| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | NP_254274 |
| express system | E.coli |
| product tag | No Tag |
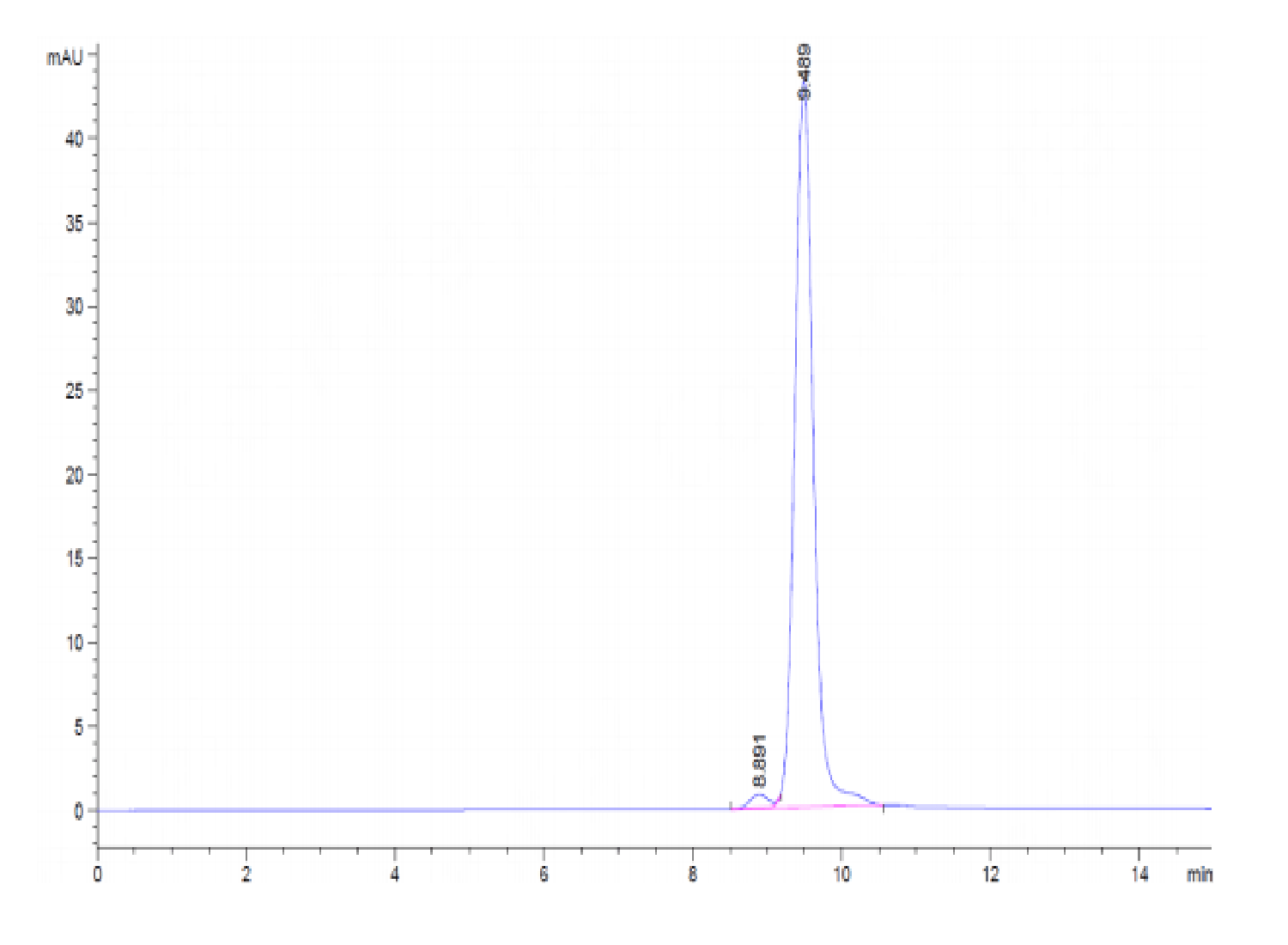
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Interleukin-33 (IL-33) is a cytokine belonging to the IL-1 family, playing a role in inflammatory, infectious and autoimmune diseases and expressed in the cellular nucleus in several tissues. High levels of IL-33 are expressed in epithelial barrier tissues and endothelial barriers. ST2 is a receptor for IL-33, expressed selectively on a subset of Th2 cells, mediating some of their functions. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 18 kDa same as Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Human IL-33 Protein 3247
$345.00 – $1,150.00
Summary
- Expression: E.coli
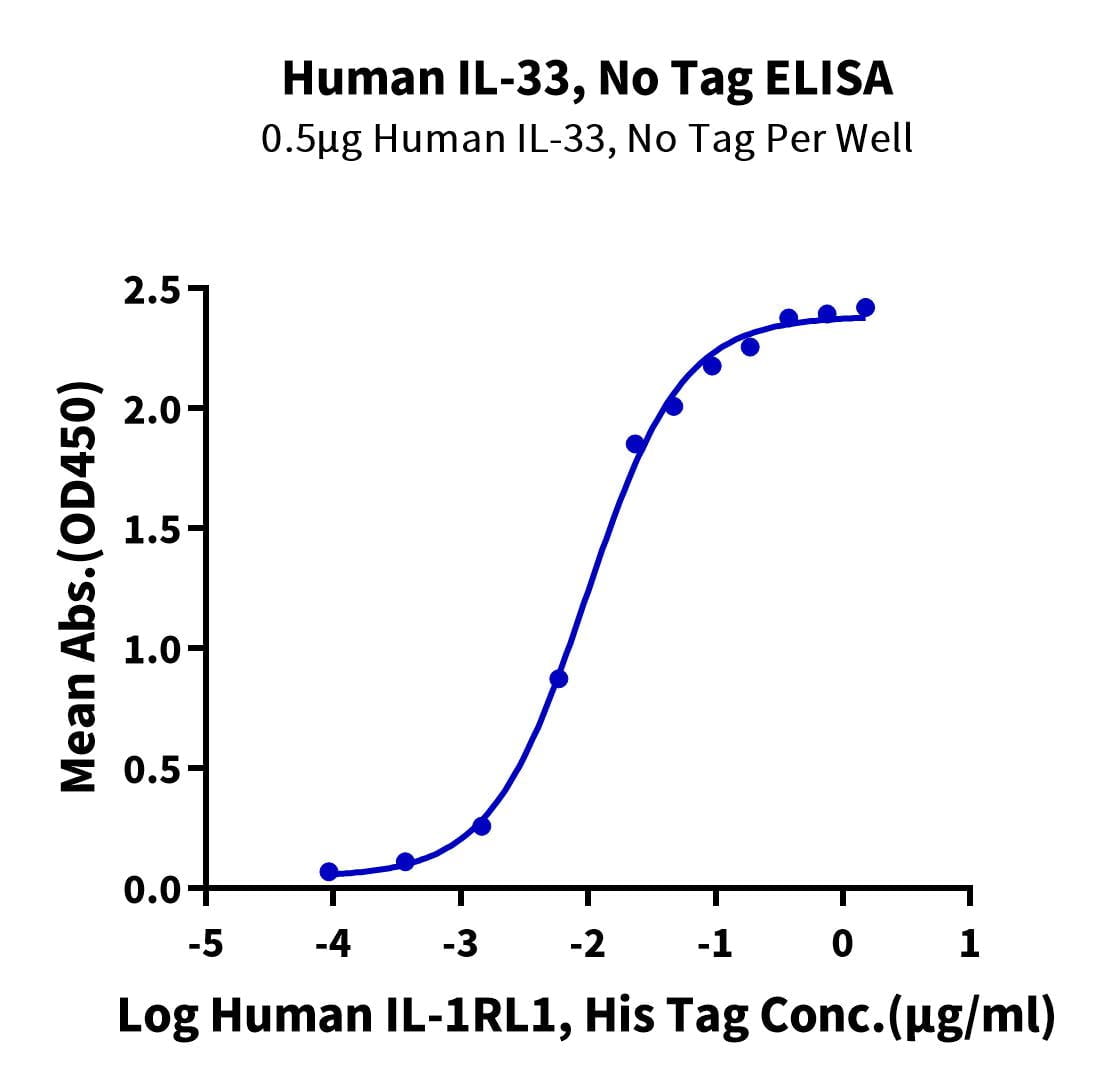
- Functional: Yes (ELISA)
- Amino Acid Range: Ser112-Thr270
Human IL-33 Protein 3247
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Interleukin-33 (IL-33) is a cytokine belonging to the IL-1 family, playing a role in inflammatory, infectious and autoimmune diseases and expressed in the cellular nucleus in several tissues. High levels of IL-33 are expressed in epithelial barrier tissues and endothelial barriers. ST2 is a receptor for IL-33, expressed selectively on a subset of Th2 cells, mediating some of their functions. |
| Protein names Interleukin-33 (IL-33) (Interleukin-1 family member 11) (IL-1F11) (Nuclear factor from high endothelial venules) (NF-HEV) [Cleaved into: Interleukin-33 (95-270); Interleukin-33 (99-270); Interleukin-33 (109-270)] |
| Protein family IL-1 family |
| Mass 30759Da |
| Function Cytokine that binds to and signals through the IL1RL1/ST2 receptor which in turn activates NF-kappa-B and MAPK signaling pathways in target cells (PubMed:16286016, PubMed:19841166). Involved in the maturation of Th2 cells inducing the secretion of T-helper type 2-associated cytokines (PubMed:17853410, PubMed:18836528). Also involved in activation of mast cells, basophils, eosinophils and natural killer cells (PubMed:17853410, PubMed:18836528). Acts as an enhancer of polarization of alternatively activated macrophages (PubMed:19841166). Acts as a chemoattractant for Th2 cells, and may function as an 'alarmin', that amplifies immune responses during tissue injury (PubMed:17853410, PubMed:18836528). Induces rapid