| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
rabbit anti-Glutamine synthetase monoclonal antibody (ZR431) 6426
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit monoclonal to Glutamine synthetase
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG
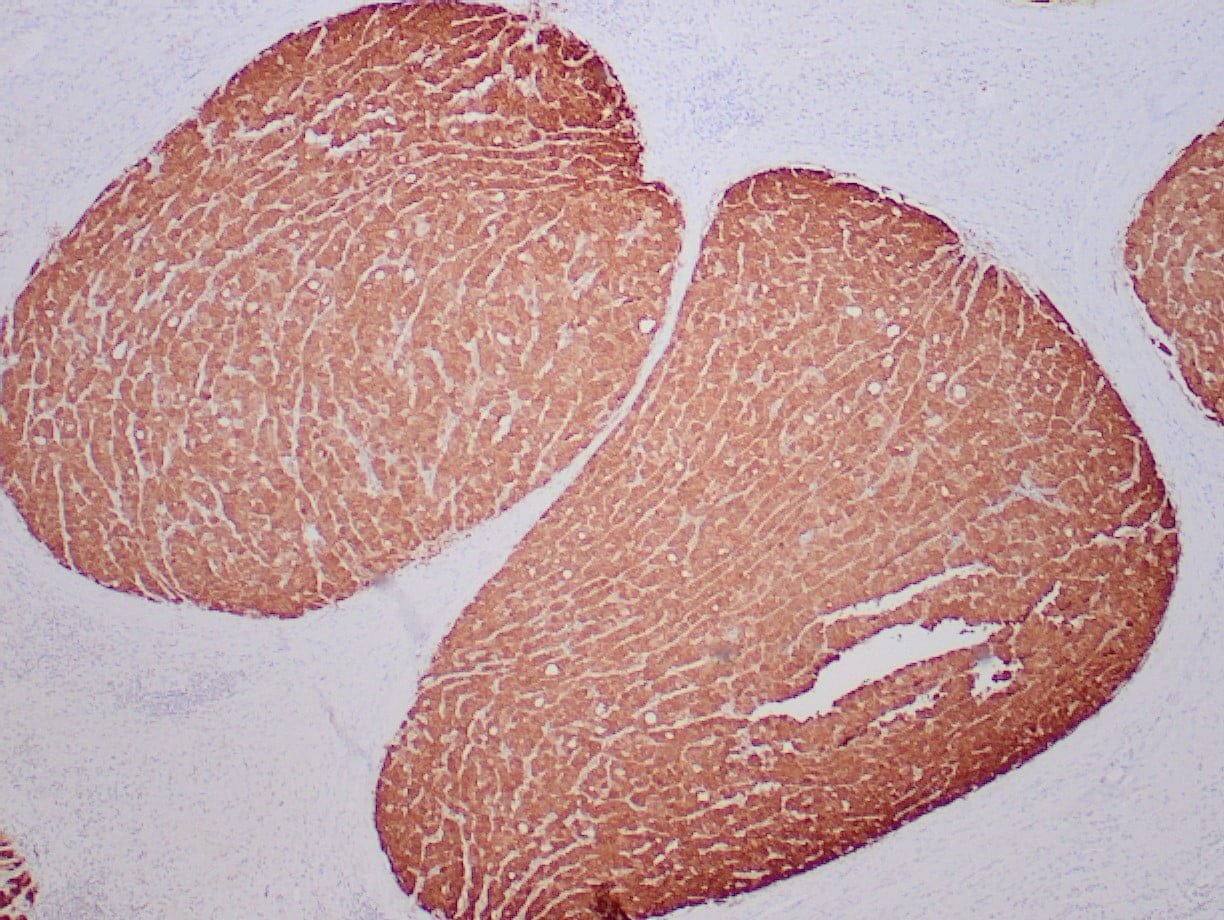
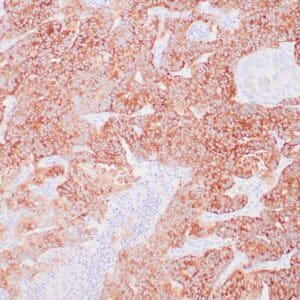
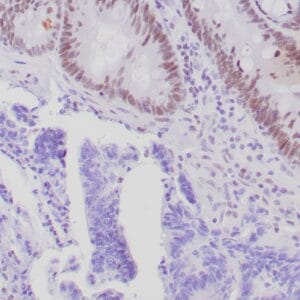
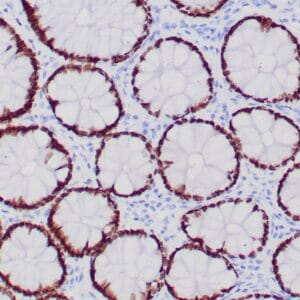
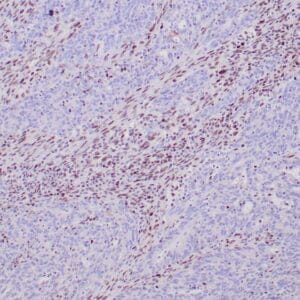
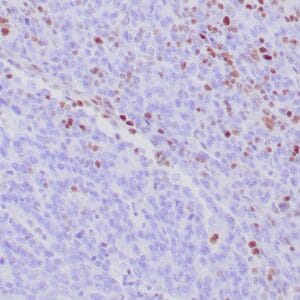
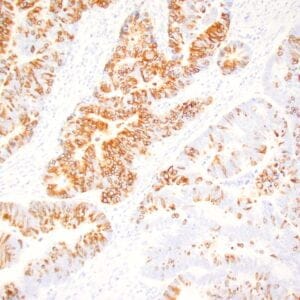
- Control: Normal liver
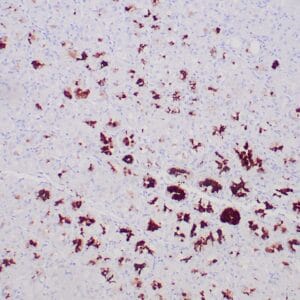
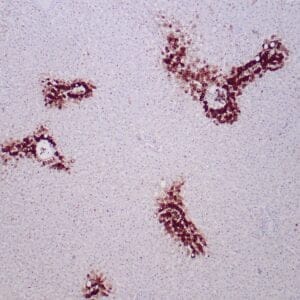
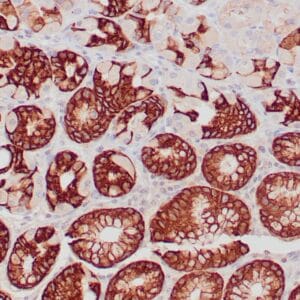
- Visualization: Cytoplasmic
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
rabbit anti-Glutamine synthetase monoclonal antibody ZR431 6426
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Glutamine synthetase (GS) (EC 6.3.1.2) (Glutamate--ammonia ligase) (Palmitoyltransferase GLUL) (EC 2.3.1.225) |
| Gene names GLUL,GLUL GLNS |
| Protein family Glutamine synthetase family |
| Mass 42064Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Glutamine synthetase that catalyzes the ATP-dependent conversion of glutamate and ammonia to glutamine (PubMed:16267323, PubMed:30158707, PubMed:36289327). Its role depends on tissue localization: in the brain, it regulates the levels of toxic ammonia and converts neurotoxic glutamate to harmless glutamine, whereas in the liver, it is one of the enzymes responsible for the removal of ammonia (By similarity). Plays a key role in ammonium detoxification during erythropoiesis: the glutamine synthetase activity is required to remove ammonium generated by porphobilinogen deaminase (HMBS) during heme biosynthesis to prevent ammonium accumulation and oxidative stress (By similarity). Essential for proliferation of fetal skin fibroblasts (PubMed:18662667). Independently of its glutamine synthetase activity, required for endothelial cell migration during vascular development: acts by regulating membrane localization and activation of the GTPase RHOJ, possibly by promoting RHOJ palmitoylation (PubMed:30158707). May act as a palmitoyltransferase for RHOJ: able to autopalmitoylate and then transfer the palmitoyl group to RHOJ (PubMed:30158707). Plays a role in ribosomal 40S subunit biogenesis (PubMed:26711351). Through the interaction with BEST2, inhibits BEST2 channel activity by affecting the gating at the aperture in the absence of intracellular L-glutamate, but sensitizes BEST2 to intracellular L-glutamate, which promotes the opening of BEST2 and thus relieves its inhibitory effect on BEST2 (PubMed:36289327). