| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | Q9NNX6 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | N-His |
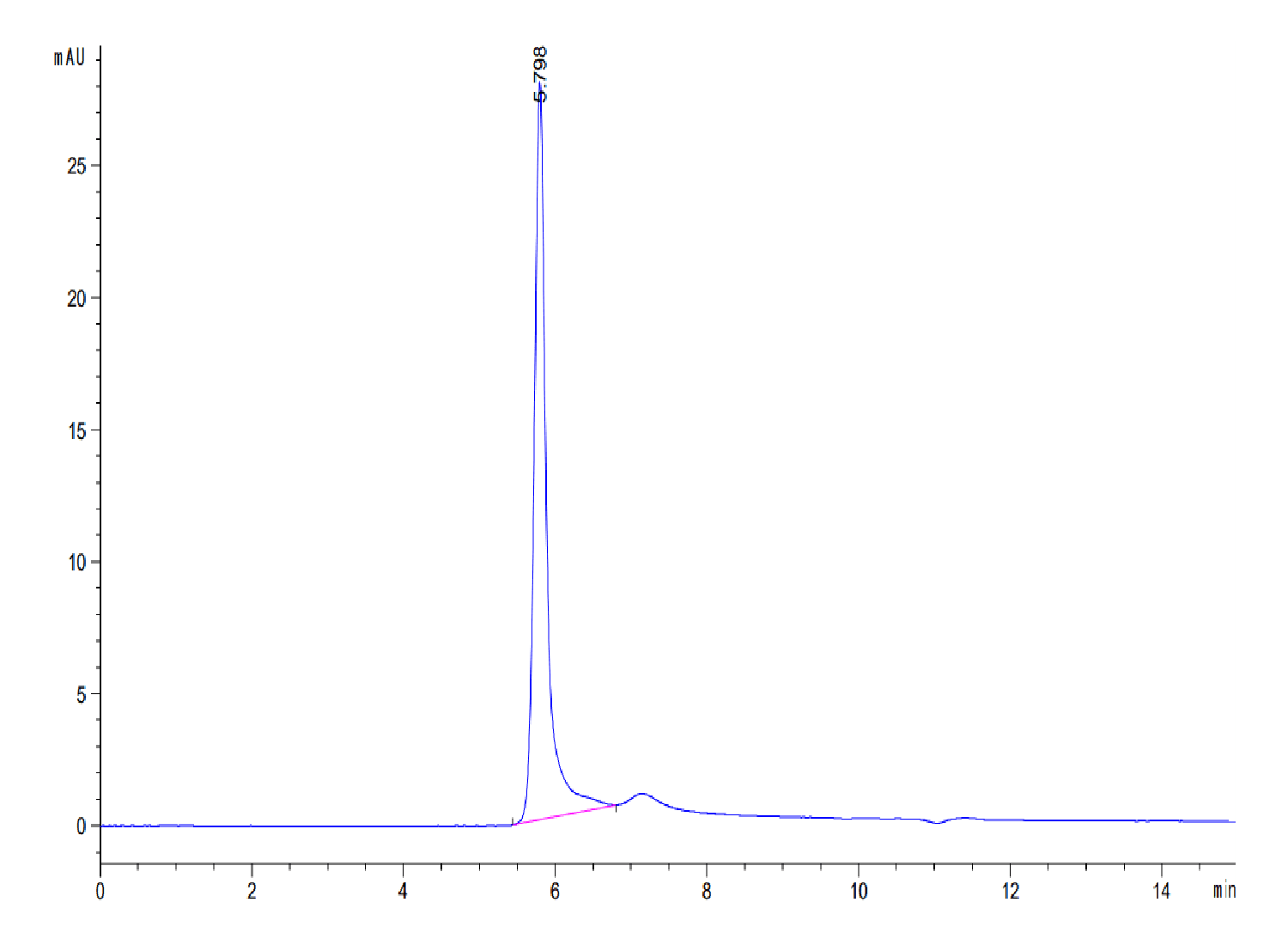
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | C-type lectin CD209/DC-SIGN and CD209L/L-SIGN proteins are distinct cell adhesion and pathogen recognition receptors that mediate cellular interactions and recognize a wide range of pathogens, including viruses such as SARS, SARS-CoV-2, bacteria, fungi and parasites. Pathogens exploit CD209 family proteins to promote infection and evade the immune recognition system. |
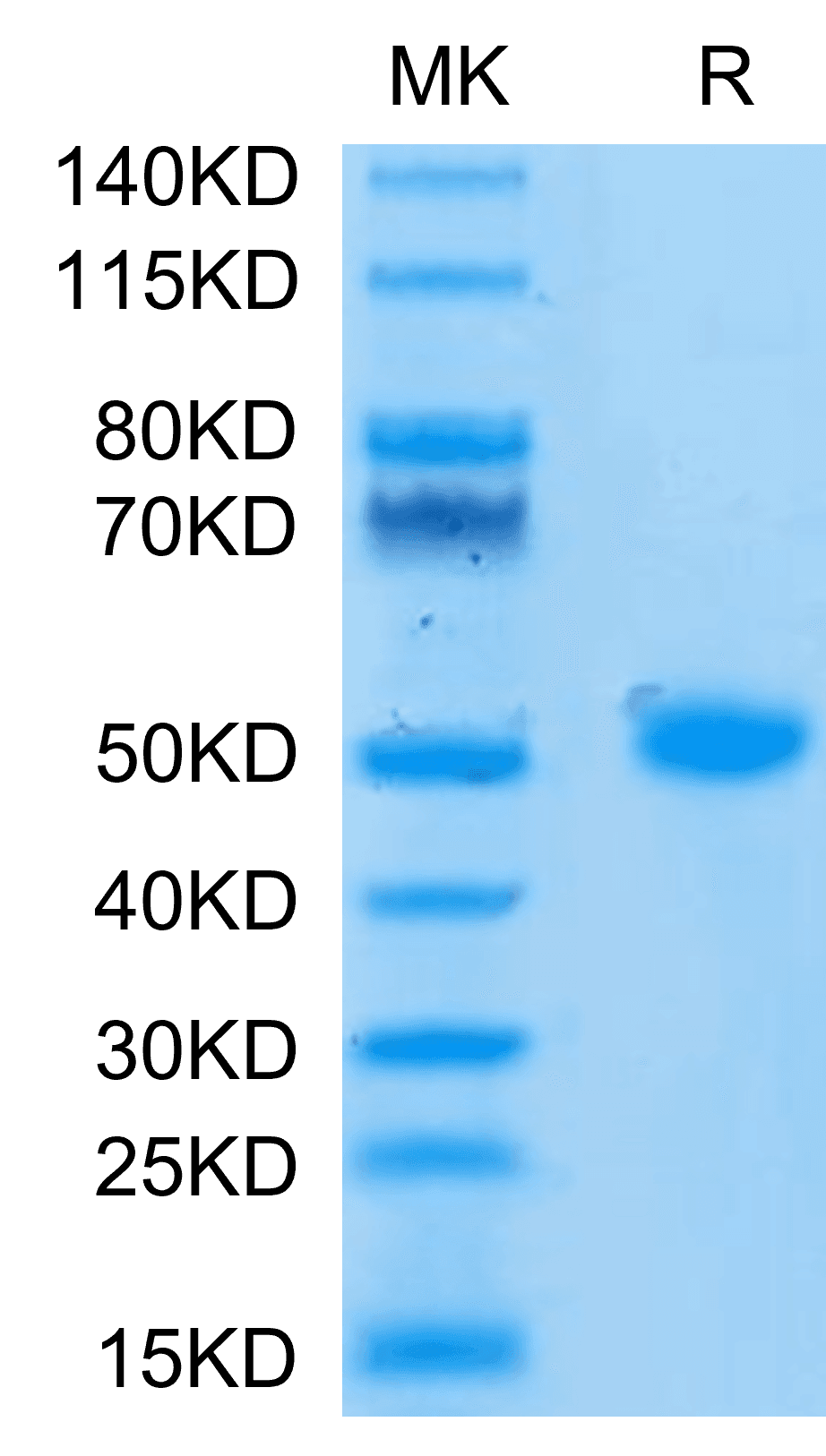
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 40.5 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 52-60 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Human CD209/DC-SIGN Protein 4084
$315.00 – $1,050.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
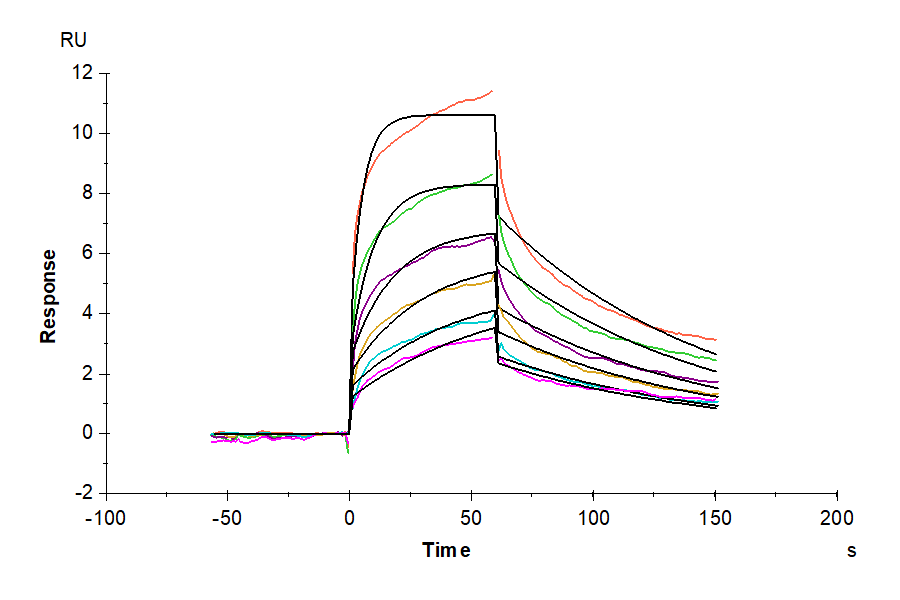
- Binding assay: Yes (SPR)
- Amino Acid Range: Gln59-Ala404
Human CD209/DC-SIGN Protein 4084
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| C-type lectin CD209/DC-SIGN and CD209L/L-SIGN proteins are distinct cell adhesion and pathogen recognition receptors that mediate cellular interactions and recognize a wide range of pathogens, including viruses such as SARS, SARS-CoV-2, bacteria, fungi and parasites. Pathogens exploit CD209 family proteins to promote infection and evade the immune recognition system. |
| Protein names CD209 antigen (C-type lectin domain family 4 member L) (Dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin 1) (DC-SIGN) (DC-SIGN1) (CD antigen CD209) |
| Gene names CD209,CD209 CLEC4L |
| Mass 45775Da |
| Function Pathogen-recognition receptor expressed on the surface of immature dendritic cells (DCs) and involved in initiation of primary immune response. Thought to mediate the endocytosis of pathogens which are subsequently degraded in lysosomal compartments. The receptor returns to the cell membrane surface and the pathogen-derived antigens are presented to resting T-cells via MHC class II proteins to initiate the adaptive immune response.; On DCs it is a high affinity receptor for ICAM2 and ICAM3 by binding to mannose-like carbohydrates. May act as a DC rolling receptor that mediates transendothelial migration of DC presursors from blood to tissues by binding endothelial ICAM2. Seems to regulate DC-induced T-cell proliferation by binding to ICAM3 on T-cells in the immunological synapse formed between DC and T-cells.