| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | P10909 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His |
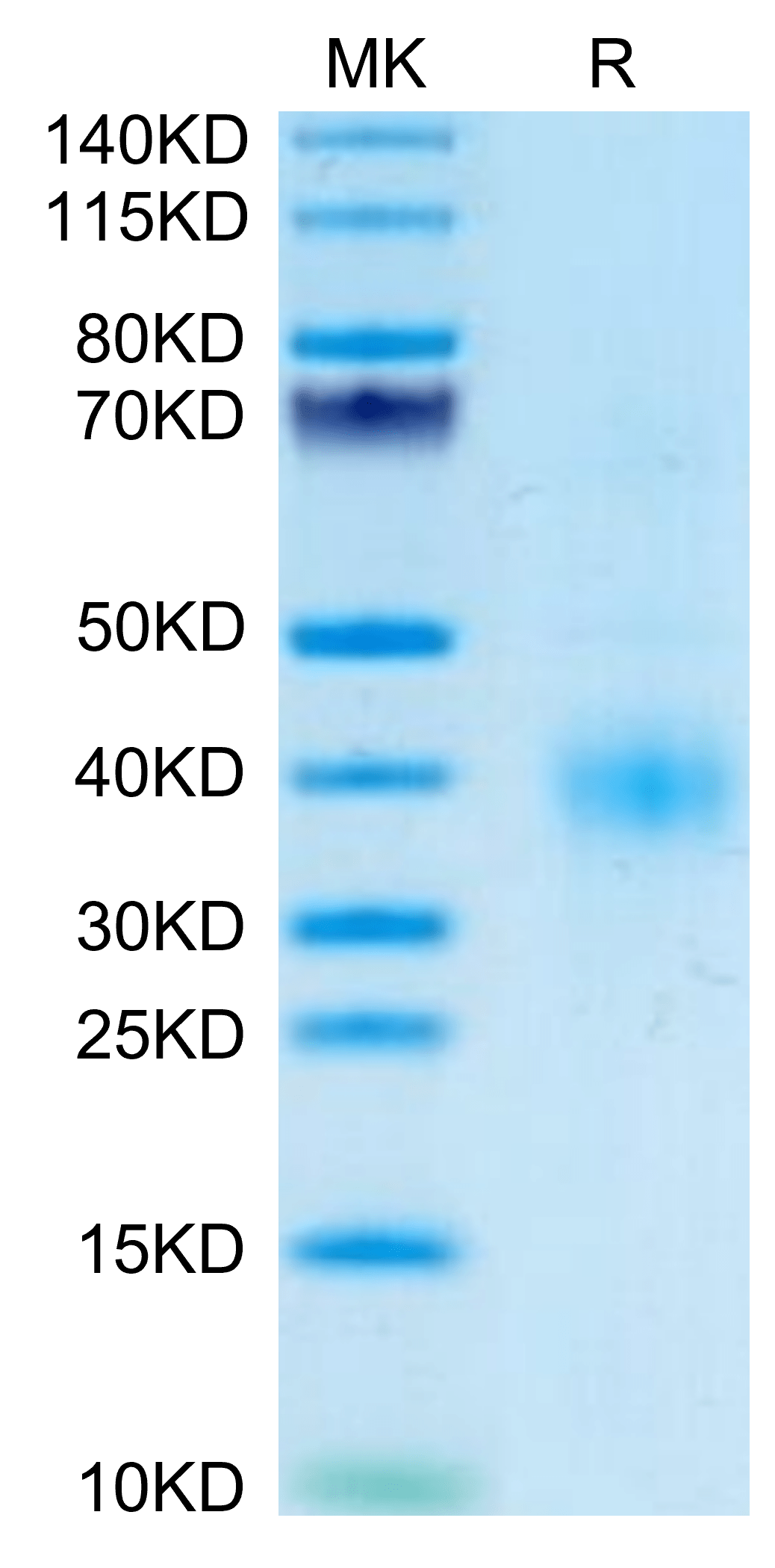
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| background | Clusterin (CLU) is a stress-activated, ATP-independent molecular chaperone, normally secreted from cells, that is up-regulated in Alzheimer disease and in many cancers. It plays important roles in protein homeostasis/proteostasis, inhibition of cell death pathways, and modulation of pro-survival signalling and transcriptional networks. Changes in the CLU gene locus are highly associated with Alzheimer disease, and many therapy-resistant cancers over-express CLU. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 51.2 kDa. The protein migrates to 38-41 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per ug by the LAL method. |
Human Clusterin Protein 5112
$270.00 – $900.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
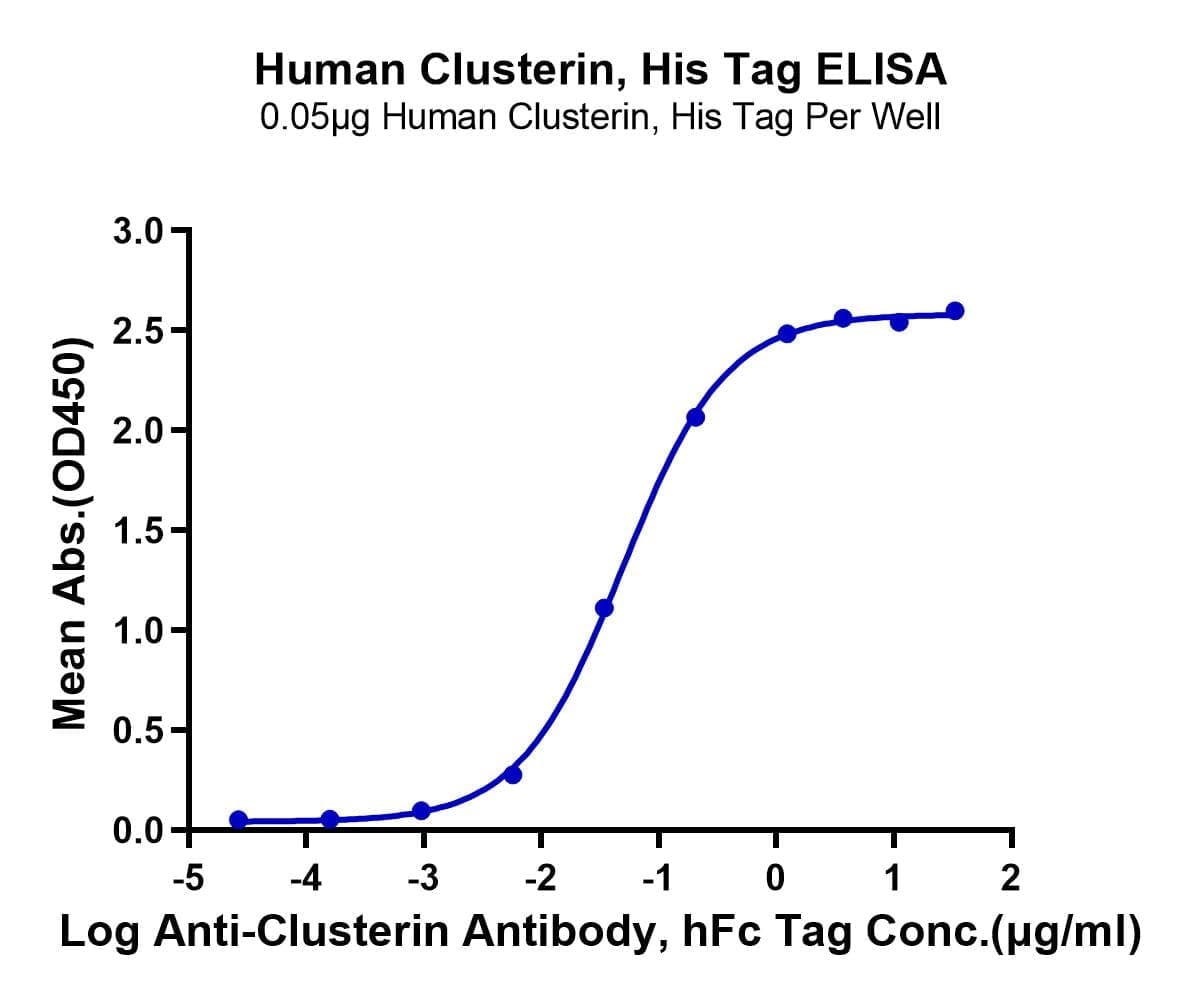
- Functional: Yes (ELISA)
- Amino Acid Range: Asp23-Glu449
Human Clusterin Protein 5112
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Clusterin (CLU) is a stress-activated, ATP-independent molecular chaperone, normally secreted from cells, that is up-regulated in Alzheimer disease and in many cancers. It plays important roles in protein homeostasis/proteostasis, inhibition of cell death pathways, and modulation of pro-survival signalling and transcriptional networks. Changes in the CLU gene locus are highly associated with Alzheimer disease, and many therapy-resistant cancers over-express CLU. |
| Protein names Clusterin (Aging-associated gene 4 protein) (Apolipoprotein J) (Apo-J) (Complement cytolysis inhibitor) (CLI) (Complement-associated protein SP-40,40) (Ku70-binding protein 1) (NA1/NA2) (Sulfated glycoprotein 2) (SGP-2) (Testosterone-repressed prostate message 2) (TRPM-2) [Cleaved into: Clusterin beta chain (ApoJalpha) (Complement cytolys |
| Gene names CLU,CLU APOJ CLI KUB1 AAG4 |
| Protein family Clusterin family |
| Mass 9606Da |
