| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-MUC-5AC monoclonal antibody (ZM148) 6270
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to MUC-5AC
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1
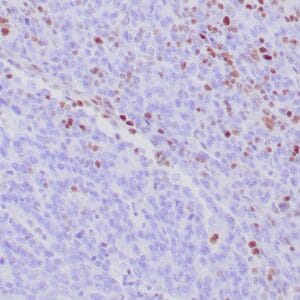
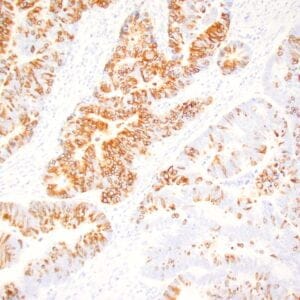
- Control: Gastric carcinoma
- Visualization: Cell membrane
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-MUC-5AC monoclonal antibody ZM148 6270
| antibody |
|---|
| Database link: human P98088 |
| Tested applications IHC |
| Recommended dilutions Concentrated 1:100-200 |
| Application Notes Positive control: Gastric carcinoma |
| Immunogen M1 mucin preparation from the fluid of an ovarian mucinous cyst belonging to an O Le(ab-) patient |
| Size and concentration 7 mL prediluted or 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL and concentrated |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions 2-8°C for short term, for longer term at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Purity affinity purified |
| Clonality monoclonal |
| Isotype IgG1 |
| Compatible secondaries goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody 5486 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated, Conjugate polyclonal antibody 2685 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 7854 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1706 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1716 goat anti-mouse IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1721 |
| Isotype control Mouse monoclonal IgG1 - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Mucin-5AC (MUC-5AC) (Gastric mucin) (Major airway glycoprotein) (Mucin-5 subtype AC, tracheobronchial) (Tracheobronchial mucin) (TBM) |
| Gene names MUC5AC,MUC5AC MUC5 |
| Mass 585570Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Gel-forming glycoprotein of gastric and respiratory tract epithelia that protects the mucosa from infection and chemical damage by binding to inhaled microorganisms and particles that are subsequently removed by the mucociliary system (PubMed:14535999, PubMed:14718370). Interacts with H.pylori in the gastric epithelium, Barrett's esophagus as well as in gastric metaplasia of the duodenum (GMD) (PubMed:14535999). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14535999, ECO:0000303|PubMed:14535999, ECO:0000303|PubMed:14718370}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Secreted {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14718370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31732694}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Highly expressed in surface mucosal cells of respiratory tract and stomach epithelia. Overexpressed in a number of carcinomas. Also expressed in Barrett's esophagus epithelium and in the proximal duodenum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14535999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7513696}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homomultimer; disulfide-linked (PubMed:14718370). The N- and