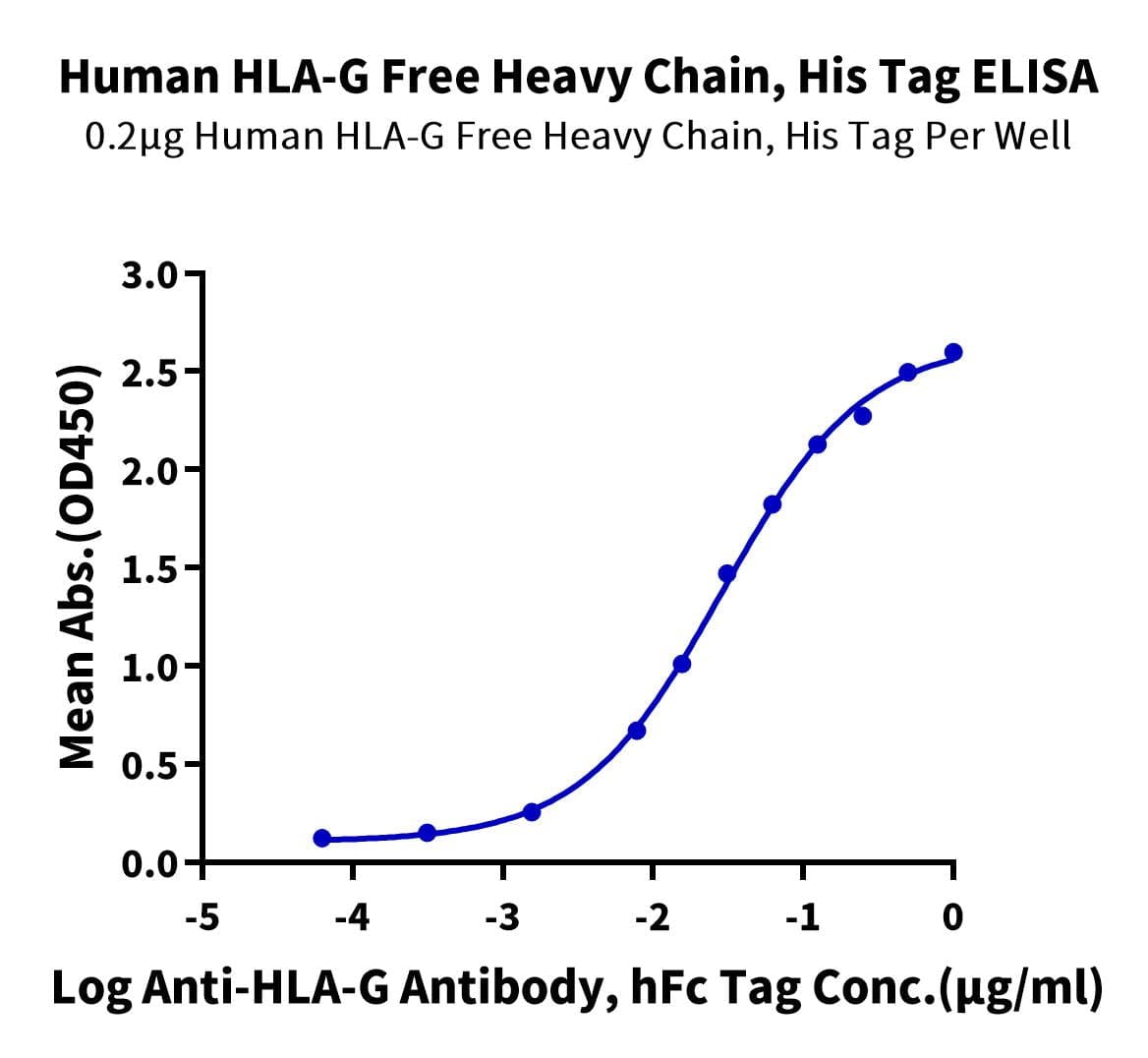
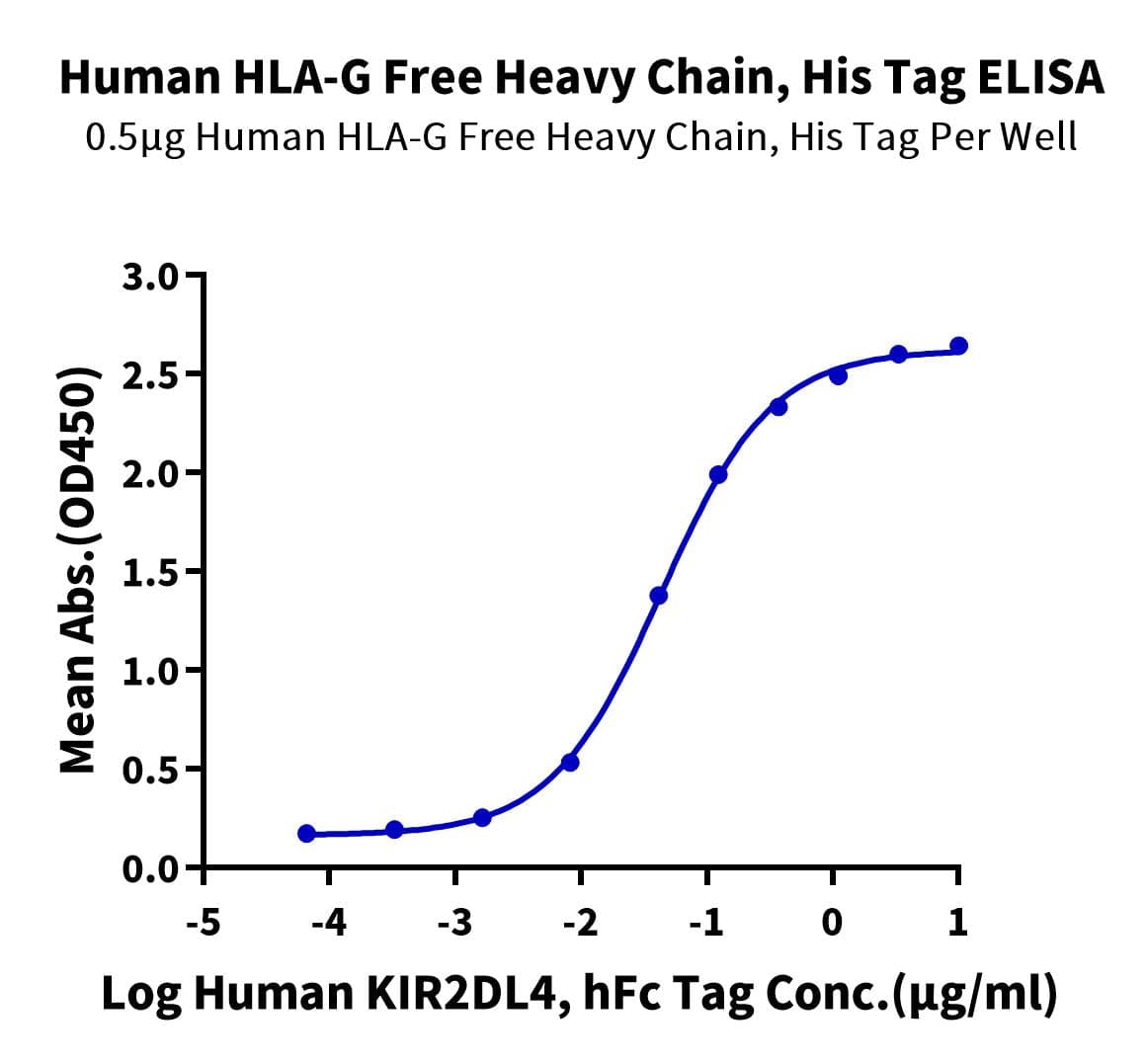
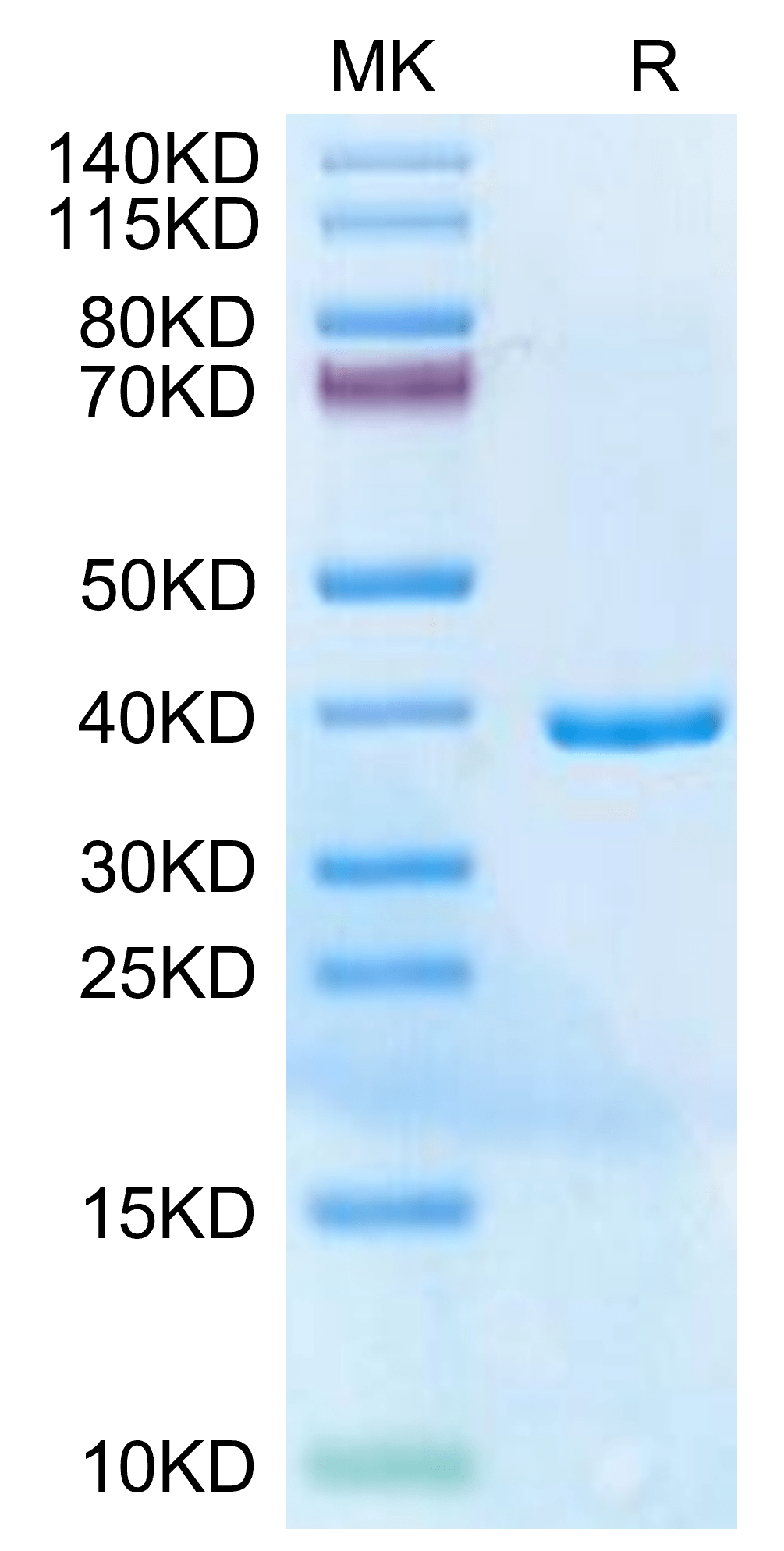
| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | P17693 |
| express system | E.coli |
| product tag | C-His-Avi |
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| background | HLA-G is a molecule that was first known to confer protection to the fetus from destruction by the immune system of its mother, thus critically contributing to fetal-maternal tolerance. The first functional finding constituted the basis for HLA-G research and can be summarized as such: HLA-G, membrane-bound or soluble, strongly binds its inhibitory receptors on immune cells (NK, T, B, monocytes/dendritic cells), inhibits the functions of these effectors, and so induces immune inhibition. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 35.5 kDa. The protein migrates to 36-40 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Human HLA-G Free Heavy Chain Protein 4338
$282.00 – $938.00
Summary
- Expression: E.coli
- Functional: Yes (ELISA)
- Amino Acid Range: Gly25-Thr305(C66S)
Human HLA-G Free Heavy Chain Protein 4338
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and liquid |
| Form Liquid |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped with dry ice. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| HLA-G is a molecule that was first known to confer protection to the fetus from destruction by the immune system of its mother, thus critically contributing to fetal-maternal tolerance. The first functional finding constituted the basis for HLA-G research and can be summarized as such: HLA-G, membrane-bound or soluble, strongly binds its inhibitory receptors on immune cells (NK, T, B, monocytes/dendritic cells), inhibits the functions of these effectors, and so induces immune inhibition. |