| Function [Isoform 1]: Functions as extracellular chaperone that prevents aggregation of non native proteins (PubMed:11123922, PubMed:19535339). Prevents stress-induced aggregation of blood plasma proteins (PubMed:11123922, PubMed:12176985, PubMed:17260971, PubMed:19996109). Inhibits formation of amyloid fibrils by APP, APOC2, B2M, CALCA, CSN3, SNCA and aggregation-prone LYZ variants (in vitro) (PubMed:12047389, PubMed:17407782, PubMed:17412999). Does not require ATP (PubMed:11123922). Maintains partially unfolded proteins in a state appropriate for subsequent refolding by other chaperones, such as HSPA8/HSC70 (PubMed:11123922). Does not refold proteins by itself (PubMed:11123922). Binding to cell surface receptors triggers internalization of the chaperone-client complex and subsequent lysosomal or proteasomal degradation (PubMed:21505792). Protects cells against apoptosis and against cytolysis by complement (PubMed:2780565). Intracellular forms interact with ubiquitin and SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes and promote the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:20068069). Promotes proteasomal degradation of COMMD1 and IKBKB (PubMed:20068069). Modulates NF-kappa-B transcriptional activity (PubMed:12882985). A mitochondrial form suppresses BAX-dependent release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm and inhibit apoptosis (PubMed:16113678, PubMed:17689225). Plays a role in the regulation of cell proliferation (PubMed:19137541). An intracellular form suppresses stress-induced apoptosis by stabilizing mitochondrial membrane integrity through interaction with HSPA5 (PubMed:22689054). Secreted form does not affect caspase or BAX-mediated intrinsic apoptosis and TNF-induced NF-kappa-B-activity (PubMed:24073260). Secreted form act as an important modulator during neuronal differentiation through interaction with STMN3 (By similarity). Plays a role in the clearance of immune complexes that arise during cell injury (By similarity).; [Isoform 6]: Does not affect caspase or BAX-mediated intrinsic apoptosis and TNF-induced NF-kappa-B-activity.; [Isoform 4]: Does not affect caspase or BAX-mediated intrinsic apoptosis and TNF-induced NF-kappa-B-activity (PubMed:24073260). Promotes cell death through interaction with BCL2L1 that releases and activates BAX (PubMed:21567405). |
| Catalytic activity #N/A |
