| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | P08226 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-hFc |
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Apolipoprotein E (apoE) is a lipid carrier in both the peripheral and the central nervous systems. Lipid-loaded apoE lipoprotein particles bind to several cell surface receptors to support membrane homeostasis and injury repair in the brain. Considering prevalence and relative risk magnitude, the ε4 allele of the APOE gene is the strongest genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD). |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 60.7 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 62-66 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Mouse APOE/Apolipoprotein E Protein 3658
$270.00 – $900.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
- Pure: Yes (HPLC)
- Amino Acid Range: Glu19-Gln311
Mouse APOE/Apolipoprotein E Protein 3658
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Apolipoprotein E (apoE) is a lipid carrier in both the peripheral and the central nervous systems. Lipid-loaded apoE lipoprotein particles bind to several cell surface receptors to support membrane homeostasis and injury repair in the brain. Considering prevalence and relative risk magnitude, the ε4 allele of the APOE gene is the strongest genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD). |
| Protein names Apolipoprotein E (Apo-E) |
| Gene names Apoe,Apoe |
| Protein family Apolipoprotein A1/A4/E family |
| Mass 10090Da |
| Function APOE is an apolipoprotein, a protein associating with lipid particles, that mainly functions in lipoprotein-mediated lipid transport between organs via the plasma and interstitial fluids. APOE is a core component of plasma lipoproteins and is involved in their production, conversion and clearance. Apolipoproteins are amphipathic molecules that interact both with lipids of the lipoprotein particle core and the aqueous environment of the plasma. As such, APOE associates with chylomicrons, chylomicron remnants, very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) and intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL) but shows a preferential binding to high-density lipoproteins (HDL). It also binds a wide range of cellular receptors including the LDL receptor/LDLR and the very low-density lipoprotein receptor/VLDLR that mediate the cellular uptake of the APOE-containing lipoprotein particles (By similarity). Finally, APOE has also a heparin-binding activity and binds heparan-sulfate proteoglycans on the surface of cells, a property that supports the capture and the receptor-mediated uptake of APOE-containing lipoproteins by cells (PubMed:23676495). |
| Catalytic activity BINDING 154..157; /ligand="heparin"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:28304"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02649"; BINDING 221..228; /ligand="heparin"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:28304"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02649" |