UCP2-dependent mitochondrial rewiring that attenuates the generation of reactive oxygen species and preserves the integrity of Krebs cycle required for persistent production of itaconate and subsequent GATA3-dependent differentiation of inflammation-resolving alternatively activated macrophages (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BVZ5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16286016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17853410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18836528, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19841166}.; In quiescent endothelia the uncleaved form is constitutively and abundantly expressed, and acts as a chromatin-associated nuclear factor with transcriptional repressor properties, it may sequester nuclear NF-kappaB/RELA, lowering expression of its targets (PubMed:21734074). This form is rapidely lost upon angiogenic or pro-inflammatory activation (PubMed:18787100). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18787100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21734074}. |
| Subellular location Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12819012, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17185418, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18787100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18836528, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21734074}. Chromosome {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17185418}. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32272059}. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22215666}. Secreted {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19465481, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35794369}. Note=Secreted and released in the extracellular milieu by passing through the gasdermin-D (GSDMD) pore following cleavage by CELA1 (PubMed:35794369). Associates with heterochromatin and mitotic chromosomes (PubMed:17185418). The secretion is dependent on protein unfolding and facilitated by the cargo receptor TMED10; it results in protein translocation from the cytoplasm into the ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment) followed by vesicle entry and secretion (PubMed:32272059). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32272059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35794369}. |
