| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | mouse |
| isotype | IgG1 |
| clonality | monoclonal |
| concentration | concentrate, predilute |
| applications | IHC |
| reactivity | human |
| available size | 0.1 mL, 0.5 mL, 1 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted |
mouse anti-DPC4 (SMAD4) monoclonal antibody (B-8) 6163
Price range: $160.00 through $528.00
Antibody summary
- Mouse monoclonal to DPC4 (SMAD4)
- Suitable for: Immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues)
- Reacts with: Human
- Isotype:IgG1
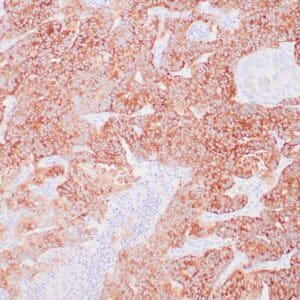
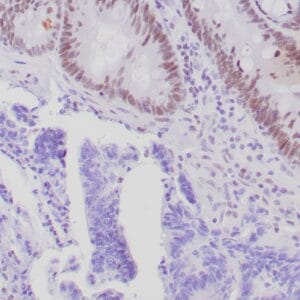
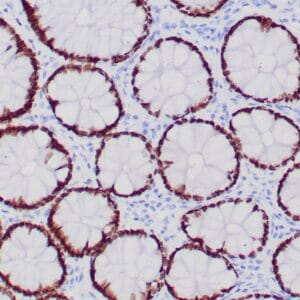
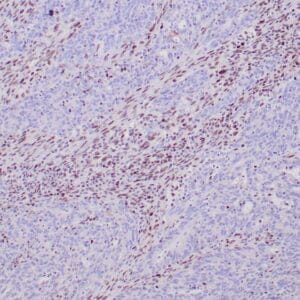
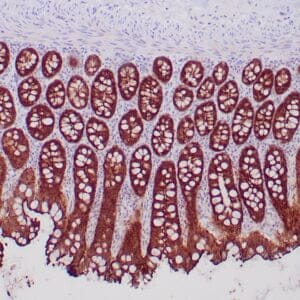
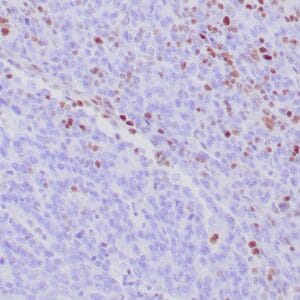
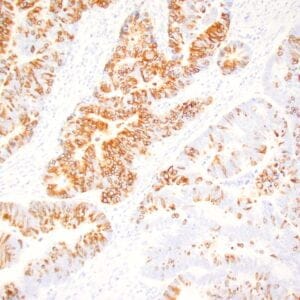
- Control: Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
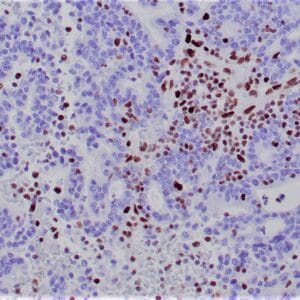
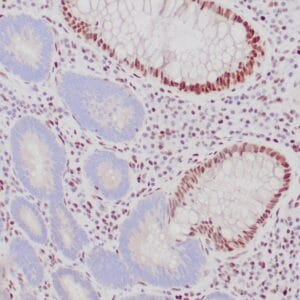
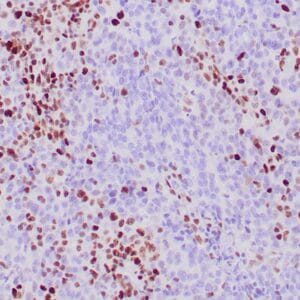
- Visualization: Nuclear
- 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mL concentrated, 7 mL prediluted
mouse anti-DPC4 (SMAD4) monoclonal antibody B-8 6163
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4 (MAD homolog 4) (Mothers against DPP homolog 4) (Deletion target in pancreatic carcinoma 4) (SMAD family member 4) (SMAD 4) (Smad4) (hSMAD4) |
| Gene names SMAD4,SMAD4 DPC4 MADH4 |
| Protein family Dwarfin/SMAD family |
| Mass 60439Da |
| Function FUNCTION: In muscle physiology, plays a central role in the balance between atrophy and hypertrophy. When recruited by MSTN, promotes atrophy response via phosphorylated SMAD2/4. MSTN decrease causes SMAD4 release and subsequent recruitment by the BMP pathway to promote hypertrophy via phosphorylated SMAD1/5/8. Acts synergistically with SMAD1 and YY1 in bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-mediated cardiac-specific gene expression. Binds to SMAD binding elements (SBEs) (5'-GTCT/AGAC-3') within BMP response element (BMPRE) of cardiac activating regions (By similarity). Common SMAD (co-SMAD) is the coactivator and mediator of signal transduction by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor). Component of the heterotrimeric SMAD2/SMAD3-SMAD4 complex that forms in the nucleus and is required for the TGF-mediated signaling (PubMed:25514493). Promotes binding of the SMAD2/SMAD4/FAST-1 complex to DNA and provides an activation function required for SMAD1 or SMAD2 to stimulate transcription. Component of the multimeric SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS complex which forms at the AP1 promoter site; required for synergistic transcriptional activity in response to TGF-beta. May act as a tumor suppressor. Positively regulates PDPK1 kinase activity by stimulating its dissociation from the 14-3-3 protein YWHAQ which acts as a negative regulator. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17327236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25514493, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9389648}. |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15799969, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17327236}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15799969}. Note=Cytoplasmic in the absence of ligand. Migrates to the nucleus when complexed with R-SMAD (PubMed:15799969). PDPK1 prevents its nuclear translocation in response to TGF-beta (PubMed:17327236). