| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
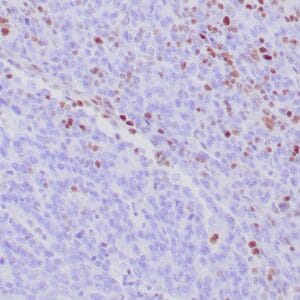
mouse anti-DOG-1 monoclonal antibody (DOG1.1) 6160
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to DOG-1
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1
- Control: Breast carcinomas
- Visualization: Cell membrane
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-DOG-1 monoclonal antibody DOG1.1 6160
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Anoctamin-1 (Discovered on gastrointestinal stromal tumors protein 1) (Oral cancer overexpressed protein 2) (Transmembrane protein 16A) (Tumor-amplified and overexpressed sequence 2) |
| Gene names ANO1,ANO1 DOG1 ORAOV2 TAOS2 TMEM16A |
| Protein family Anoctamin family |
| Mass 114078Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) (PubMed:20056604, PubMed:22178883, PubMed:22946059, PubMed:32487539). Plays a role in transepithelial anion transport and smooth muscle contraction. Required for the normal functioning of the interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) which generate electrical pacemaker activity in gastrointestinal smooth muscles. Acts as a major contributor to basal and stimulated chloride conductance in airway epithelial cells and plays an important role in tracheal cartilage development. Required for CFTR activation by enhancing endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) store release and is also required for CFTR membrane expression (PubMed:28963502). Required for basal and ATP-dependent mucus secretion in airways and intestine, probably by controlling exocytosis of mucus-filled granules by providing Ca(2+) to an apical signaling compartment (By similarity). Contributes to airway mucus expression induced by interleukins IL3 and IL8 and by the asthma-associated protein CLCA1 and is required for expression of mucin MUC5AC (PubMed:33026825). However, was shown in another study not to be required for MUC5AC expression (PubMed:31732694). Plays a role in the propagation of Ca(2+) waves in Kolliker's organ in the cochlea and contributes to the refinement of auditory brainstem circuitries prior to hearing onset (By similarity). In vomeronasal sensory neurons, modulates spontaneous firing patterns in the absence of stimuli as well as the firing pattern of pheromone-evoked activity (By similarity). Responsible for calcium-activated chloride channel activity in type I taste cells of the vallate papillae (By similarity). Acts as a heat sensor in nociceptive neurons (By similarity). In dorsal root ganglion neurons, plays a role in mediating non-histaminergic Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor (MRGPR)-dependent itching, acting as a downstream effector of MRGPRs (By similarity). In the developing brain, required for the Ca(2+)-dependent process extension of radial glial cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BHY3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20056604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22178883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22946059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28963502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31732694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32487539, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33026825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37253099}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 4]: Calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC). Contributes to calcium-activated chloride secretion in human sweat gland epithelial cells. Shows increased basal chloride permeability and decreased Ca(2+)-induced chloride permeability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25220078}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC). Shows increased sensitivity to intracellular Ca(2+). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26359375}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=chloride(in) = chloride(out); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:29823, ChEBI:CHEBI:17996; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:20056604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22178883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22946059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32487539, ECO:0000269|PubMed:37253099}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Apical cell membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15215166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20056604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22178883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22946059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28559167, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31732694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32487539}; Multi-pass membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BHY3}. Presynapse {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BHY3}. Note=In differentiating airway epithelial cells, predominantly intracellular at day 0 but is apically localized by day 30. Expressed in the presynapse of retinal neurons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BHY3}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Expressed in nasal epithelial cells (at protein level) (PubMed:32487539). In the kidney, expressed in the collecting duct (at protein level) (PubMed:24913262). Broadly expressed with higher levels in liver, skeletal muscle and gastrointestinal muscles (PubMed:15215166, PubMed:16906560). Expressed in eccrine sweat glands (PubMed:25220078). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15215166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16906560, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24913262, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25220078, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32487539}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homodimer (PubMed:21056985, PubMed:28559167). Interacts with CFTR (PubMed:22178883, PubMed:28963502). Interacts with TRPV4 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BHY3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21056985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22178883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28559167, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28963502}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The region spanning the fifth and sixth transmembrane domains probably forms the pore-forming region. {ECO:0000250}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Intestinal dysmotility syndrome (IDMTS) [MIM:620045]: An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by impaired intestinal peristalsis, recurrent episodes of haemorrhagic diarrhea, and distention of intestinal loops. Intestinal and hepatic portal venous gas, dysmorphic features, and developmental delay may also be present. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32487539}. Note=The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Moyamoya disease 7 (MYMY7) [MIM:620687]: A form of Moyamoya disease, a progressive cerebral angiopathy characterized by bilateral intracranial carotid artery stenosis and telangiectatic vessels in the region of the basal ganglia. The abnormal vessels resemble a 'puff of smoke' (moyamoya) on cerebral angiogram. Affected individuals can develop transient ischemic attacks and/or cerebral infarction, and rupture of the collateral vessels can cause intracranial hemorrhage. Hemiplegia of sudden onset and epileptic seizures constitute the prevailing presentation in childhood, while subarachnoid bleeding occurs more frequently in adults. MYMY7 inheritance can be autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:37253099}. Note=The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q5XXA6 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
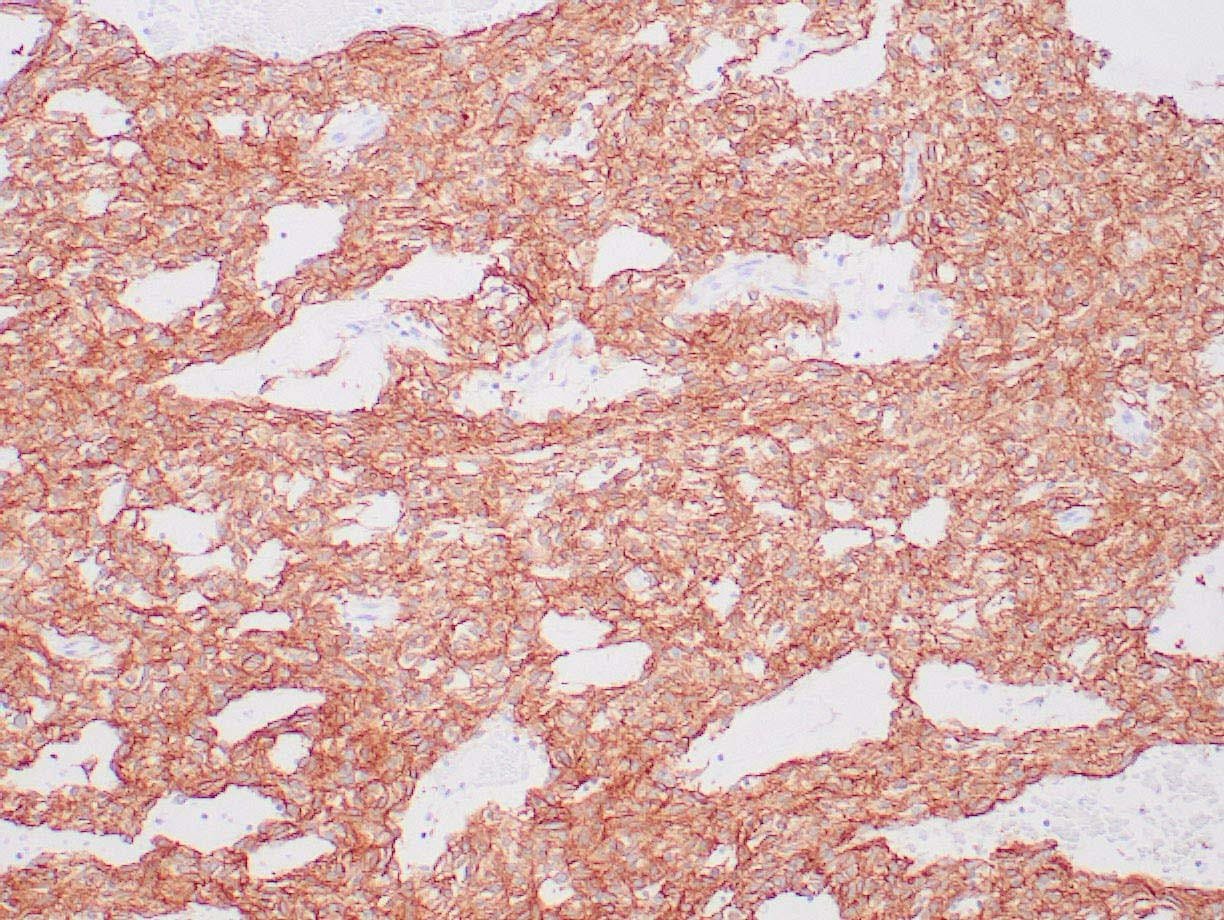 |
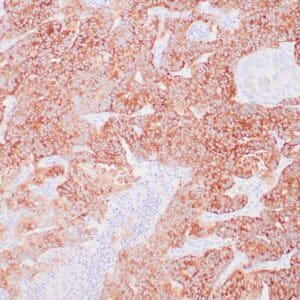
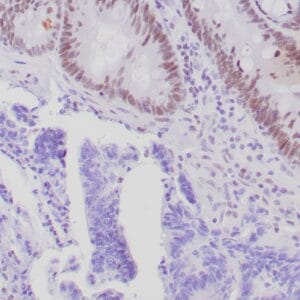
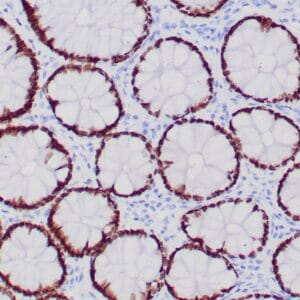
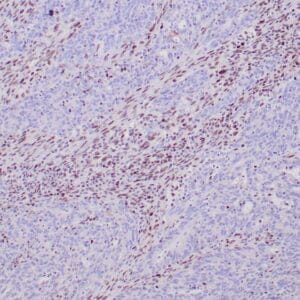
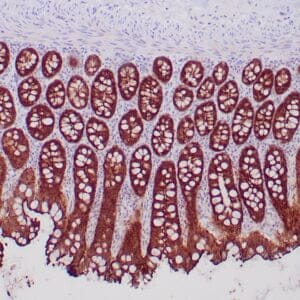
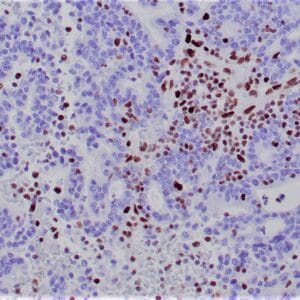
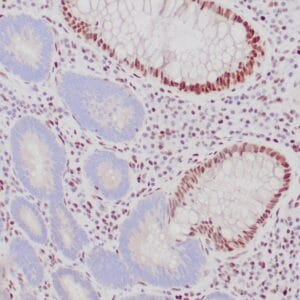
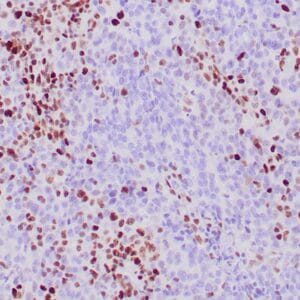
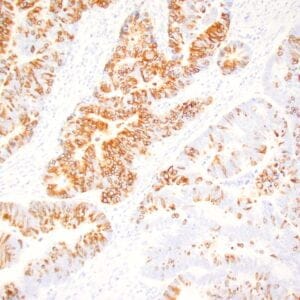
| GIST stained with DOG-1 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the strong cytoplasmic staining of tumor cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.