| Protein names HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, alpha chain G (HLA G antigen) (MHC class I antigen G) [Cleaved into: Soluble HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, alpha chain G (sHLA-G)] |
| Gene names HLA-G,HLA-G HLA-6.0 HLAG |
| Protein family MHC class I family |
| Mass 9606Da |
| Function [Isoform 1]: Non-classical major histocompatibility class Ib molecule involved in immune regulatory processes at the maternal-fetal interface (PubMed:19304799, PubMed:23184984, PubMed:29262349). In complex with B2M/beta-2 microglobulin binds a limited repertoire of nonamer self-peptides derived from intracellular proteins including histones and ribosomal proteins (PubMed:7584149, PubMed:8805247). Peptide-bound HLA-G-B2M complex acts as a ligand for inhibitory/activating KIR2DL4, LILRB1 and LILRB2 receptors on uterine immune cells to promote fetal development while maintaining maternal-fetal tolerance (PubMed:16366734, PubMed:19304799, PubMed:20448110, PubMed:23184984, PubMed:27859042, PubMed:29262349). Upon interaction with KIR2DL4 and LILRB1 receptors on decidual NK cells, it triggers NK cell senescence-associated secretory phenotype as a molecular switch to promote vascular remodeling and fetal growth in early pregnancy (PubMed:16366734, PubMed:19304799, PubMed:23184984, PubMed:29262349). Through interaction with KIR2DL4 receptor on decidual macrophages induces pro-inflammatory cytokine production mainly associated with tissue remodeling (PubMed:19304799). Through interaction with LILRB2 receptor triggers differentiation of type 1 regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, both of which actively maintain maternal-fetal tolerance (PubMed:20448110, PubMed:27859042). May play a role in balancing tolerance and antiviral-immunity at maternal-fetal interface by keeping in check