| Subellular location [Isoform 1]: Secreted. Note=Can retrotranslocate from the secretory compartments to the cytosol upon cellular stress.; [Isoform 4]: Cytoplasm. Note=Keeps cytoplasmic localization in stressed and unstressed cell.; [Isoform 6]: Cytoplasm. Note=Keeps cytoplasmic localization in stressed and unstressed cell.; Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Mitochondrion membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Microsome. Endoplasmic reticulum. Mitochondrion. Mitochondrion membrane. Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, chromaffin granule. Note=Secreted isoforms can retrotranslocate from the secretory compartments to the cytosol upon cellular stress (PubMed:17451556). Detected in perinuclear foci that may be aggresomes containing misfolded, ubiquitinated proteins (PubMed:20068069). Detected at the mitochondrion membrane upon induction of apoptosis (PubMed:17689225). Under ER stress, a immaturely glycosylated pre-secreted form retrotranslocates from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-Golgi network to the cytoplasm to localize in the mitochondria through HSPA5 interaction (PubMed:22689054). ER stress reduces secretion (PubMed:22689054). Under the stress, minor amounts of non-secreted forms accumulate in cytoplasm (PubMed:17451556, PubMed:22689054, PubMed:24073260). Non-secreted forms emerge mainly from failed translocation, alternative splicing or non-canonical initiation start codon (PubMed:12551933, PubMed:24073260). |
| Tissues Detected in blood plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, milk, seminal plasma and colon mucosa. Detected in the germinal center of colon lymphoid nodules and in colon parasympathetic ganglia of the Auerbach plexus (at protein level). Ubiquitous. Detected in brain, testis, ovary, liver and pancreas, and at lower levels in kidney, heart, spleen and lung. |
| Structure Antiparallel disulfide-linked heterodimer of an alpha chain and a beta chain (PubMed:12047389, PubMed:1491011, PubMed:1551440, PubMed:2387851, PubMed:2780565, PubMed:8328966). Self-associates and forms higher oligomers (PubMed:1903064). Interacts with a broad range of misfolded proteins, including APP, APOC2 and LYZ (PubMed:17407782, PubMed:17412999, PubMed:8328966). Slightly acidic pH promotes interaction with misfolded proteins (PubMed:12176985). Forms high-molecular weight oligomers upon interaction with misfolded proteins (PubMed:19535339). Interacts with APOA1, LRP2, CLUAP1 and PON1 (PubMed:15480429, PubMed:17260971, PubMed:1742316, PubMed:1903064, PubMed:8292612). Interacts with the complement complex (PubMed:2601725). Interacts (via alpha chain) with XRCC6 (By similarity). Interacts