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15105, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16267323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18662667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26711351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30158707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36289327}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-glutamate + NH4(+) + ATP = L-glutamine + ADP + phosphate + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:16169, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:28938, ChEBI:CHEBI:29985, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:43474, ChEBI:CHEBI:58359, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=6.3.1.2; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:16267323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30158707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36289327}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-cysteinyl-[protein] + hexadecanoyl-CoA = S-hexadecanoyl-L-cysteinyl-[protein] + CoA; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:36683, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:10131, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11032, ChEBI:CHEBI:29950, ChEBI:CHEBI:57287, ChEBI:CHEBI:57379, ChEBI:CHEBI:74151; EC=2.3.1.225; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:30158707}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm, cytosol {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30158707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36289327}. Microsome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P09606}. Mitochondrion {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P09606}. Cell membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30158707}; Lipid-anchor {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30158707}. Note=Mainly localizes in the cytosol, with a fraction associated with the cell membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30158707}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed in endothelial cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30158707}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Decamer; composed of two pentamers (PubMed:18005987). Interacts with PALMD (By similarity). Interacts with RHOJ (PubMed:30158707). Interacts with BEST2; this interaction tethers a fraction of GLUL to the membrane, causing a decrease of cytosolic glutamine synthase (GS) activity and inhibits the chloride channel activity of BEST2 by affecting the gating at the aperture in the absence of intracellular glutamate (PubMed:36289327). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15105, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18005987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30158707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:36289327}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Acetylated by EP300/p300; acetylation is stimulated by increased glutamine levels and promotes ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26990986}.; PTM: Palmitoylated; undergoes autopalmitoylation. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:30158707}.; PTM: Ubiquitinated by ZNRF1 (By similarity). Ubiquitinated by the DCX (DDB1-CUL4-X-box) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex called CRL4(CRBN), leading to proteasomal degradation (PubMed:26990986). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15105, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26990986}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Glutamine deficiency, congenital (GLND) [MIM:610015]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by variable brain malformations, encephalopathy, severe developmental delay, seizures, and decreased glutamine levels in bodily fluids. Death in early infancy may occur. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16267323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26711351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 116 (DEE116) [MIM:620806]: A form of epileptic encephalopathy, a heterogeneous group of early-onset epilepsies characterized by refractory seizures, neurodevelopmental impairment, and poor prognosis. Development is normal prior to seizure onset, after which cognitive and motor delays become apparent. DEE116 is autosomal dominant form characterized by severe developmental delay, seizures, and white matter abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. DEE116 is caused by variants that disrupt the canonical translation start codon in GLUL resulting in initiation of translation at Met-18 (PubMed:38579670). The resulting protein is enzymatically competent but insensitive to negative feedback regulation via glutamine-induced degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:38579670}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P15104 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

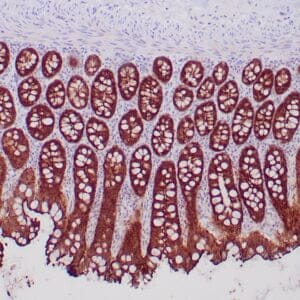
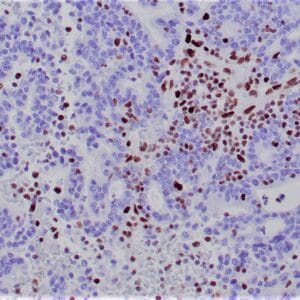
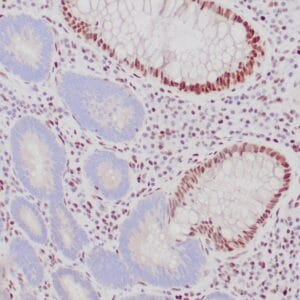
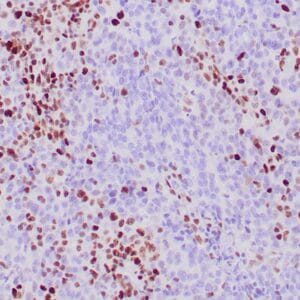

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.