the effector functions of NK, CD8+ T cells and B cells (PubMed:10190900, PubMed:11290782, PubMed:24453251). Reprograms B cells toward an immune suppressive phenotype via LILRB1 (PubMed:24453251). May induce immune activation/suppression via intercellular membrane transfer (trogocytosis), likely enabling interaction with KIR2DL4, which resides mostly in endosomes (PubMed:20179272, PubMed:26460007). Through interaction with the inhibitory receptor CD160 on endothelial cells may control angiogenesis in immune privileged sites (PubMed:16809620).; [Isoform 2]: Likely does not bind B2M and presents peptides. Negatively regulates NK cell- and CD8+ T cell-mediated cytotoxicity (PubMed:11290782).; [Isoform 3]: Likely does not bind B2M and presents peptides. Negatively regulates NK cell- and CD8+ T cell-mediated cytotoxicity (PubMed:11290782).; [Isoform 4]: Likely does not bind B2M and presents peptides. Negatively regulates NK cell- and CD8+ T cell-mediated cytotoxicity (PubMed:11290782).; [Isoform 5]: Non-classical major histocompatibility class Ib molecule involved in immune regulatory processes at the maternal-fetal interface (PubMed:19304799, PubMed:23184984, PubMed:29262349). In complex with B2M/beta-2 microglobulin binds a limited repertoire of nonamer self-peptides derived from intracellular proteins including histones and ribosomal proteins (PubMed:7584149, PubMed:8805247). Peptide-bound HLA-G-B2M complex acts as a ligand for inhibitory/activating KIR2DL4, LILRB1 and LILRB2 receptors on uterine immune cells to promote fetal development while maintaining maternal-fetal tolerance (PubMed:16366734, PubMed:19304799, PubMed:20448110, PubMed:23184984, PubMed:29262349). Upon interaction with KIR2DL4 and LILRB1 receptors on decidual NK cells, it triggers NK cell senescence-associated secretory phenotype as a molecular switch