| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | P35918 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His |
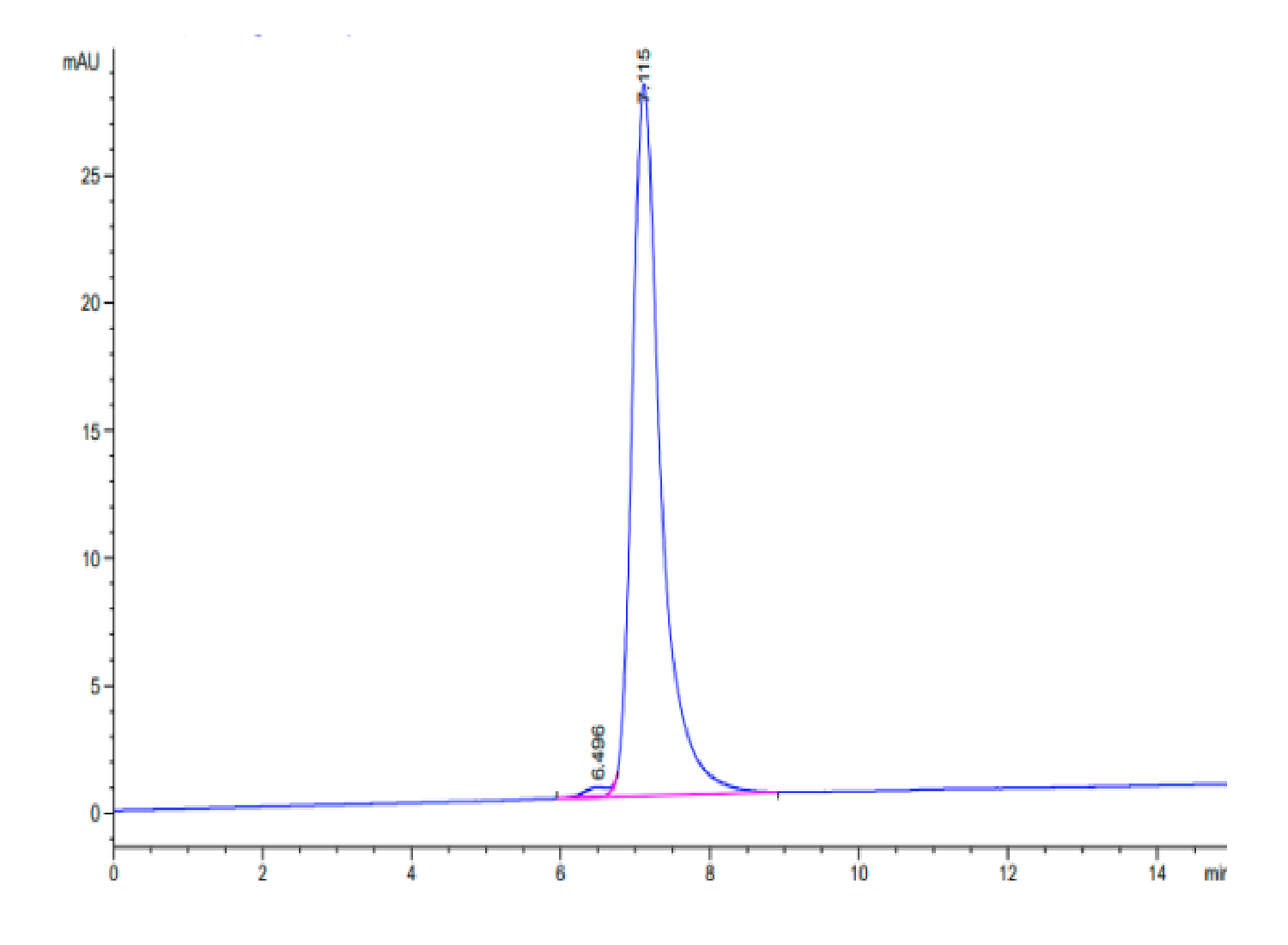
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFB and PGF, and plays an essential role in the development of embryonic vasculature, the regulation of angiogenesis, cell survival, cell migration, macrophage function, chemotaxis, and cancer cell invasion. The tyrosine kinase receptor vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) is a key regulator of angiogenesis. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 84.11 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 110-140 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Mouse VEGF R2/KDR Protein 3016
$270.00 – $900.00
Summary
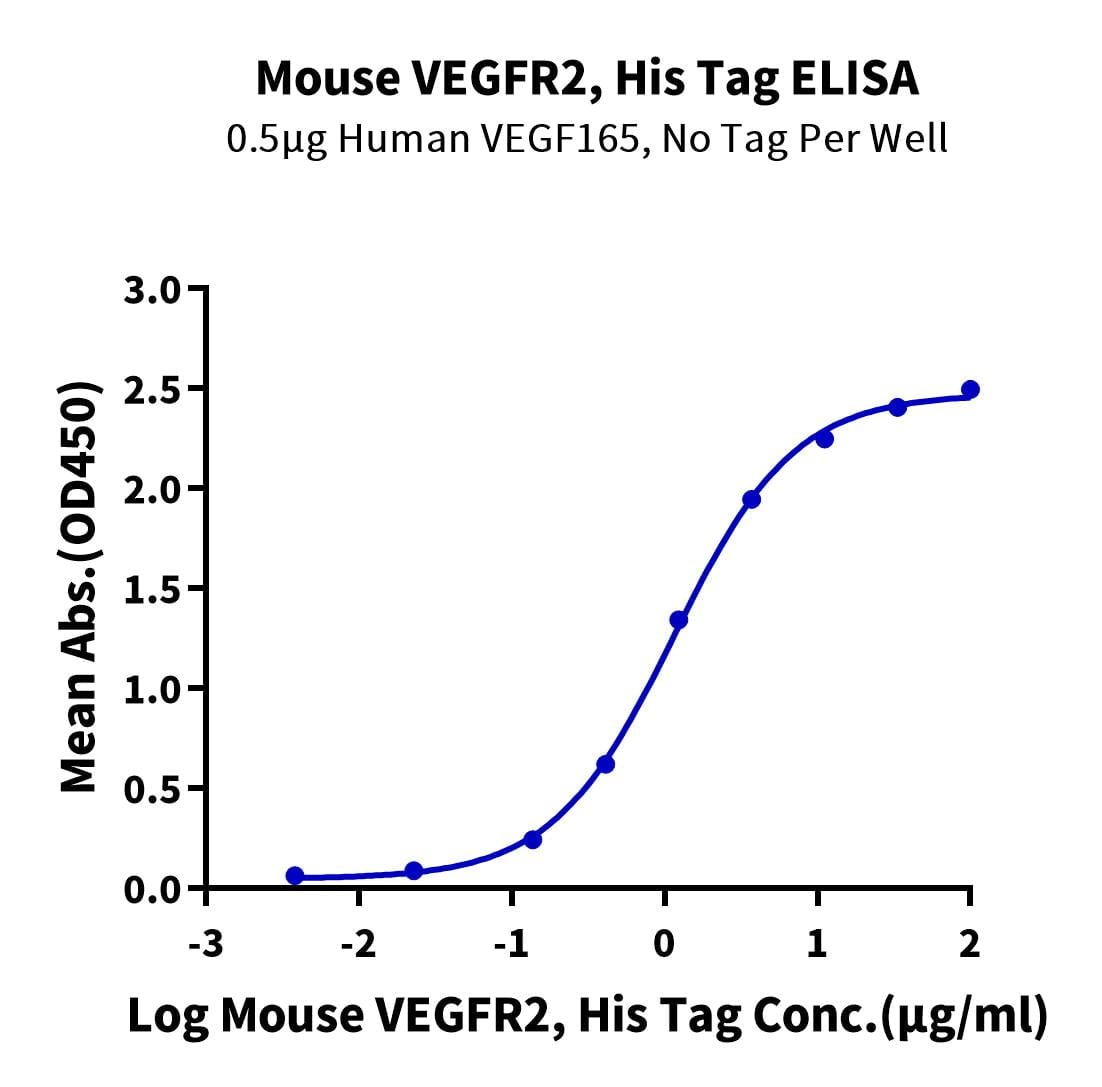
- Expression: HEK293
- Functional: Yes (ELISA)
- Amino Acid Range: Ala20-Glu762
Mouse VEGF R2/KDR Protein 3016
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFB and PGF, and plays an essential role in the development of embryonic vasculature, the regulation of angiogenesis, cell survival, cell migration, macrophage function, chemotaxis, and cancer cell invasion. The tyrosine kinase receptor vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) is a key regulator of angiogenesis. |
| Protein names Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) (EC 2.7.10.1) (Fetal liver kinase 1) (FLK-1) (Kinase NYK) (Protein-tyrosine kinase receptor flk-1) (CD antigen CD309) |
| Gene names Kdr,Kdr Flk-1 Flk1 |
| Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamil |
| Mass 10090Da |
| Function Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFC and VEGFD. Plays an essential role in the regulation of angiogenesis, vascular development, vascular permeability, and embryonic hematopoiesis. Promotes proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation of endothelial cells. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. Isoforms lacking a transmembrane domain, such as isoform 2, may function as decoy receptors for VEGFA, VEGFC and/or VEGFD. Isoform 2 plays an important role as a negative regulator of VEGFA- and VEGFC-mediated lymphangiogenesis by limiting the amount of free VEGFA and/or VEGFC and by preventing their binding to FLT4. Modulates FLT1 and FLT4 signaling by forming heterodimers. Binding of vascular growth factors to isoform 1 leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the activation of protein kinase C. Mediates activation of MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Mediates phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and activation of PTK2/FAK1. Required for VEGFA-mediated induction of NOS2 and NOS3, leading to the production of the signaling molecule nitric oxide (NO) by endothelial cells. Phosphorylates PLCG1. Promotes phosphorylation of FYN, NCK1, NOS3, PIK3R1, PTK2/FAK1 and SRC. |
| Catalytic activity #N/A |
| Subellular location Cell junction. Endoplasmic reticulum. Cell membrane. Note=Colocalizes with ERN1 and XBP1 in the endoplasmic reticulum in endothelial cells in a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent manner (By similarity). Localized with RAP1A at cell-cell junctions.; [Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasmic vesicle. Early endosome. Note=Detected on caveolae-enriched lipid rafts at the cell surface. Is recycled from the plasma membrane to endosomes and back again. Phosphorylation triggered by VEGFA binding promotes internalization and subsequent degradation. VEGFA binding triggers internalization and translocation to the nucleus (By similarity).; [Isoform 2]: Secreted. |
| Tissues Expressed in endothelial cells (at protein level). Detected in embryonic endothelial cells, as well as hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Detected in vascular endothelium. Expressed at high levels in adult heart, lung, kidney, brain and skeletal muscle, but is also expressed at lower levels in most other adult tissues. |
| Structure Homodimer in the presence of bound dimeric VEGFA, VEGFC or VEGFD ligands; monomeric in the absence of bound ligands. Can also form heterodimers with FLT1/VEGFR1 and KDR/VEGFR2. Interacts (tyrosine phosphorylated) with LFYN, NCK1, PLCG1. Interacts (tyrosine-phosphorylated active form preferentially) with DAB2IP (via C2 domain and active form preferentially); the interaction occurs at the late phase of VEGFA response and inhibits KDR/VEGFR2 activity. Interacts