| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | NP_000148.2 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His |
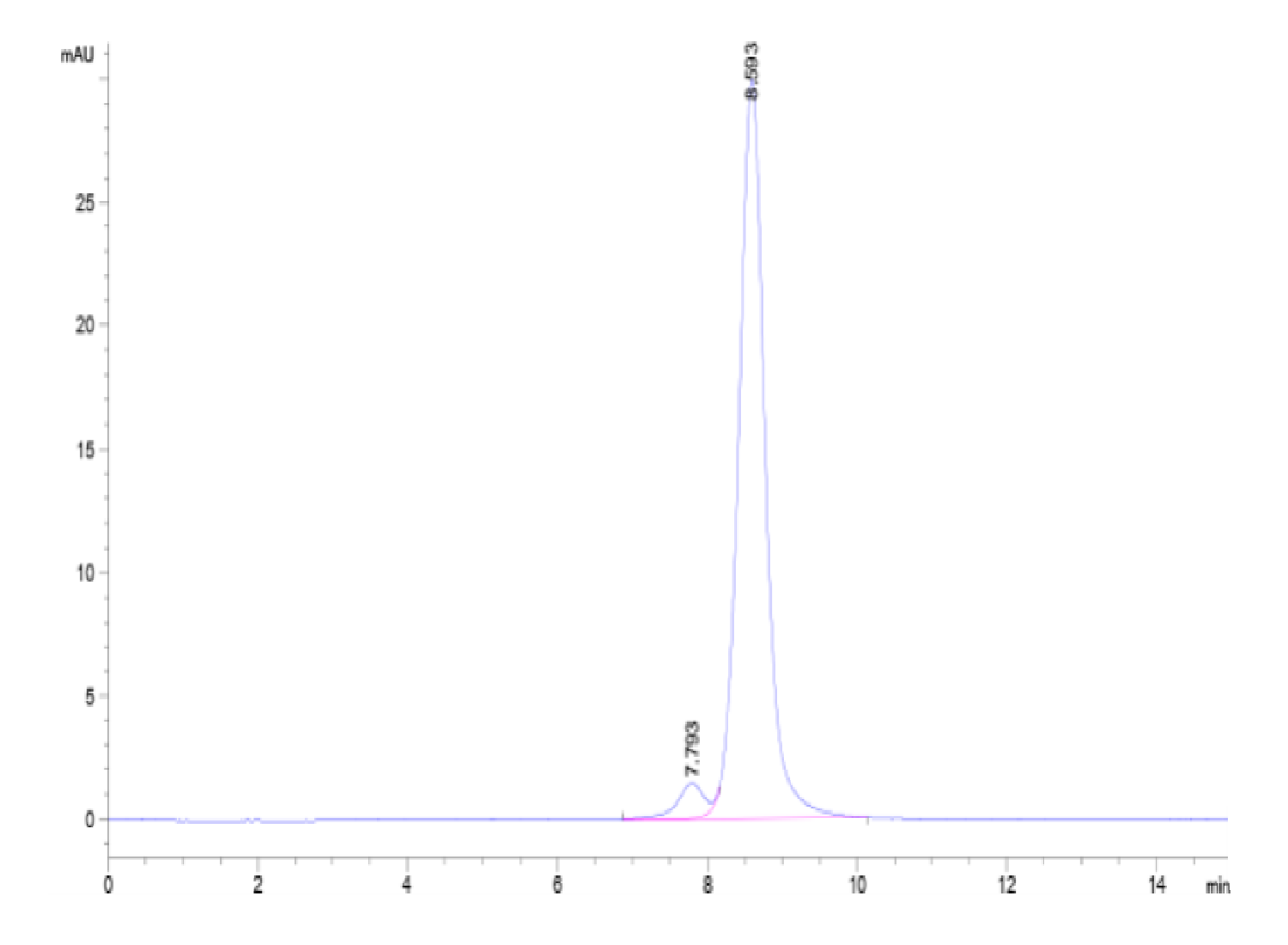
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Glucocerebrosidase (GBA) mutations are the most important genetic risk factor for the development of Parkinson disease (PD). GBA encodes the lysosomal enzyme glucocerebrosidase (GCase). |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 56.69 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 60-70 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Human GBA/glucocerebrosidase Protein 2951
$750.00 – $2,500.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
- Active: Yes (catalytic)
- Amino Acid Range: Ala40-Gln536
Human GBA/glucocerebrosidase Protein 2951
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Glucocerebrosidase (GBA) mutations are the most important genetic risk factor for the development of Parkinson disease (PD). GBA encodes the lysosomal enzyme glucocerebrosidase (GCase). |
| Protein names Lysosomal acid glucosylceramidase (Lysosomal acid GCase) (EC 3.2.1.45) (Acid beta-glucosidase) (Alglucerase) (Beta-glucocerebrosidase) (Beta-GC) (Beta-glucosylceramidase 1) (Cholesterol glucosyltransferase) (SGTase) (EC 2.4.1.-) (Cholesteryl-beta-glucosidase) (EC 3.2.1.-) (D-glucosyl-N-acylsphingosine glucohydrolase) (Glucosylceramidase b |
| Protein family Glycosyl hydrolase 30 family |
| Mass 59716Da |
| Function Glucosylceramidase that catalyzes, within the lysosomal compartment, the hydrolysis of glucosylceramides/GlcCers (such as beta-D-glucosyl-(1<->1')-N-acylsphing-4-enine) into free ceramides (such as N-acylsphing-4-enine) and glucose (PubMed:15916907, PubMed:24211208, PubMed:32144204, PubMed:9201993). Plays a central role in the degradation of complex lipids and the turnover of cellular membranes (PubMed:27378698). Through the production of ceramides, participates in the PKC-activated salvage pathway of ceramide formation (PubMed:19279011). Catalyzes the glucosylation of cholesterol, through a transglucosylation reaction where glucose is transferred from GlcCer to cholesterol (PubMed:24211208, PubMed:26724485, PubMed:32144204). GlcCer containing mono-unsaturated fatty acids (such as beta-D-glucosyl-N-(9Z-octadecenoyl)-sphing-4-enine) are preferred as glucose donors for cholesterol glucosylation when compared with GlcCer containing same chain length of saturated fatty acids (such as beta-D-glucosyl-N-octadecanoyl-sphing-4-enine) (PubMed:24211208). Under specific conditions, may alternatively catalyze the reverse reaction, transferring glucose from cholesteryl 3-beta-D-glucoside to ceramide (Probable) (PubMed:26724485). Can also hydrolyze cholesteryl 3-beta-D-glucoside producing glucose and cholesterol (PubMed:24211208, PubMed:26724485). Catalyzes the hydrolysis of galactosylceramides/GalCers (such as beta-D-galactosyl-(1<->1')-N-acylsphing-4-enine), as well as the transfer of galactose between GalCers and cholesterol in vitro, but with lower activity than with GlcCers (PubMed:32144204). Contrary to GlcCer and GalCer, xylosylceramide/XylCer (such as beta-D-xyosyl-(1<->1')-N-acylsphing-4-enine) is not a good substrate for hydrolysis, however it is a good xylose donor for transxylosylation activity to form cholesteryl 3-beta-D-xyloside (PubMed:33361282). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15916907, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19279011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24211208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26724485, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27378698, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33361282, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9201993, ECO:0000305|PubMed:32144204}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=a beta-D-glucosyl-(1<->1')-N-acylsphing-4-enine + H2O = an N-acylsphing-4-enine + D-glucose; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:13269, ChEBI:CHEBI:4167, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:22801, ChEBI:CHEBI:52639; EC=3.2.1.45; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:15916907, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16293621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24211208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9201993}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:13270; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:16293621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=a beta-D-galactosyl-(1<->1')-N-acylsphing-4-enine + H2O = an N-acylsphing-4-enine + D-galactose; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:14297, ChEBI:CHEBI:4139, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:18390, ChEBI:CHEBI:52639; EC=3.2.1.46; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:14298; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:32144204}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=cholesteryl 3-beta-D-glucoside + H2O = cholesterol + D-glucose; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:11956, ChEBI:CHEBI:4167, ChEBI:CHEBI:15377, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:17495; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:24211208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33361282}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:11957; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:33361282, ECO:0000305|PubMed:24211208}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=a beta-D-glucosyl-(1<->1')-N-acylsphing-4-enine + cholesterol = an N-acylsphing-4-enine + cholesteryl 3-beta-D-glucoside; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:58264, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:17495, ChEBI:CHEBI:22801, ChEBI:CHEBI:52639; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:24211208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26724485, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:58265; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204, ECO:0000305|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=right-to-left; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:58266; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:32144204}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=beta-D-glucosyl-N-(9Z-octadecenoyl)-sphing-4E-enine + cholesterol = cholesteryl 3-beta-D-glucoside + N-(9Z-octadecenoyl)-sphing-4-enine; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:58324, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:17495, ChEBI:CHEBI:77996, ChEBI:CHEBI:139140; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:24211208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:58325; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204, ECO:0000305|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=right-to-left; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:58326; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:32144204}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=beta-D-glucosyl-(1<->1')-N-hexadecanoylsphing-4-enine + cholesterol = cholesteryl 3-beta-D-glucoside + N-hexadecanoylsphing-4-enine; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:58316, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:17495, ChEBI:CHEBI:72959, ChEBI:CHEBI:84716; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:58317; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=right-to-left; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:58318; Evidence={ECO:0000305}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=beta-D-glucosyl-N-octanoylsphing-4E-enine + cholesterol = cholesteryl 3-beta-D-glucoside + N-octanoylsphing-4-enine; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70303, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:17495, ChEBI:CHEBI:45815, ChEBI:CHEBI:65222; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70304; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=right-to-left; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70305; Evidence={ECO:0000305}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=beta-D-glucosyl-N-dodecanoylsphing-4-enine + cholesterol = cholesteryl 3-beta-D-glucoside + N-dodecanoylsphing-4-enine; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70307, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:17495, ChEBI:CHEBI:72956, ChEBI:CHEBI:76297; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70308; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=right-to-left; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70309; Evidence={ECO:0000305}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=beta-D-glucosyl-(1<->1)-N-octadecanoylsphing-4-enine + cholesterol = cholesteryl 3-beta-D-glucoside + N-octadecanoylsphing-4-enine; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70311, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:17495, ChEBI:CHEBI:72961, ChEBI:CHEBI:84719; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70312; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=right-to-left; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70313; Evidence={ECO:0000305}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=beta-D-glucosyl-(1<->1')-N-(15Z-tetracosenoyl)-sphing-4-enine + cholesterol = cholesteryl 3-beta-D-glucoside + N-(15Z-tetracosenoyl)-sphing-4-enine; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70315, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:17495, ChEBI:CHEBI:74450, ChEBI:CHEBI:76302; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70316; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:24211208}; PhysiologicalDirection=right-to-left; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70317; Evidence={ECO:0000305}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=a beta-D-galactosyl-(1<->1')-N-acylsphing-4-enine + cholesterol = an N-acylsphing-4-enine + cholesteryl 3-beta-D-galactoside; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70235, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:18390, ChEBI:CHEBI:52639, ChEBI:CHEBI:189066; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70236; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204}; PhysiologicalDirection=right-to-left; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70237; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:32144204}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=1-(beta-D-galactosyl)-N-dodecanoylsphing-4-enine + cholesterol = cholesteryl 3-beta-D-galactoside + N-dodecanoylsphing-4-enine; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70255, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:72956, ChEBI:CHEBI:73432, ChEBI:CHEBI:189066; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70256; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144204}; PhysiologicalDirection=right-to-left; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70257; Evidence={ECO:0000305|PubMed:32144204}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=a beta-D-xylosyl-(1<->1')-N-acylsphing-4-enine + cholesterol = an N-acylsphing-4-enine + cholesteryl 3-beta-D-xyloside; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70239, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:52639, ChEBI:CHEBI:189067, ChEBI:CHEBI:189068; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:33361282}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70240; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:33361282}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=beta-D-xylosyl-(1<->1')-N-(9Z-octadecenoyl)-sphing-4-enine + cholesterol = cholesteryl 3-beta-D-xyloside + N-(9Z-octadecenoyl)-sphing-4-enine; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70251, ChEBI:CHEBI:16113, ChEBI:CHEBI:77996, ChEBI:CHEBI:189067, ChEBI:CHEBI:189081; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:33361282}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:70252; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:33361282}; |
| Pathway PATHWAY: Steroid metabolism; cholesterol metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24211208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26724485}.; PATHWAY: Sphingolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16293621, ECO:0000269|PubMed: |
| Subellular location Lysosome membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17187079, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17897319, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18022370}; Peripheral membrane protein {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10781797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18022370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1848227}; Lumenal side {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18022370}. Note=Interaction with saposin-C promotes membrane association (PubMed:10781797). Targeting to lysosomes occurs through an alternative MPR-independent mechanism via SCARB2 (PubMed:18022370). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10781797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18022370}. |
| Structure Interacts with saposin-C (PubMed:10781797). Interacts with SCARB2 (PubMed:18022370). Interacts with TCP1 (PubMed:21098288). May interacts with SNCA; this interaction may inhibit the glucosylceramidase activity (PubMed:23266198). Interacts with GRN; this interaction prevents aggregation of GBA1-SCARB2 complex via interaction with HSPA1A upon stress (PubMed:27789271). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10781797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18022370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21098288, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23266198, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27789271}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P04062 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||