to promote vascular remodeling and fetal growth in early pregnancy (PubMed:16366734, PubMed:19304799, PubMed:23184984, PubMed:29262349). Through interaction with KIR2DL4 receptor on decidual macrophages induces pro-inflammatory cytokine production mainly associated with tissue remodeling (PubMed:19304799). Through interaction with LILRB2 receptor triggers differentiation of type 1 regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, both of which actively maintain maternal-fetal tolerance (PubMed:20448110). Reprograms B cells toward an immune suppressive phenotype via LILRB1 (PubMed:24453251).; [Isoform 6]: Likely does not bind B2M and presents peptides.; [Isoform 7]: Likely does not bind B2M and presents peptides. |
| Catalytic activity #N/A |
| Subellular location [Isoform 1]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Early endosome membrane .; [Soluble HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, alpha chain G]: Secreted .; [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein .; [Isoform 3]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein .; [Isoform 4]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein .; [Isoform 5]: Secreted. Early endosome .; [Isoform 6]: Secreted .; [Isoform 7]: Secreted .; Cell projection, filopodium membrane. Note=HLA-G trogocytosis from extravillous trophoblast's filopodia occurs in the majority of decidual NK cells. |
| Tissues Expressed in adult eye (PubMed:1570318). Expressed in immune cell subsets including monocytes, myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells and regulatory T cells (Tr1)(at protein level) (PubMed:20448110). Secreted by follicular dendritic cell and follicular helper T cells (PubMed:24453251).; [Isoform 5]: Detected in physiological fluids including amniotic fluid and serum.; [Isoform 7]: Expressed in placenta, amniotic membrane, skin, cord blood and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. |
