| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| host | goat |
| isotype | IgG |
| clonality | polyclonal |
| concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| applications | ICC/IF, WB |
| reactivity | ATM |
| available sizes | 100 µg |
goat anti-ATM polyclonal antibody 4950
$518.00
Antibody summary
- Goat polyclonal to ATM
- Suitable for: WB,IP
- Isotype: Whole IgG
- 100 µg
goat anti-ATM polyclonal antibody 4950
| antibody |
|---|
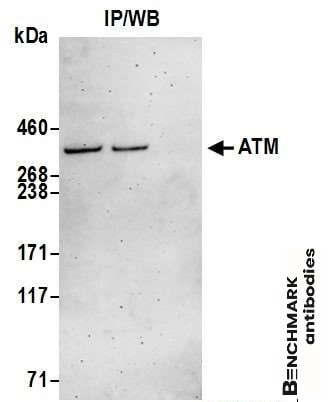
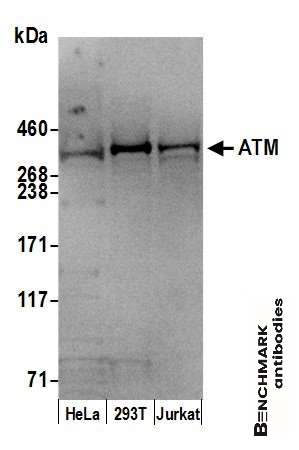
| Tested applications WB,IP |
| Recommended dilutions Western Blot: 0.1 - 0.4 ug/ml. Immunoprecipitation: 10 - 20 ug/mg lysate |
| Immunogen Synthetic peptide representing a portion of the protein encoded within exon 53 (LocusLink ID 472). |
| Size and concentration 100µg and lot specific |
| Form liquid |
| Storage Instructions Store at 2 - 8°C. Antibody is stable at 2 - 8°C for 1 year. |
| Storage buffer Tris-citrate/phosphate buffer, pH 7 to 8 contai |
| Purity immunogen affinity purification |
| Clonality polyclonal |
| Isotype IgG |
| Compatible secondaries donkey anti-goat IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody 1689 donkey anti-goat IgG, H&L chain specific, biotin conjugated polyclonal antibody 1699 donkey anti-goat IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody 1704 donkey anti-goat IgG, H&L chain specific, peroxidase conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1709 donkey anti-goat IgG, H&L chain specific, FITC conjugated polyclonal antibody, crossabsorbed 1705 |
| Isotype control Goat polyclonal - Isotype Control |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Protein names Serine-protein kinase ATM (EC 2.7.11.1) (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated) (A-T mutated) |
| Gene names ATM,ATM |
| Protein family PI3/PI4-kinase family, ATM subfamily |
| Mass 350687Da |
| Function FUNCTION: Serine/threonine protein kinase which activates checkpoint signaling upon double strand breaks (DSBs), apoptosis and genotoxic stresses such as ionizing ultraviolet A light (UVA), thereby acting as a DNA damage sensor (PubMed:10550055, PubMed:10839545, PubMed:10910365, PubMed:12556884, PubMed:14871926, PubMed:15064416, PubMed:15448695, PubMed:15456891, PubMed:15790808, PubMed:15916964, PubMed:17923702, PubMed:21757780, PubMed:24534091, PubMed:35076389, PubMed:9733514). Recognizes the substrate consensus sequence [ST]-Q (PubMed:10550055, PubMed:10839545, PubMed:10910365, PubMed:12556884, PubMed:14871926, PubMed:15448695, PubMed:15456891, PubMed:15916964, PubMed:17923702, PubMed:24534091, PubMed:9733514). Phosphorylates 'Ser-139' of histone variant H2AX at double strand breaks (DSBs), thereby regulating DNA damage response mechanism (By similarity). Also plays a role in pre-B cell allelic exclusion, a process leading to expression of a single immunoglobulin heavy chain allele to enforce clonality and monospecific recognition by the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) expressed on individual B-lymphocytes. After the introduction of DNA breaks by the RAG complex on one immunoglobulin allele, acts by mediating a repositioning of the second allele to pericentromeric heterochromatin, preventing accessibility to the RAG complex and recombination of the second allele. Also involved in signal transduction and cell cycle control. May function as a tumor suppressor. Necessary for activation of ABL1 and SAPK. Phosphorylates DYRK2, CHEK2, p53/TP53, FBXW7, FANCD2, NFKBIA, BRCA1, CREBBP/CBP, RBBP8/CTIP, MRE11, nibrin (NBN), RAD50, RAD17, PELI1, TERF1, UFL1, RAD9, UBQLN4 and DCLRE1C (PubMed:10550055, PubMed:10766245, PubMed:10802669, PubMed:10839545, PubMed:10910365, PubMed:10973490, PubMed:11375976, PubMed:12086603, PubMed:15456891, PubMed:19965871, PubMed:21757780, PubMed:24534091, PubMed:26240375, PubMed:26774286, PubMed:30612738, PubMed:30886146, PubMed:30952868, PubMed:38128537, PubMed:9733515, PubMed:9843217). May play a role in vesicle and/or protein transport. Could play a role in T-cell development, gonad and neurological function. Plays a role in replication-dependent histone mRNA degradation. Binds DNA ends. Phosphorylation of DYRK2 in nucleus in response to genotoxic stress prevents its MDM2-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent proteasome degradation (PubMed:19965871). Phosphorylates ATF2 which stimulates its function in DNA damage response (PubMed:15916964). Phosphorylates ERCC6 which is essential for its chromatin remodeling activity at DNA double-strand breaks (PubMed:29203878). Phosphorylates TTC5/STRAP at 'Ser-203' in the cytoplasm in response to DNA damage, which promotes TTC5/STRAP nuclear localization (PubMed:15448695). Also involved in pexophagy by mediating phosphorylation of PEX5: translocated to peroxisomes in response to reactive oxygen species (ROS), and catalyzes phosphorylation of PEX5, promoting PEX5 ubiquitination and induction of pexophagy (PubMed:26344566). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62388, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10550055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10766245, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10802669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10839545, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10910365, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10973490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11375976, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12086603, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12556884, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14871926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15448695, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15456891, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15916964, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16086026, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16858402, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17923702, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19431188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19965871, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21757780, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24534091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26240375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26344566, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26774286, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29203878, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30612738, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30886146, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30952868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35076389, ECO:0000269|PubMed:38128537, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9733514, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9733515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9843217}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-seryl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein] + ADP + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:17989, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:9863, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11604, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:29999, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:83421, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.11.1; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:15448695, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15790808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16858402, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26240375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26344566, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28508083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30886146, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30952868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:38128537, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8988033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9843217}; PhysiologicalDirection=left-to-right; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:17990; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:15790808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21757780, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26240375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30952868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9843217, ECO:0000305|PubMed:15448695}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=L-threonyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein] + ADP + H(+); Xref=Rhea:RHEA:46608, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11060, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11605, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:30013, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:61977, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.11.1; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:24534091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28508083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30952868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8988033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9843217}; |
| Subellular location SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9050866, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9150358}. Cytoplasmic vesicle {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9050866, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9150358}. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62388}. Peroxisome matrix {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26344566}. Note=Primarily nuclear (PubMed:9050866, PubMed:9150358). Found also in endocytic vesicles in association with beta-adaptin (PubMed:9707615). Translocated to peroxisomes in response to reactive oxygen species (ROS) by PEX5 (PubMed:26344566). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26344566, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9050866, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9150358, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9707615}. |
| Tissues TISSUE SPECIFICITY: Found in pancreas, kidney, skeletal muscle, liver, lung, placenta, brain, heart, spleen, thymus, testis, ovary, small intestine, colon and leukocytes. |
| Structure SUBUNIT: Homodimer (PubMed:12556884, PubMed:15790808, PubMed:28508083). Dimers or tetramers in inactive state (PubMed:12556884, PubMed:15790808, PubMed:28508083). On DNA damage, autophosphorylation dissociates ATM into monomers rendering them catalytically active (PubMed:12556884, PubMed:28508083). Binds p53/TP53, ABL1, BRCA1 and TERF1 (PubMed:15790808, PubMed:9168117, PubMed:9843217). Interacts with NBN (via FxF/Y motif) (PubMed:35076389). Part of the BRCA1-associated genome surveillance complex (BASC), which contains BRCA1, MSH2, MSH6, MLH1, ATM, BLM, PMS2 and the RAD50-MRE11-NBN protein complex (PubMed:10783165). This association could be a dynamic process changing throughout the cell cycle and within subnuclear domains (PubMed:10783165). Interacts with RAD17; DNA damage promotes the association (PubMed:11418864). Interacts with EEF1E1; the interaction, induced on DNA damage, up-regulates TP53 (PubMed:15680327). Interacts with KAT8, NABP2, ATMIN and CEP164 (PubMed:15923642, PubMed:17525732, PubMed:18283122, PubMed:18449195). Interacts with AP2B1 and AP3B2; the interaction occurs in cytoplasmic vesicles (By similarity). Interacts with TELO2 and TTI1 (PubMed:20427287, PubMed:20801936, PubMed:20810650). Interacts with DDX1 (PubMed:18710941). Interacts with BRAT1 (PubMed:22977523). Interacts with CYREN (via XLF motif) (By similarity). Interacts (via microbody targeting signal) with PEX5; promoting translocation to peroxisomes in response to reactive oxygen species (ROS) (PubMed:26344566). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62388, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10783165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11418864, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12556884, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15680327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15790808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15923642, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17525732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18283122, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18449195, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18710941, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20427287, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20801936, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20810650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22977523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26344566, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28508083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35076389, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9168117, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9843217}. |