C-terminus mediate their assembly into higher order structures to form filaments (By similarity). The CTCK domains of two polypeptides associate in the endoplasmic reticulum to generate intermolecularly disulfide-bonded dimers (By similarity). These dimers progress to the Golgi apparatus, which is a more acidic environment than the endoplasmic reticulum. Under acidic conditions, the N-termini form non-covalent intermolecular interactions that juxtapose assemblies from different CTCK-linked dimers to produce long, disulfide-linked polymers that remain highly compact until secretion (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q02817, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9HC84, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14718370}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: C-, O- and N-glycosylated (PubMed:14718370). O-glycosylated on the second and last Thr of the Thr-/Ser-rich tandem repeats TTPSPVPTTSTTSA (PubMed:14718370, PubMed:22186971, PubMed:25939779). One form of glycosylation is also known as Lewis B (LeB) blood group antigen, a tetrasaccharide consisting of N-acetylglucosamine having a fucosyl residue attached (PubMed:14535999). It has a role as an epitope and antigen and functions as a receptor for H.pylori binding and facilitates infection (PubMed:14535999). C-mannosylation in the Cys-rich subdomains may be required for proper folding of these regions and for export from the endoplasmic reticulum during biosynthesis (PubMed:14718370). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14535999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14718370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25939779}.; PTM: Proteolytic cleavage in the C-terminal is initiated early in the secretory pathway and does not involve a serine protease. The extent of cleavage is increased in the acidic parts of the secretory pathway. Cleavage generates a reactive group which could link the protein to a primary amide. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16787389}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The cysteine residues in the Cys-rich subdomain repeats are not involved in disulfide bonding.; DOMAIN: The CTCK domain mediates interchain disulfide bonds with another molecule of MUC5AC. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9HC84}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P98088 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
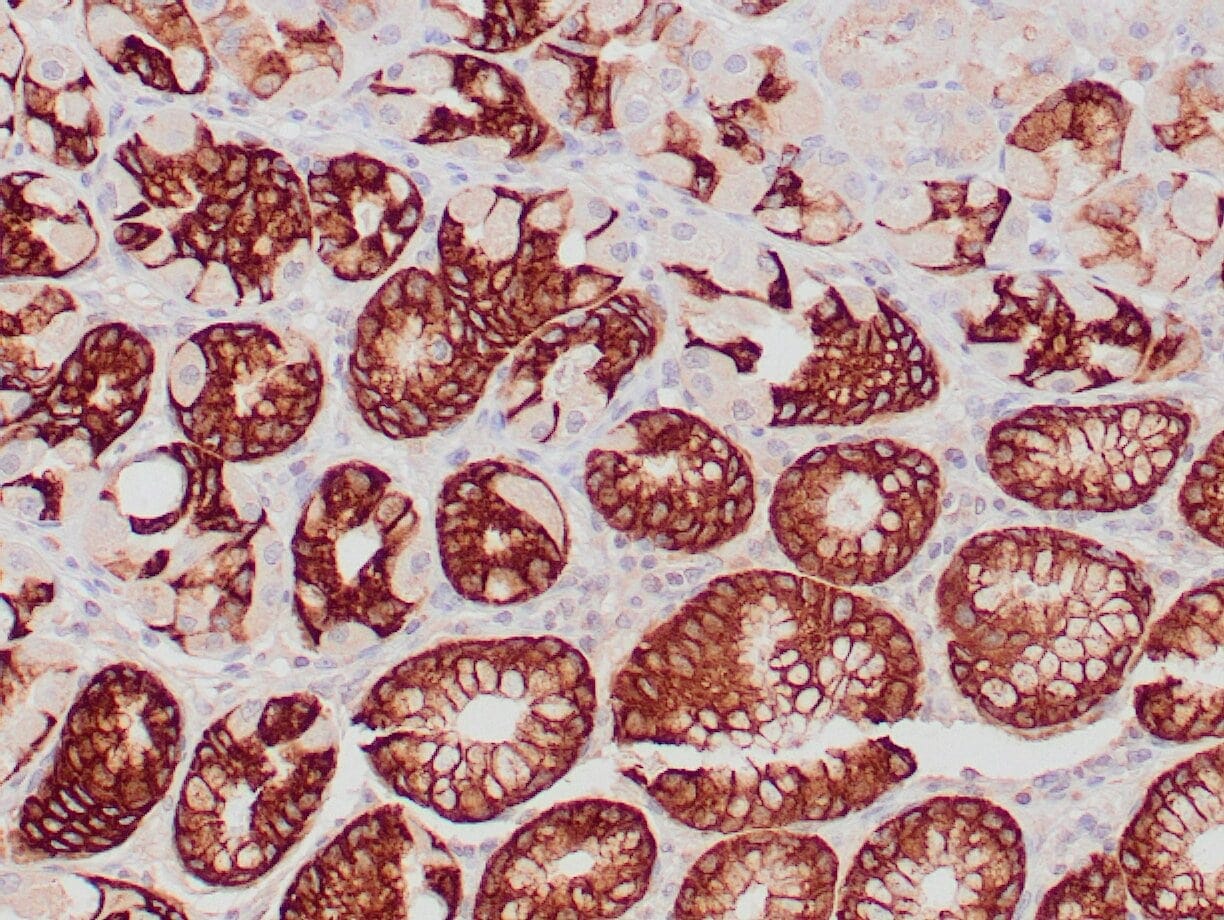 |
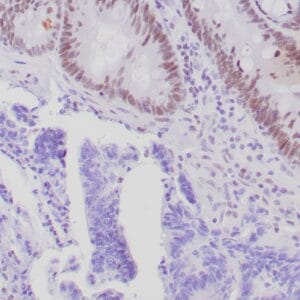
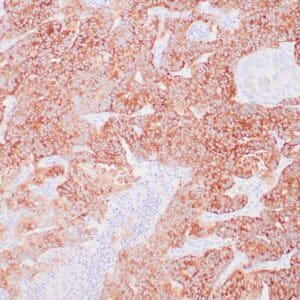
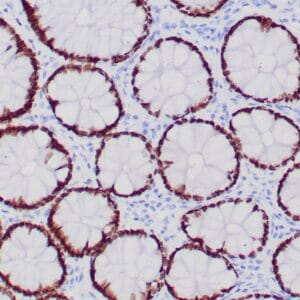
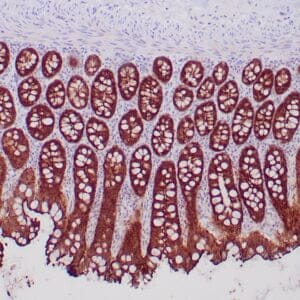
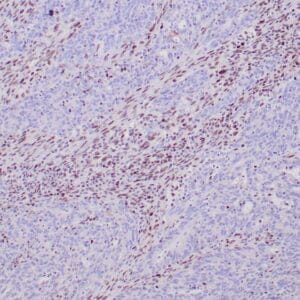
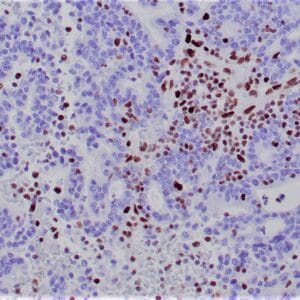
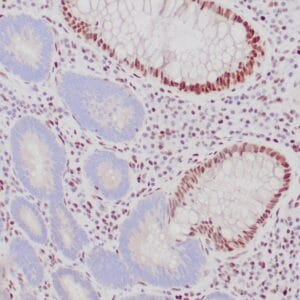
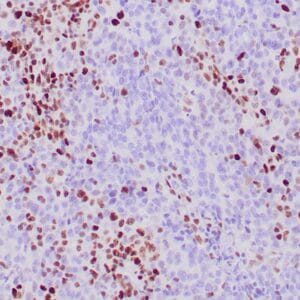
| Human gastric mucosa stained with anti MUC-5AC antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and DAB chromogen. Note the cytoplasmic staining of glandular cells. |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.