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15799969, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17327236}. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Monomer; in the absence of TGF-beta activation (PubMed:9670020). Heterotrimer; on TGF-beta activation (PubMed:15799969). Heterotrimer composed of two molecules of a C-terminally phosphorylated R-SMAD molecule, SMAD2 or SMAD3, and one molecule of SMAD4 to form the transcriptional active SMAD2/SMAD3-SMAD4 complex (PubMed:15350224, PubMed:15799969). Found in a ternary complex composed of SMAD4, STK11/LKB1 and STK11IP. Found in a complex with SMAD1 and YY1 (By similarity). Identified in a complex that contains at least ZNF451, SMAD2, SMAD3 and SMAD4 (PubMed:24324267). Interacts with ATF2, COPS5, DACH1, MSG1, SKI, STK11/LKB1, STK11IP and TRIM33. Associates with ZNF423 or ZNF521 in response to BMP2 leading to activate transcription of BMP target genes. Interacts with USP9X. Interacts (via the MH1 and MH2 domains) with RBPMS. Interacts with WWTR1 (via coiled-coil domain). Interacts with CITED1 and CITED2. Interacts with PDPK1 (via PH domain) (By similarity). Interacts with VPS39; this interaction affects heterodimer formation with SMAD3, but not with SMAD2, and leads to inhibition of SMAD3-dependent transcription activation. Interactions with VPS39 and SMAD2 may be mutually exclusive. Interacts (via MH2 domain) with ZNF451 (via N-terminal zinc-finger domains) (PubMed:24324267). Interacts with ZC3H3 (By similarity). Interacts weakly with ZNF8 (PubMed:12370310). Interacts with NUP93 and IPO7; translocates SMAD4 to the nucleus through the NPC upon BMP7 stimulation resulting in activation of SMAD4 signaling (PubMed:26878725). Interacts with CREB3L1, the interaction takes place upon TGFB1 induction and SMAD4 acts as a CREB3L1 coactivator to induce the expression of genes involved in the assembly of collagen extracellular matrix (PubMed:25310401). Interacts with DLX1 (PubMed:14671321). Interacts with ZBTB7A; the interaction is direct and stimulated by TGFB1 (PubMed:25514493). Interacts with CREBBP; the recruitment of this transcriptional coactivator is negatively regulated by ZBTB7A (PubMed:25514493). Interacts with EP300; the interaction with this transcriptional coactivator is negatively regulated by ZBTB7A (PubMed:25514493). Interacts with HDAC1 (PubMed:25514493). Interacts (via MH2 domain) with ZMIZ1 (via SP-RING-type domain); in the TGF-beta signaling pathway increases the activity of the SMAD3/SMAD4 transcriptional complex (PubMed:16777850). Interacts (via N-terminus) with TSC22D1 (PubMed:15881652). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O70437, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97471, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10660046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11224571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11741830, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11818334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12370310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12941698, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14525983, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14630787, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14671321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15350224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15799969, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15820681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15881652, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16777850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17099224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17327236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18568018, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19135894, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24324267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25310401, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25514493, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26878725, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9670020, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9707553}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylated by PDPK1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17327236}.; PTM: Monoubiquitinated on Lys-519 by E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM33. Monoubiquitination hampers its ability to form a stable complex with activated SMAD2/3 resulting in inhibition of TGF-beta/BMP signaling cascade. Deubiquitination by USP9X restores its competence to mediate TGF-beta signaling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19135894}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The MH1 domain is required for DNA binding.; DOMAIN: The MH2 domain is required for both homomeric and heteromeric interactions and for transcriptional regulation. Sufficient for nuclear import. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Pancreatic cancer (PNCA) [MIM:260350]: A malignant neoplasm of the pancreas. Tumors can arise from both the exocrine and endocrine portions of the pancreas, but 95% of them develop from the exocrine portion, including the ductal epithelium, acinar cells, connective tissue, and lymphatic tissue. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8553070}. Note=The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis.; DISEASE: Juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) [MIM:174900]: Autosomal dominant gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyposis syndrome in which patients are at risk for developing gastrointestinal cancers. The lesions are typified by a smooth histological appearance, predominant stroma, cystic spaces and lack of a smooth muscle core. Multiple juvenile polyps usually occur in a number of Mendelian disorders. Sometimes, these polyps occur without associated features as in JPS; here, polyps tend to occur in the large bowel and are associated with an increased risk of colon and other gastrointestinal cancers. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12417513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9811934}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Juvenile polyposis/hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia syndrome (JP/HHT) [MIM:175050]: JP/HHT syndrome phenotype consists of the coexistence of juvenile polyposis (JIP) and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) [MIM:187300] in a single individual. JIP and HHT are autosomal dominant disorders with distinct and non-overlapping clinical features. The former, an inherited gastrointestinal malignancy predisposition, is caused by mutations in SMAD4 or BMPR1A, and the latter is a vascular malformation disorder caused by mutations in ENG or ACVRL1. All four genes encode proteins involved in the transforming-growth-factor-signaling pathway. Although there are reports of patients and families with phenotypes of both disorders combined, the genetic etiology of this association is unknown. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15031030}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Colorectal cancer (CRC) [MIM:114500]: A complex disease characterized by malignant lesions arising from the inner wall of the large intestine (the colon) and the rectum. Genetic alterations are often associated with progression from premalignant lesion (adenoma) to invasive adenocarcinoma. Risk factors for cancer of the colon and rectum include colon polyps, long-standing ulcerative colitis, and genetic family history. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16959974}. Note=The disease may be caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Note=SMAD4 variants may be associated with susceptibility to pulmonary hypertension, a disorder characterized by plexiform lesions of proliferating endothelial cells in pulmonary arterioles. The lesions lead to elevated pulmonary arterial pression, right ventricular failure, and death. The disease can occur from infancy throughout life and it has a mean age at onset of 36 years. Penetrance is reduced. Although familial pulmonary hypertension is rare, cases secondary to known etiologies are more common and include those associated with the appetite-suppressant drugs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21898662}.; DISEASE: Myhre syndrome (MYHRS) [MIM:139210]: An autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by pre- and postnatal growth deficiency, intellectual disability, generalized muscle hypertrophy and striking muscular build, decreased joint mobility, cryptorchidism, and unusual facies. Dysmorphic facial features include microcephaly, midface hypoplasia, prognathism, and blepharophimosis. Typical skeletal anomalies are short stature, square body shape, broad ribs, iliac hypoplasia, brachydactyly, flattened vertebrae, and thickened calvaria. Other features, such as congenital heart disease, may also occur. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22158539, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22243968}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q13485 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| IHC |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
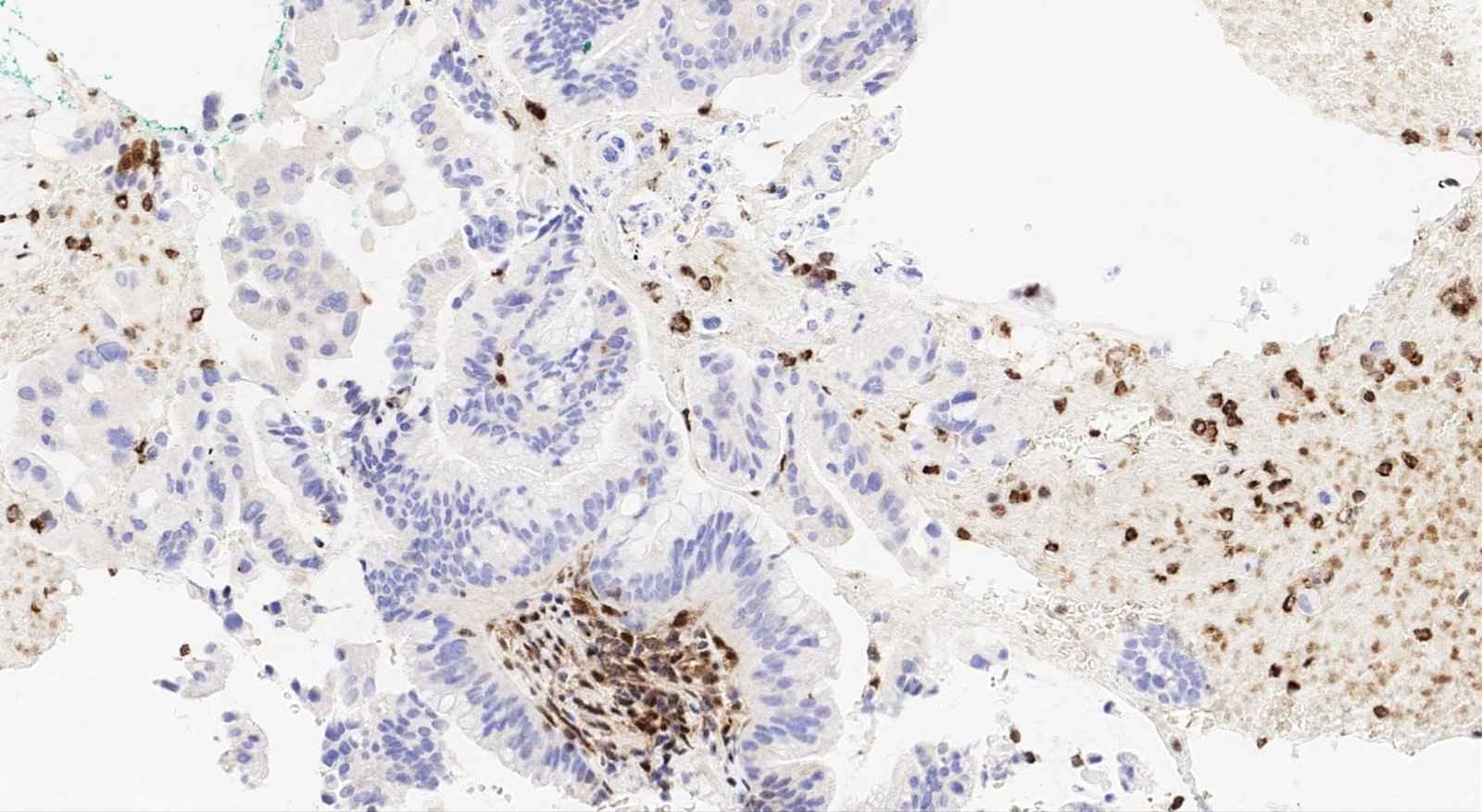
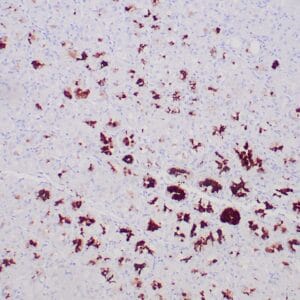
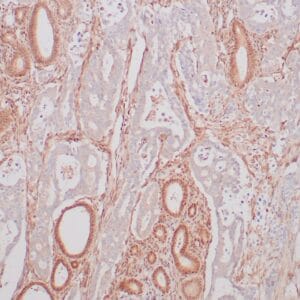
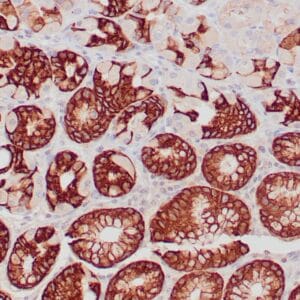


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.