with SHBSH2D2A/TSAD, GRB2, MYOF, CBL and PDCD6 (PubMed:12796773, PubMed:12881528, PubMed:15026417, PubMed:15673613, PubMed:17702744, PubMed:19668192, PubMed:7681362, PubMed:8356051). Interacts (via C-terminus domain) with ERN1 (via kinase domain); the interaction is facilitated in a XBP1 isoform 1- and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent manner in endothelial cells (By similarity). Interacts (via juxtamembrane region) with chaperone PDCL3 (via thioredoxin fold region); the interaction leads to increased KDR/VEGFR2 abundance through inhibition of its ubiquitination and degradation (By similarity). Interacts (tyrosine phosphorylated) with CCDC88A/GIV (via SH2-like region); binding requires autophosphorylation of the KDR/VEGFR2 C-terminal region (By similarity). Interacts with isoform 2 of BSG (By similarity). Interacts with SLC31A1; this interaction is induced upon VEGFA stimulation leading to SLC31A1 and KDR subsequent co-internalization to early endosomes, thereby activating KDR downstream signaling in endothelial cells (By similarity). |
| Post-translational modification N-glycosylated.; Ubiquitinated. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the receptor promotes its poly-ubiquitination, leading to its degradation via the proteasome or lysosomal proteases (By similarity).; Autophosphorylated on tyrosine residues upon ligand binding. Autophosphorylation occurs in trans, i.e. one subunit of the dimeric receptor phosphorylates tyrosine residues on the other subunit. Phosphorylation at Tyr-949 is important for interaction with SH2D2A/TSAD and VEGFA-mediated reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. Phosphorylation at Tyr-1173 is important for interaction with PLCG1 and SHB. Phosphorylation at Tyr-1212 is important for interaction with NCK1 and FYN. Dephosphorylated by PTPRJ at Tyr-799, Tyr-949, Tyr-994, Tyr-1052, Tyr-1057, Tyr-1173 and Tyr-1212 (By similarity).; The inhibitory disulfide bond between Cys-1022 and Cys-1043 may serve as a specific molecular switch for H(2)S-induced modification that regulates KDR/VEGFR2 function. |
| Domain Th |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P35918 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||