| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His-Avi |
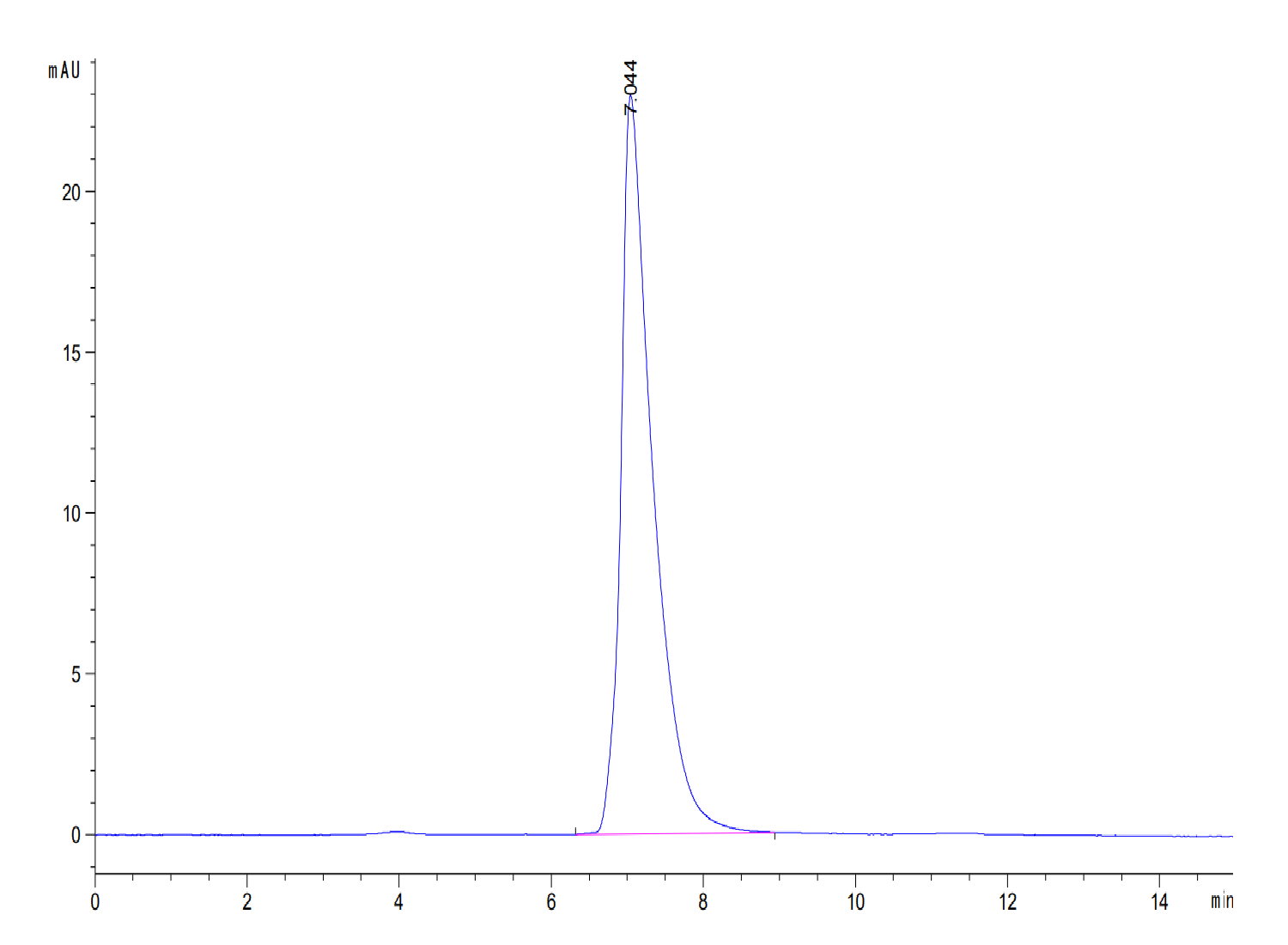
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Brain metastasis (BM) in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has a very poor prognosis. Recent studies have demonstrated the importance of cell adhesion molecules in tumor metastasis.Elevated levels of ALCAM expression promote BM formation in NSCLC through increased tumor cell dissemination and interaction with the brain endothelial cells. Therefore, ALCAM could be targeted to reduce the occurrence of BM. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 58.9 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 75-85 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per ug by the LAL method. |
Biotinylated Mouse ALCAM/CD166 Protein 3410
$525.00 – $1,750.00
Summary
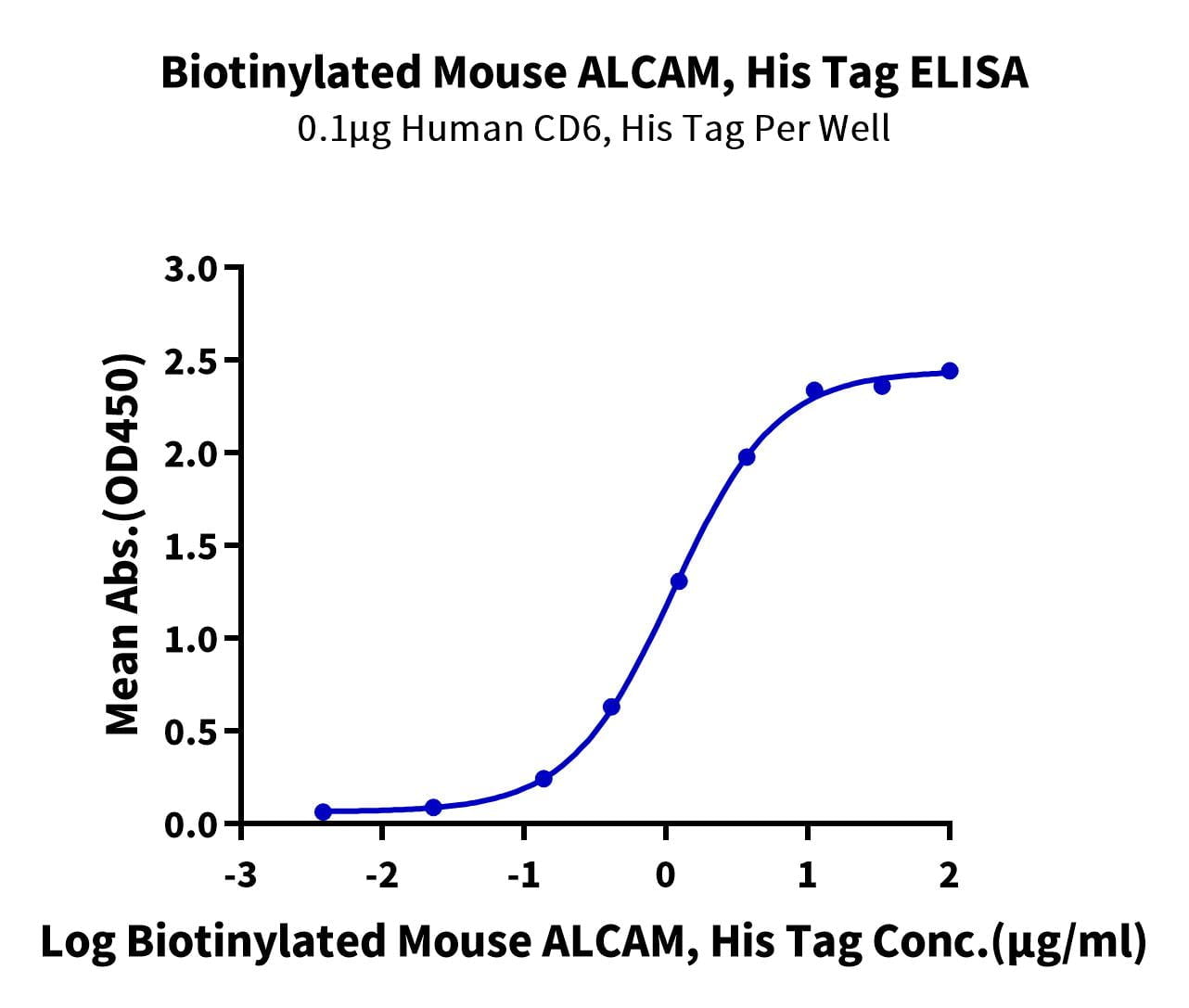
- Expression: HEK293
- Functional: Yes (ELISA)
- Amino Acid Range: Tyr28-Lys527
Biotinylated Mouse ALCAM/CD166 Protein 3410
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Brain metastasis (BM) in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has a very poor prognosis. Recent studies have demonstrated the importance of cell adhesion molecules in tumor metastasis.Elevated levels of ALCAM expression promote BM formation in NSCLC through increased tumor cell dissemination and interaction with the brain endothelial cells. Therefore, ALCAM could be targeted to reduce the occurrence of BM. |
| Protein names CD166 antigen (Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule) (BEN) (Protein DM-GRASP) (CD antigen CD166) |
| Gene names Alcam,Alcam |
| Mass 10090Da |
