24318877). Interacts with BAG3 (PubMed:24318877, PubMed:27474739). Interacts with DNAJC12 (PubMed:24122553). Interacts with ZMYND10 (PubMed:29601588). Interacts with HSPC138 (PubMed:25760597). Interacts with BCL2L1, GIMAP5 and MCL1; the interaction with BCL2L1 or MCL1 is impaired in the absence of GIMAP5 (By similarity). Interacts with NLPR12 (PubMed:17947705). Interacts with TTC4 (PubMed:18320024). Interacts with TOMM70; the interaction is required for preprotein mitochondrial import (PubMed:12526792). May interact with DNJC9; the interaction seems to be histone-dependent (PubMed:33857403). Interacts with BAG5 and JPH2; the interaction with JPH2 is increased in the presence of BAG5 (PubMed:35044787). Interacts with VGF-derived peptide TLQP-21 (PubMed:28934328). Interacts with molecular chaperone MIPEP155 (via N-terminal ATP-binding region); the interaction results in reduced ATPase activity of HSPA8, impaired interaction of HSPA8 with HSP90 and reduced lysosomal antigen trafficking (PubMed:32671205). Interacts with CDKN1B; the interaction may be associated with susceptibility to ubiquitination (PubMed:26775844). Interacts with HTN3 peptide Hst3; the interaction enhances HSPA8-CDKN1B complex formation (PubMed:26775844). Interacts with DNAJC6 (via J domain) in an ATP-dependent manner; this interaction stimulates the HSPA8's ATPase activity. Forms a complex composed of HSPA8, CLTC and DNAJC6 (By similarity). Interacts with HSPA8; this interaction modulates migratory and antigen-presenting capacities of dendritic cells (PubMed:17785435). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P19120, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63017, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63018, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10722728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11276205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12526792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14532270, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15708368, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15936278, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15963462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16815975, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17182002, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17289661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17785435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17947705, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18320024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19131338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20053985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21148293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21150129, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23018488, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23865999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23921388, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23973223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23990462