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for HIV-1 and HIV-2.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Ebolavirus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Cytomegalovirus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for HCV.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Dengue virus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Measles virus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Herpes simplex virus 1.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Influenzavirus A.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for SARS-CoV.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Japanese encephalitis virus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Lassa virus (PubMed:23966408). Acts as an attachment receptor for Marburg virusn.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Respiratory syncytial virus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Rift valley fever virus and uukuniemi virus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for West-nile virus.; (Microbial infection) Probably recognizes in a calcium-dependent manner high mannose N-linked oligosaccharides in a variety of bacterial pathogen antigens, including Leishmania pifanoi LPG, Lewis-x antigen in Helicobacter pylori LPS, mannose in Klebsiella pneumonae LPS, di-mannose and tri-mannose in Mycobacterium tuberculosis ManLAM and Lewis-x antigen in Schistosoma mansoni SEA (PubMed:16379498). Recognition of M.tuberculosis by dendritic cells occurs partially via this molecule (PubMed:16092920, PubMed:21203928). |
| Subellular location [Isoform 1]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type II membrane protein .; [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type II membrane protein .; [Isoform 3]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type II membrane protein .; [Isoform 4]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type II membrane protein .; [Isoform 5]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type II membrane protein .; [Isoform 6]: Secreted .; [Isoform 7]: Secreted .; [Isoform 8]: Secreted .; [Isoform 9]: Secreted .; [Isoform 10]: Secreted .; [Isoform 11]: Secreted .; [Isoform 12]: Secreted . |
