| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | IP, WB |
| reactivity | MDA ApoB, protein |
| available sizes | 0.5 mg, 1 mg |
MDA (malondialdehyde) modified Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) antigen 1015
Price range: $578.00 through $926.00
Antibody summary
- Rabbit polyclonal to MDA ApoB
- Suitable for: WB,IP
- Reacts with: Hu MDA ApoB
- Isotype:
- 0.5 mg, 1 mg
mdaapob antigen 1015
| kit |
|---|
| Storage Store at -20°C |
| Form liquid |
| Additional information Natural MDA ApoB |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Organism Homo sapiens (Human) |
| Protein names Malondialdehyde-modified LDL |
| Gene names APOB |
| Mass 515545 Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Apolipoprotein B is a major protein constituent of chylomicrons (apo B-48), LDL (apo B-100) and VLDL (apo B-100). Apo B-100 functions as a recognition signal for the cellular binding and internalization of LDL particles by the apoB/E receptor. |
| Subcellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22580899}. Secreted {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22580899, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26224785}. Lipid droplet {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28183703}. |
| Structure and strains SUBUNIT: Interacts with PCSK9 (PubMed:22580899). Interacts with MTTP (PubMed:26224785, PubMed:27206948). Interacts with AUP1 (PubMed:28183703). Interacts with CIDEB (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9Q414, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22580899, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26224785, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27206948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28183703}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Palmitoylated; structural requirement for proper assembly of the hydrophobic core of the lipoprotein particle. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10679026}. |
| Disease DISEASE: Hypobetalipoproteinemia, familial, 1 (FHBL1) [MIM:615558]: A disorder of lipid metabolism characterized by less than 5th percentile age- and sex-specific levels of low density lipoproteins, and dietary fat malabsorption. Clinical presentation may vary from no symptoms to severe gastrointestinal and neurological dysfunction similar to abetalipoproteinemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12551903, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21981844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27206948}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Most cases of FHBL1 result from nonsense mutations in the APOB gene that lead to a premature stop codon, which generate prematurely truncated apo B protein products (PubMed:21981844). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21981844}.; DISEASE: Hypercholesterolemia, familial, 2 (FHCL2) [MIM:144010]: A form of hypercholesterolemia, a disorder of lipoprotein metabolism characterized by elevated serum low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels, which result in excess deposition of cholesterol in tissues and leads to xanthelasma, xanthomas, accelerated atherosclerosis and increased risk of premature coronary heart disease. FHCL2 inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21382890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2563166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7883971, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9259199}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Note=Defects in APOB associated with defects in other genes (polygenic) can contribute to hypocholesterolemia. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P04114 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
| No results found |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
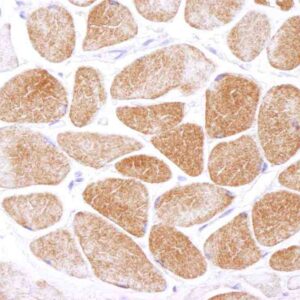


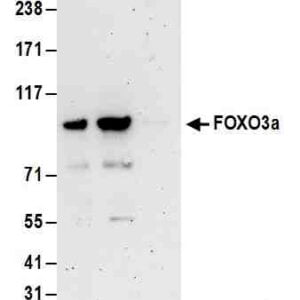
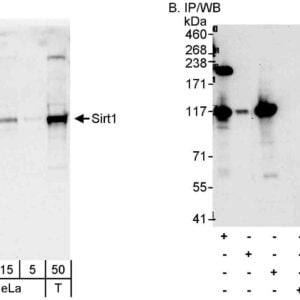
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.