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24122553, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24270810, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24318877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24732912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24880125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25281747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25760597, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26775844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27346687, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27474739, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27708256, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27916661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28934328, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29601588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32671205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33857403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35044787, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9305631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9499401, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9679980}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with SV40 VP1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11147964}.; SUBUNIT: (Microbial infection) Interacts with human herpes virus 1 (HHV-1) transcriptional regulator ICP22; this interaction recruits HSPA8/HSP40 to discrete nuclear foci. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31748398}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Acetylated. {ECO:0000269|Ref.5, ECO:0000269|Ref.6}.; PTM: ISGylated. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16139798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16815975}.; PTM: Trimethylation at Lys-561 reduces fibrillar SNCA binding. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The N-terminal nucleotide binding domain (NBD) (also known as the ATPase domain) is responsible for binding and hydrolyzing ATP. The C-terminal substrate-binding domain (SBD) (also known as peptide-binding domain) binds to the client/substrate proteins. The two domains are allosterically coupled so that, when ATP is bound to the NBD, the SBD binds relatively weakly to clients. When ADP is bound in the NBD, a conformational change enhances the affinity of the SBD for client proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9305631}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P11142 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
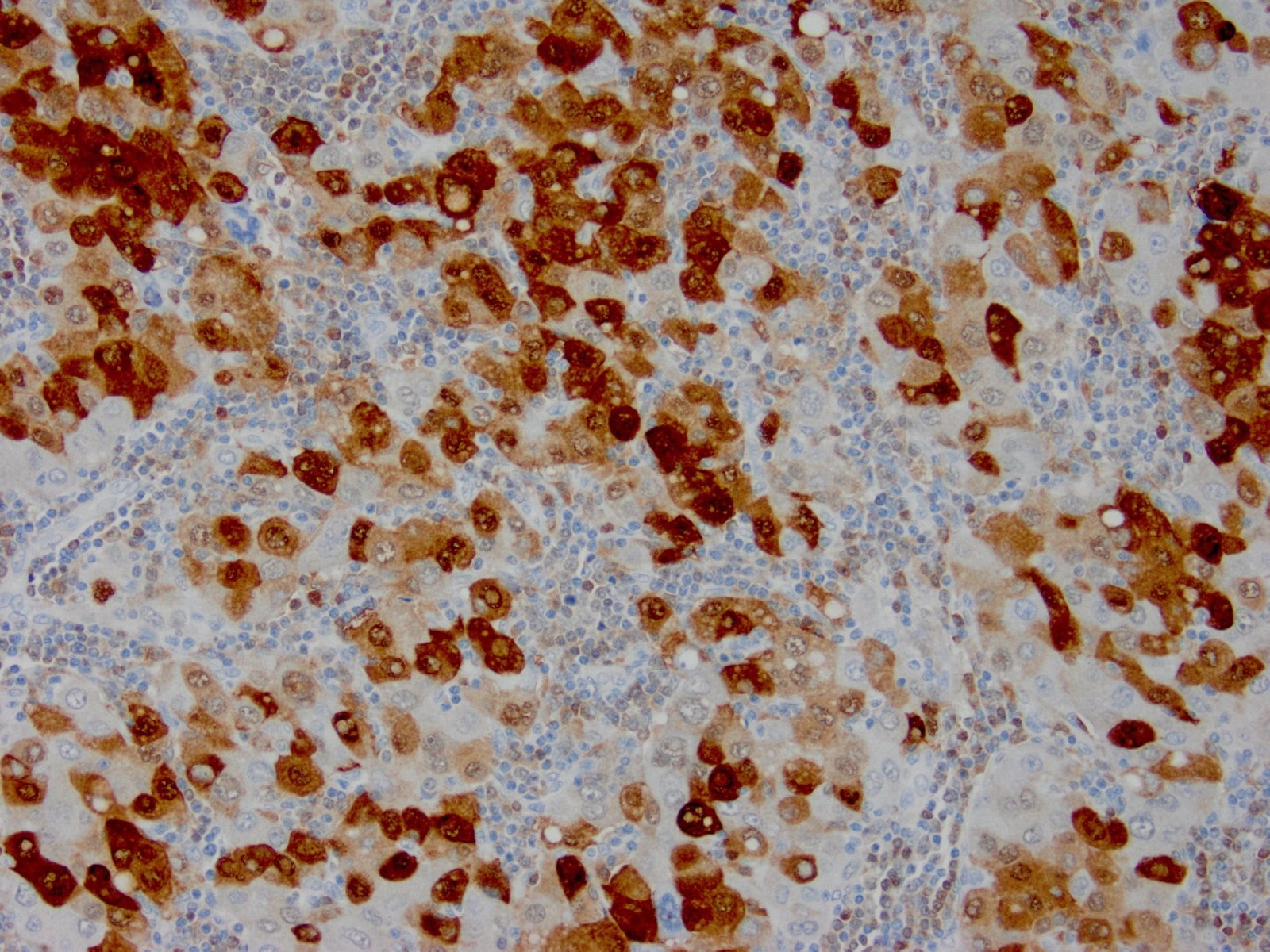 |
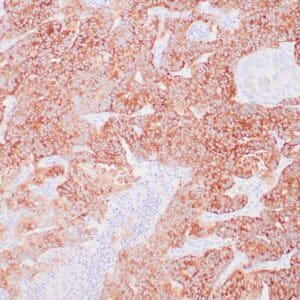
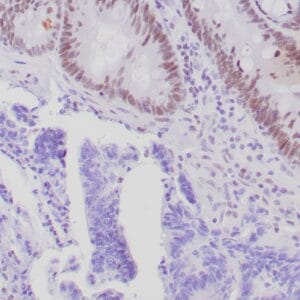
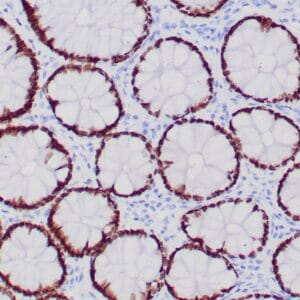
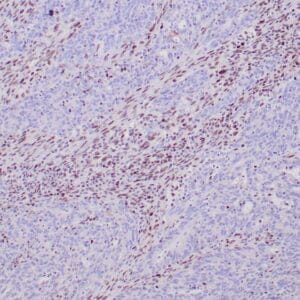
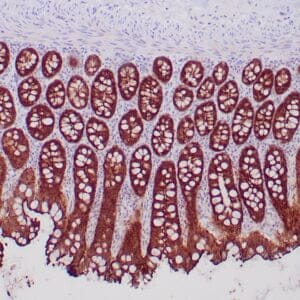
| Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human hepatocellular carcinoma stained with anti-HSP70 using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note cell cytoplasmic staining of tumor cells |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.