| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | O75874 |
| express system | E.coli |
| product tag | C-His |
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 90% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) is a metabolic enzyme that converts isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG). Genetic gain-of-function mutations in IDH1 and IDH2 confer a neomorphic activity that allow reduction of α -KG to (R)-2- hydroxyglutarate, the accumulation of which results in the development of cancers like low grade gliomas and leukemia.Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) is the most frequently mutated metabolic gene in cancer. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 47.35 kDa same as Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Human IDH1 Protein 2854
$270.00 – $900.00
Summary
- Expression: E.coli
- Pure: Yes (HPLC)
- Amino Acid Range: Ser2-Leu414
Human IDH1 Protein 2854
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and liquid |
| Form Liquid |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped with dry ice. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) is a metabolic enzyme that converts isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG). Genetic gain-of-function mutations in IDH1 and IDH2 confer a neomorphic activity that allow reduction of α -KG to (R)-2- hydroxyglutarate, the accumulation of which results in the development of cancers like low grade gliomas and leukemia.Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) is the most frequently mutated metabolic gene in cancer. |
| Protein names Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP] cytoplasmic (IDH) (IDH1) (EC 1.1.1.42) (Cytosolic NADP-isocitrate dehydrogenase) (IDPc) (NADP(+)-specific ICDH) (Oxalosuccinate decarboxylase) |
| Gene names IDH1,IDH1 PICD |
| Protein family Isocitrate and isopropylmalate dehydrogenases family |
| Mass 9606Da |
| Function Catalyzes the NADP(+)-dependent oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate (D-threo-isocitrate) to 2-ketoglutarate (2-oxoglutarate), which is required by other enzymes such as the phytanoyl-CoA dioxygenase (PubMed:10521434, PubMed:19935646). Plays a critical role in the generation of NADPH, an important cofactor in many biosynthesis pathways (PubMed:10521434). May act as a corneal epithelial crystallin and may be involved in maintaining corneal epithelial transparency (By similarity). |
| Catalytic activity BINDING 