| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | XP_005558436.2 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His |
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Tim4 is a transmembrane protein as the phosphatidylserine (PS) receptor, known as T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain containing protein-4. It is expressed highly in macrophages, and macrophage Tim-4 inhibits inflammation under various conditions of immune activation. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 31.55 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 70-80 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Cynomolgus TIM4 Protein 2930
$315.00 – $1,050.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
- Pure: Yes (HPLC)
- Amino Acid Range: Glu25-Gln305
Cynomolgus TIM4 Protein 2930
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Tim4 is a transmembrane protein as the phosphatidylserine (PS) receptor, known as T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain containing protein-4. It is expressed highly in macrophages, and macrophage Tim-4 inhibits inflammation under various conditions of immune activation. |
| Protein names T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 4 (TIMD-4) (Spleen, mucin-containing, knockout of lymphotoxin protein) (SMUCKLER) (T-cell immunoglobulin mucin receptor 4) (TIM-4) (T-cell membrane protein 4) |
| Protein family Immunoglobulin superfamily, TIM family |
| Mass 37548Da |
| Function Phosphatidylserine receptor that plays different role in immune response including phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and T-cell regulation (PubMed:17960135). Controls T-cell activation in a bimodal fashion, decreasing the activation of naive T-cells by inducing cell cycle arrest, while increasing proliferation of activated T-cells by activating AKT1 and ERK1/2 phosphorylations and subsequent signaling pathways. Also plays a role in efferocytosis which is the process by which apoptotic cells are removed by phagocytic cells (PubMed:18354194, PubMed:18367551). Mechanistically, promotes the engulfment of apoptotic cells or exogenous particles by securing them to phagocytes through direct binding to phosphatidylserine present on apoptotic cells, while other engulfment receptors such as MERTK efficiently recognize apoptotic cells and mediate their ingestion (By similarity). Additionally, promotes autophagy process by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activity via activation of STK11/PRKAA1 pathway in a phosphatidylserine-dependent mechanism (PubMed:31263038). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q96H15, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17960135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18354194, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18367551, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31263038}. |
| Subellular location Membrane {ECO:0000305}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000305}. |
| Tissues Predominantly expressed in lymphoid tissues, such as spleen, lymph nodes, and Peyer patches. Also expressed in fetal liver, salivary gland, and spleen stromal cells, predominantly in the marginal zone and to a lesser extent throughout the white pulp. Not expressed in bone marrow-derived cells. Expressed mainly by antigen presenting cells (APCs) in T- and B-cell areas, but not by T- or B-lymphocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14768054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17960135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18354194}. |
| Structure Homodimer. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:17960135, ECO:0000305|PubMed:18083575}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q6U7R4 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
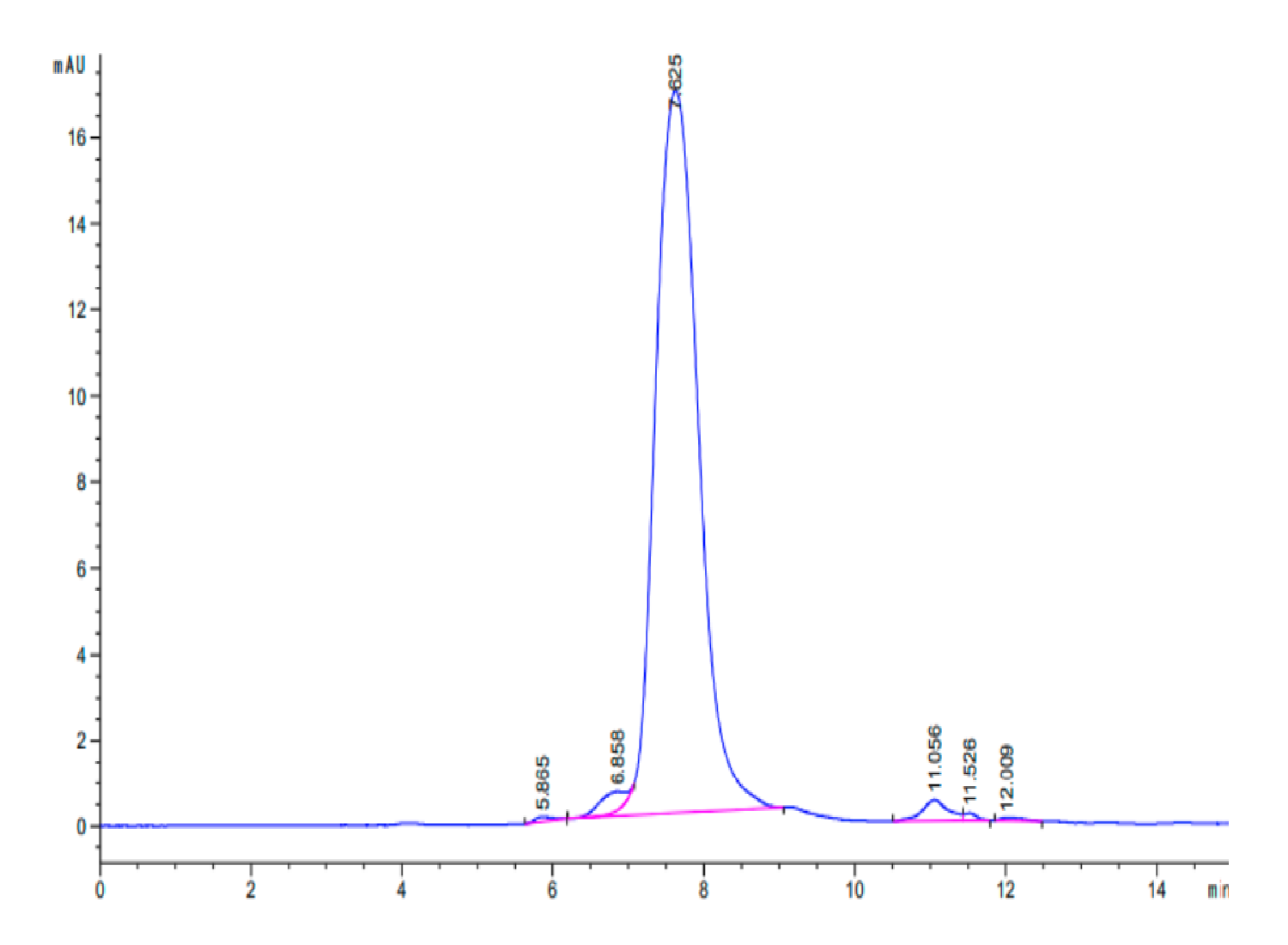 |
| The purity of Cynomolgus TIM4 is greater than 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC. |
 |
| Cynomolgus TIM4 on Tris-Bis PAGE under reduced condition. The purity is greater than 95%. |
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||