with SYVN1, COMMD1, BTRC, CUL1 and with ubiquitin and SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes (PubMed:17451556, PubMed:20068069). Interacts (via alpha chain) with BAX in stressed cells, where BAX undergoes a conformation change leading to association with the mitochondrial membrane (PubMed:16113678). Does not interact with BAX in unstressed cells (PubMed:16113678). Found in a complex with LTF, CLU, EPPIN and SEMG1 (PubMed:17567961). Interacts (immaturely glycosylated pre-secreted form) with HSPA5; this interaction promotes CLU stability and facilitates stress-induced CLU retrotranslocation from the secretory pathway to the mitochondria, thereby reducing stress-induced apoptosis by stabilizing mitochondrial membrane integrity (PubMed:22689054). Interacts (isoform 4) with BCL2L1; this interaction releases and activates BAX and promotes cell death (PubMed:21567405). Interacts with TGFBR2 and ACVR1 (PubMed:8555189). Interacts (secreted form) with STMN3; this interaction may act as an important modulator during neuronal differentiation (By similarity). Interacts with VLDLR and LRP8 (PubMed:24381170). |
| Post-translational modification Proteolytically cleaved on its way through the secretory system, probably within the Golgi lumen (PubMed:2387851). Proteolytic cleavage is not necessary for its chaperone activity (PubMed:25402950). All non-secreted forms are not proteolytically cleaved (PubMed:24073260). Chaperone activity of uncleaved forms is dependent on a non-reducing environment (PubMed:25402950).; Polyubiquitinated, leading to proteasomal degradation (PubMed:17451556, PubMed:19137541). Under cellular stress, the intracellular level of cleaved form is reduced due to proteasomal degradation (PubMed:17451556).; Extensively glycosylated with sulfated N-linked carbohydrates (PubMed:17260971, PubMed:2387851). About 30% of the protein mass is comprised of complex N-linked carbohydrate (PubMed:2387851). Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress induces changes in glycosylation status and increases level of hypoglycosylated forms (PubMed:22689054). Core carbohydrates are essential for chaperone activity (PubMed:25402950). Non-secreted forms are hypoglycosylated or unglycosylated (PubMed:24073260). |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P10909 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||