| Post-translational modification PTM: Phosphorylated by NUAK1/ARK5 (PubMed:12409306). Autophosphorylation on Ser-367, Ser-1893, Ser-1981 correlates with DNA damage-mediated activation of the kinase (PubMed:12556884, PubMed:15790808, PubMed:16141325, PubMed:16858402, PubMed:21144835, PubMed:27664052). During the late stages of DNA damage response, dephosphorylated following deacetylation by SIRT7, leading to ATM deactivation (PubMed:30944854). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12409306, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12556884, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15790808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16141325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16858402, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21144835, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27664052, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30944854}.; PTM: Acetylation, on DNA damage, is required for activation of the kinase activity, dimer-monomer transition, and subsequent autophosphorylation on Ser-1981 (PubMed:12556884, PubMed:16141325, PubMed:16858402, PubMed:17923702, PubMed:21144835). Acetylated in vitro by KAT5/TIP60 (PubMed:16141325). Deacetylated by SIRT7 during the late stages of DNA damage response, promoting ATM dephosphorylation and subsequent deactivation (PubMed:30944854). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12556884, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16141325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16858402, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17923702, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21144835, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30944854}. |
| Domain DOMAIN: The FATC domain is required for interaction with KAT5. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16141325}. |
| Involvement in disease DISEASE: Ataxia telangiectasia (AT) [MIM:208900]: A rare recessive disorder characterized by progressive cerebellar ataxia, dilation of the blood vessels in the conjunctiva and eyeballs, immunodeficiency, growth retardation and sexual immaturity. Patients have a strong predisposition to cancer; about 30% of patients develop tumors, particularly lymphomas and leukemias. Cells from affected individuals are highly sensitive to damage by ionizing radiation and resistant to inhibition of DNA synthesis following irradiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10234507, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10425038, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10817650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10873394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19431188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27664052, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7792600, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8589678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8665503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8698354, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8755918, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8789452, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8797579, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8808599, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8845835, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9043869, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9150358, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9443866, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9450874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9463314, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9497252, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9521587, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9711876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9792409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9792410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9872980, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9887333}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.; DISEASE: Note=Defects in ATM may contribute to T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (TALL) and T-prolymphocytic leukemia (TPLL). TPLL is characterized by a high white blood cell count, with a predominance of prolymphocytes, marked splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, skin lesions and serous effusion. The clinical course is highly aggressive, with poor response to chemotherapy and short survival time. TPLL occurs both in adults as a sporadic disease and in younger AT patients. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9288106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9334731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9463314, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9488043, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9573030}.; DISEASE: Note=Defects in ATM may contribute to B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (BNHL), including mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10397742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10706620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9288106}.; DISEASE: Note=Defects in ATM may contribute to B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (BCLL). BCLL is the commonest form of leukemia in the elderly. It is characterized by the accumulation of mature CD5+ B-lymphocytes, lymphadenopathy, immunodeficiency and bone marrow failure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10023947, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10397742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9892178}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q13315 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| Western blot |
Documents
| # | SDS | Certificate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | |||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.