| Structure Forms a heterotrimer with B2M and a self-peptide (peptide-bound HLA-G-B2M) (PubMed:7584149, PubMed:8805247). HLA-G-B2M complex interacts with components of the antigen processing machinery TAPBP and TAP1-TAP2 complex; this interaction is required for loading of high affinity peptides and heterotrimer translocation to the cell surface (PubMed:7584149). Interacts with CALCR; this interaction is required for appropriate folding (PubMed:9640257). Interacts with COPB1; this interaction mediates the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) retrieval of HLA-G-B2M complexes that bind low affinity peptides (PubMed:11520457, PubMed:12582157). On the cell surface, peptide-bound HLA-G-B2M molecules (referred to as monomers) can form disulfide-linked homomultimers, homodimers and homotrimers (PubMed:12454284, PubMed:12874224, PubMed:16455647). Interacts with KIR2DL4; this interaction is direct (PubMed:10190900, PubMed:16366734). Interacts with LILRB1 and LILRB2 receptors; this interaction is direct (PubMed:12853576, PubMed:16366734, PubMed:16455647, PubMed:17056715). Interacts with CD160; this interactions is direct (PubMed:16809620). Interacts with CD8A homodimer; this interaction is direct and might down-regulate T cell receptor signaling (PubMed:12853576). Isoform 2: Forms a non-disulfide-linked homodimer and interacts with LILRB2 (PubMed:28348268). |
| Post-translational modification N-glycosylated.; [Soluble HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, alpha chain G]: Produced by proteolytic cleavage at the cell surface (shedding) by matrix metalloproteinase MMP2. |
| Domain Th |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P17693 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||