| Tissues Predominantly expressed in dendritic cells and in DC-residing tissues. Also found in placental macrophages, endothelial cells of placental vascular channels, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and THP-1 monocytes. |
| Structure Homotetramer. Interacts with C1QBP; the interaction is indicative for a C1q:C1QBP:CD209 signaling complex. Interacts with ICAM2 and ICAM3 by binding to mannose-like carbohydrates. Interacts (via C-type lectin domain) with CEACAM1 (via Lewis X moieties); this interaction is regulated by the glycosylation pattern of CEACAM1 on cell types and regulates contact between dendritic cells and neutrophils (PubMed:16246332).; (Microbial infection) Interacts with HIV-1 and HIV-2 gp120 (PubMed:11799126, PubMed:12502850, PubMed:1518869).; (Microbial infection) Interacts with ebolavirus envelope glycoproteins (PubMed:12502850, PubMed:12504546).; (Microbial infection) Interacts with cytomegalovirus gB protein (PubMed:12433371, PubMed:22496863).; (Microbial infection) Interacts with HCV E2 protein (PubMed:15371595, PubMed:16816373).; (Microbial infection) Interacts with dengue virus major envelope protein E.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with measles hemagglutinin.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with herpes simplex virus 1 surface proteins.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with Influenzavirus A hemagglutinin.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with Japanese encephalitis virus E protein.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with Lassa virus Glycoprotein.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with marburg virus glycoprotein.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with Respiratory syncytial virus glycoprotein G.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with Rift valley fever virus and uukuniemi virus envelope glycoprotein.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with west-nile virus envelope glycoprotein.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with whole M.bovis cells in a Ca(2+)-dependent and independent manner; in vitro experiments suggest it interacts with CH60.1 (groL1), DnaK, GADPH (gap) and LrpG (PubMed:21203928). |
| Domain TOPO_DOM 1 |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q9NNX6 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||