75..77; /ligand="NADP(+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:58349"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T09, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L, ECO:0007744|PDB:3INM, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAP, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAR, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAS, ECO:0007744|PDB:4I3K, ECO:0007744|PDB:4I3L, ECO:0007744|PDB:4KZO, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L03, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L04, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L06, ECO:0007744|PDB:4UMX, ECO:0007744|PDB:4UMY, ECO:0007744|PDB:4XRX, ECO:0007744|PDB:4XS3, ECO:0007744|PDB:5DE1, ECO:0007744|PDB:5L57, ECO:0007744|PDB:5L58, ECO:0007744|PDB:5LGE, ECO:0007744|PDB:5SUN, ECO:0007744|PDB:5SVF, ECO:0007744|PDB:5TQH"; BINDING 77; /ligand="substrate"; /ligand_note="ligand shared between two neighboring subunits"; /note="in other chain"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L"; BINDING 82; /ligand="NADP(+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:58349"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T09, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L, ECO:0007744|PDB:3INM, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAP, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAR, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAS, ECO:0007744|PDB:4I3K, ECO:0007744|PDB:4I3L, ECO:0007744|PDB:4KZO, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L03, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L04, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L06, ECO:0007744|PDB:4UMX, ECO:0007744|PDB:4UMY, ECO:0007744|PDB:4XRX, ECO:0007744|PDB:4XS3, ECO:0007744|PDB:5DE1, ECO:0007744|PDB:5L57, ECO:0007744|PDB:5LGE, ECO:0007744|PDB:5SUN, ECO:0007744|PDB:5SVF, ECO:0007744|PDB:5TQH"; BINDING 94..100; /ligand="substrate"; /ligand_note="ligand shared between two neighboring subunits"; /note="in other chain"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L"; BINDING 109; /ligand="substrate"; /ligand_note="ligand shared between two neighboring subunits"; /note="in other chain"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L"; BINDING 132; /ligand="substrate"; /ligand_note="ligand shared between two neighboring subunits"; /note="in other chain"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L"; BINDING 212; /ligand="substrate"; /ligand_note="ligand shared between two neighboring subunits"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L"; BINDING 252; /ligand="Mn(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29035"; /ligand_note="ligand shared between two neighboring subunits"; /evidence="ECO:0000305|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19935646, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L, ECO:0007744|PDB:3INM"; BINDING 260; /ligand="NADP(+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:58349"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L, ECO:0007744|PDB:3INM"; BINDING 275; /ligand="Mn(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29035"; /ligand_note="ligand shared between two neighboring subunits"; /note="in other