| Tissues Expressed at high level in high endothelial venules found in tonsils, Peyer patches and mesenteric lymph nodes. Almost undetectable in placenta. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12819012}. |
| Structure Forms a 1:1:1 heterotrimeric complex with its primary high-affinity receptor IL1RL1 and the coreceptor IL1RAP (PubMed:19836339, PubMed:23980170). Interacts with cargo receptor TMED10; the interaction mediates the translocation from the cytoplasm into the ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment) and thereby secretion (PubMed:32272059). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19836339, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23980170, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32272059}.; (Microbial infection) Interacts (in reduced form) with H.polygyrus ARI. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29045903}. |
| Post-translational modification The full-length protein can be released from cells and is able to signal via the IL1RL1/ST2 receptor. However, proteolytic processing by CELA1, CSTG/cathepsin G and ELANE/neutrophil elastase produces C-terminal peptides that are more active than the unprocessed full length protein (PubMed:22307629, PubMed:35794369). May also be proteolytically processed by calpains (PubMed:19596270, PubMed:22307629). Proteolytic cleavage mediated by apoptotic caspases including CASP3 and CASP7 results in IL33 inactivation (PubMed:19559631). In vitro proteolytic cleavage by CASP1 was reported (PubMed:16286016, PubMed:19439663) but could not be confirmed in vivo (PubMed:19465481) suggesting that IL33 is probably not a direct substrate for that caspase (PubMed:19439663, PubMed:19465481). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16286016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19439663, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19465481, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19559631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19596270, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22307629, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35794369}. |
| Domain The homeodomain-like HTH domain mediates nuclear localization and heterochromatin associatio |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: O95760 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||