| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | Q9EPU5 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His |
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| background | beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP) and death receptor 6 (DR6, also known as TNFRSF21) activate a widespread caspase-dependent self-destruction program. DR6 is broadly expressed by developing neurons, and is required for normal cell body death and axonal pruning both in vivo and after trophic-factor deprivation in vitro.DR6 is activated locally by an inactive surface ligand(s) that is released in an active form after trophic-factor deprivation. |
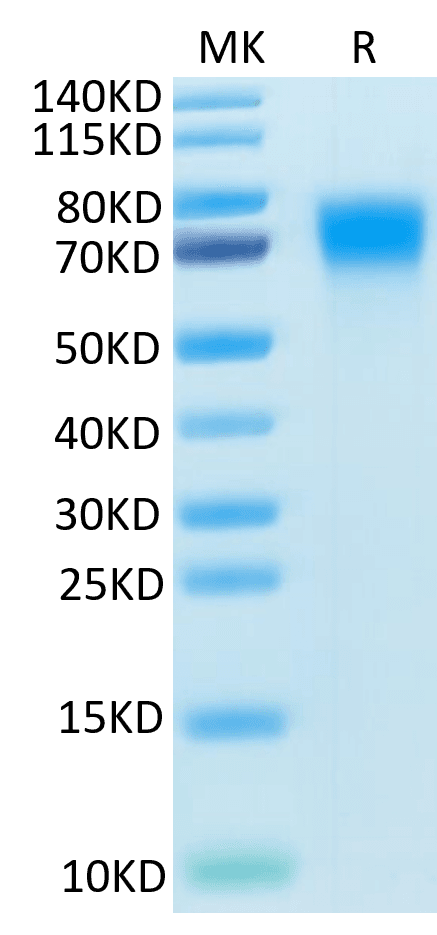
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 34.4 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 70-80 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Mouse DR6/TNFRSF21 Protein 3944
$150.00 – $500.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
- Pure: Yes (SDS-PAGE)
- Amino Acid Range: Gln42-His349
Mouse DR6/TNFRSF21 Protein 3944
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP) and death receptor 6 (DR6, also known as TNFRSF21) activate a widespread caspase-dependent self-destruction program. DR6 is broadly expressed by developing neurons, and is required for normal cell body death and axonal pruning both in vivo and after trophic-factor deprivation in vitro.DR6 is activated locally by an inactive surface ligand(s) that is released in an active form after trophic-factor deprivation. |
| Protein names Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 21 (Death receptor 6) (CD antigen CD358) |
| Gene names Tnfrsf21,Tnfrsf21 Dr6 |
| Mass 10090Da |
| Function Promotes apoptosis, possibly via a pathway that involves the activation of NF-kappa-B (PubMed:11485735, PubMed:11714751, PubMed:12515813, PubMed:19225519, PubMed:21725297, PubMed:23559013). Can also promote apoptosis mediated by BAX and by the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm (By similarity). Plays a role in neuronal apoptosis, including apoptosis in response to amyloid peptides derived from APP, and is required for both normal cell body death and axonal pruning (PubMed:19225519). Trophic-factor deprivation triggers the cleavage of surface APP by beta-secretase to release sAPP-beta which is further cleaved to release an N-terminal fragment of APP (N-APP) (PubMed:23559013). N-APP binds TNFRSF21; this triggers caspase activation and degeneration of both neuronal cell bodies (via caspase-3) and axons (via caspase-6) (PubMed:23559013). Negatively regulates oligodendrocyte survival, maturation and myelination (PubMed:21725297). Plays a role in signaling cascades triggered by stimulation of T-cell receptors, in the adaptive immune response and in the regulation of T-cell differentiation and proliferation (By similarity). Negatively regulates T-cell responses and the release of cytokines such as IL4, IL5, IL10, IL13 and IFNG by Th2 cells (By similarity). Negatively regulates the production of IgG, IgM and IgM in response to antigens (By similarity). May inhibit the activation of JNK in response to T-cell stimulation (By similarity). Also acts as a regulator of pyroptosis: recruits CASP8 in response to reactive oxygen species (ROS) and subsequent oxidation, leading to activation of GSDMC (By similarity). |
| Subellular location Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Note=Endocytosed following oxidation in response to reactive oxygen species (ROS). |
| Tissues Detected in spleen B-cells (at protein level). Ubiquitous. Highly expressed in adult spleen, thymus, testis, prostate, ovary, small intestine, colon, brain, lung and kidney, and in fetal brain, liver and lung. Detected at lower levels in adult peripheral blood leukocytes, lung, and in fetal muscle, heart, kidney, small intestine and skin. Detected in T-cells, B-cells and monocytes. In T-cells expression is highest in Th0 cells, intermediate in Th2 cells and lower in Th1 cells. Expressed at low levels in proliferating progenitors in the spinal cord, but is highly expressed by differentiating neurons within the spinal cord and adjacent dorsal root ganglia. Expressed by developing neurons as they differentiate and enter a pro-apoptotic state. Expressed by both cell bodies and axons. |
| Structure Associates with TRADD (By similarity). Interacts with NGFR. Interacts with CASP8 (By similarity). Interacts with N-APP (PubMed:19225519). |
| Post-translational modification Oxidized in response to reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to endocytosis. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q9EPU5 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||