chain"; /evidence="ECO:0000305|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19935646, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L, ECO:0007744|PDB:3INM"; BINDING 279; /ligand="Mn(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29035"; /ligand_note="ligand shared between two neighboring subunits"; /note="in other chain"; /evidence="ECO:0000305|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19935646, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L, ECO:0007744|PDB:3INM"; BINDING 310..315; /ligand="NADP(+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:58349"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T09, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L, ECO:0007744|PDB:3INM, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAP, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAR, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAS, ECO:0007744|PDB:4I3K, ECO:0007744|PDB:4I3L, ECO:0007744|PDB:4KZO, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L03, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L04, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L06, ECO:0007744|PDB:4UMX, ECO:0007744|PDB:4UMY, ECO:0007744|PDB:4XRX, ECO:0007744|PDB:4XS3, ECO:0007744|PDB:5DE1, ECO:0007744|PDB:5L57, ECO:0007744|PDB:5L58, ECO:0007744|PDB:5LGE, ECO:0007744|PDB:5SUN, ECO:0007744|PDB:5SVF, ECO:0007744|PDB:5TQH"; BINDING 328; /ligand="NADP(+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:58349"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:15173171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935646, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T09, ECO:0007744|PDB:1T0L, ECO:0007744|PDB:3INM, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAP, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAR, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MAS, ECO:0007744|PDB:4I3K, ECO:0007744|PDB:4I3L, ECO:0007744|PDB:4KZO, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L03, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L04, ECO:0007744|PDB:4L06, ECO:0007744|PDB:4UMX, ECO:0007744|PDB:4UMY, ECO:0007744|PDB:4XRX, ECO:0007744|PDB:4XS3, ECO:0007744|PDB:5DE1, ECO:0007744|PDB:5L57, ECO:0007744|PDB:5L58, ECO:0007744|PDB:5LGE, ECO:0007744|PDB:5SUN, ECO:0007744|PDB:5SVF, ECO:0007744|PDB:5TQH" |
| Subellular location Cytoplasm, cytosol. Peroxisome . |
| Structure Homodimer. |
| Post-translational modification Acetylation at Lys-374 dramatically reduces catalytic activity. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: O75874 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
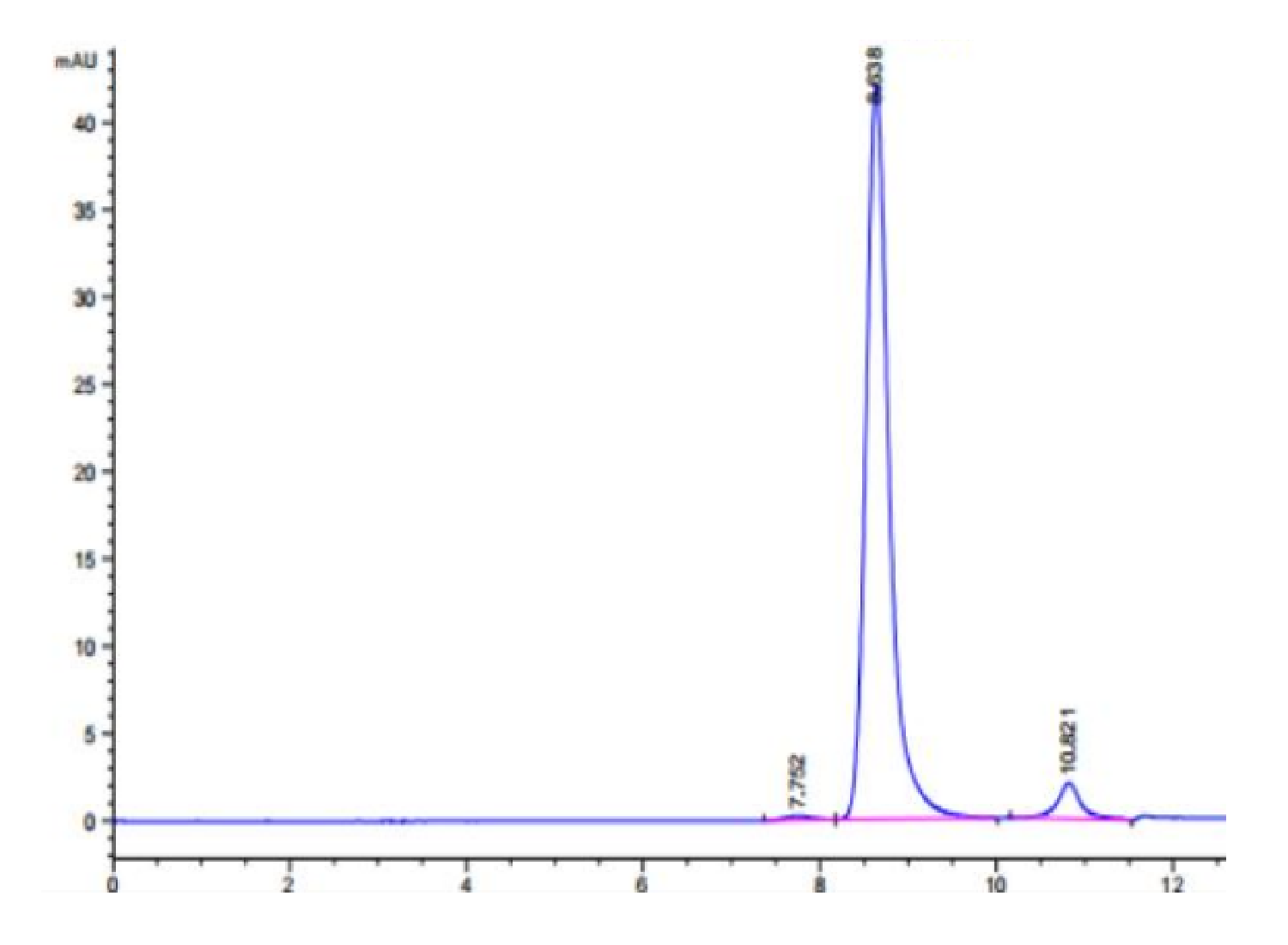 |
| The purity of Human IDH1 is greater than 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC. |
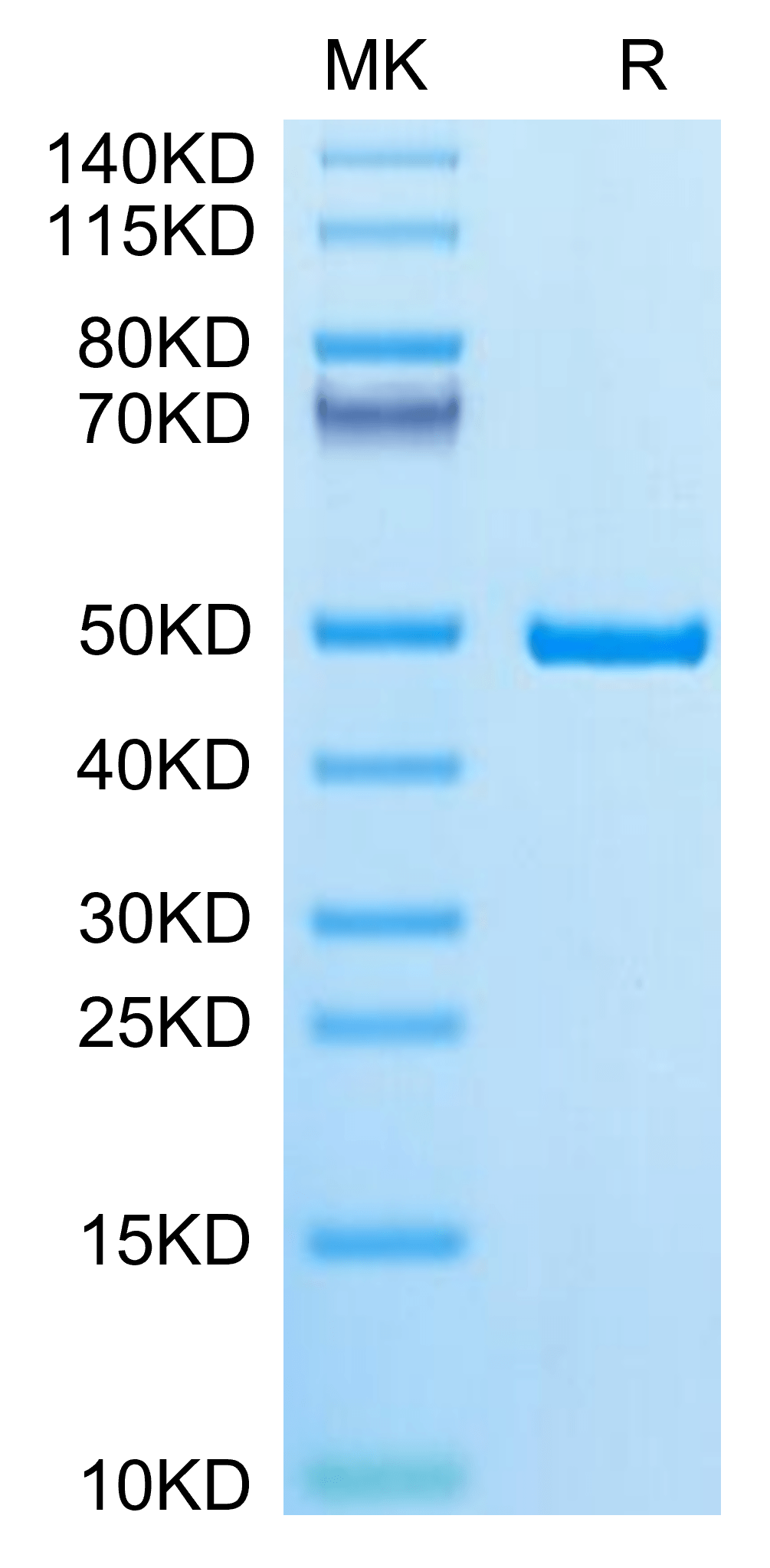 |
| Human IDH1 on Tris-Bis PAGE under reduced condition. The purity is greater than 95%. |
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||