| Subellular location Secreted. Secreted, extracellular space. Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix. Extracellular vesicle. Endosome, multivesicular body. Note=In the plasma, APOE is associated with chylomicrons, chylomicrons remnants, VLDL, LDL and HDL lipoproteins. Lipid poor oligomeric APOE is associated with the extracellular matrix in a calcium- and heparan-sulfate proteoglycans-dependent manner. Lipidation induces the release from the extracellular matrix. Colocalizes with CD63 and PMEL at exosomes and in intraluminal vesicles within multivesicular endosomes. |
| Structure Homotetramer. May interact with ABCA1; functionally associated with ABCA1 in the biogenesis of HDLs. May interact with APP/A4 amyloid-beta peptide; the interaction is extremely stable in vitro but its physiological significance is unclear. May interact with MAPT. May interact with MAP2. In the cerebrospinal fluid, interacts with secreted SORL1. Interacts with PMEL; this allows the loading of PMEL luminal fragment on ILVs to induce fibril nucleation. |
| Post-translational modification APOE exists as multiple glycosylated and sialylated glycoforms within cells and in plasma. The extent of glycosylation and sialylation are tissue and context specific.; Glycated in plasma VLDL.; Phosphorylated by FAM20C in the extracellular medium. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P08226 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
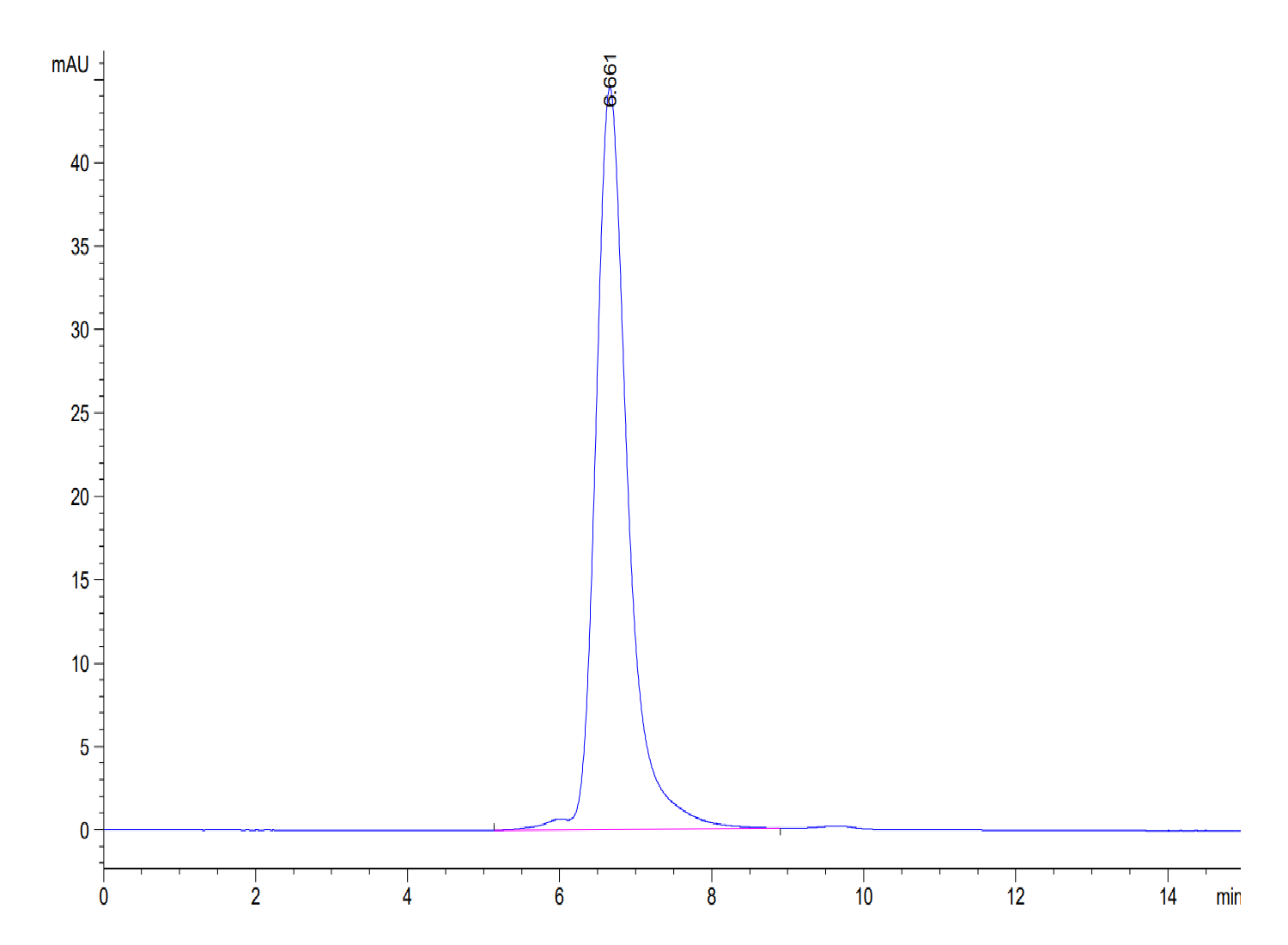 |
| The purity of Mouse APOE is greater than 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC. |
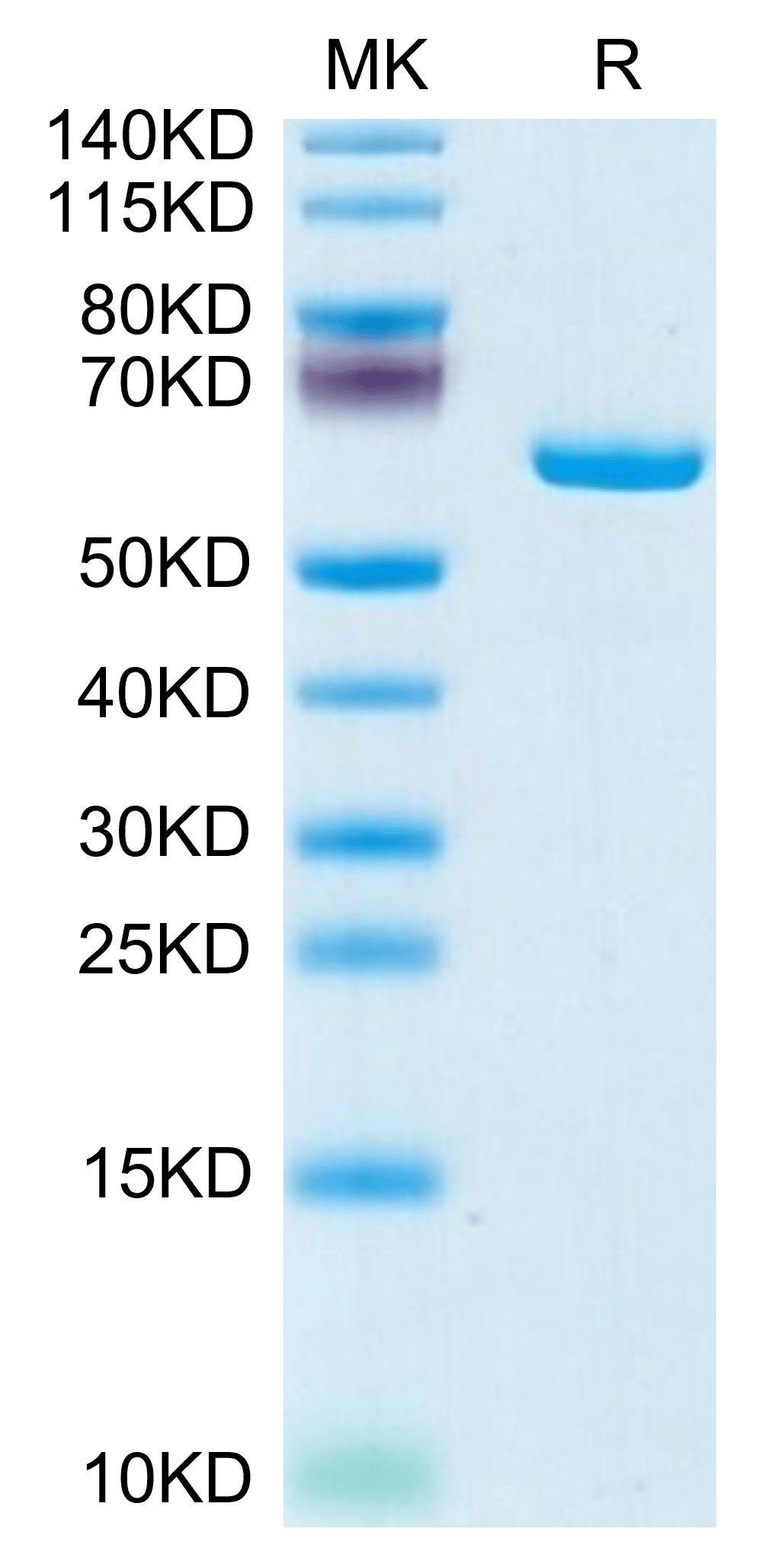 |
| Mouse APOE on Tris-Bis PAGE under reduced condition. The purity is greater than 95%. |
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||