| Function Cell adhesion molecule that mediates both heterotypic cell-cell contacts via its interaction with CD6, as well as homotypic cell-cell contacts. Promotes T-cell activation and proliferation via its interactions with CD6 (By similarity). Contributes to the formation and maturation of the immunological synapse via its interactions with CD6 (By similarity). Mediates homotypic interactions with cells that express ALCAM (PubMed:24740813). Mediates attachment of dendritic cells onto endothelial cells via homotypic interaction. Inhibits endothelial cell migration and promotes endothelial tube formation via homotypic interactions (PubMed:23169771). Required for normal organization of the lymph vessel network (PubMed:23169771). Required for normal hematopoietic stem cell engraftment in the bone marrow (PubMed:24740813). Plays a role in hematopoiesis; required for normal numbers of hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow (PubMed:25730656). Promotes in vitro osteoblast proliferation and differentiation (PubMed:25730656). Promotes neurite extension, axon growth and axon guidance; axons grow preferentially on surfaces that contain ALCAM (By similarity). Mediates outgrowth and pathfinding for retinal ganglion cell axons (PubMed:15345243). |
| Subellular location Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, axon. Cell projection, dendrite. Note=Detected at the immunological synapse, i.e, at the contact zone between antigen-presenting dendritic cells and T-cells. Colocalizes with CD6 and the TCR/CD3 complex at the immunological synapse. |
| Tissues Detected on brain motor neurons, in differentiating retinal ganglion cells and in adult retina (PubMed:15345243). Detected on leukocytes and on lymphatic endothelial cells (PubMed:23169771). Detected in spleen B cells and T-cells (at protein level) (PubMed:9209500). Detected in adult brain and embryonic spinal cord (PubMed:15345243). Expressed at high levels in the brain, and lung, and at lower levels in the liver, and the kidney, as well as by activated leukocytes (PubMed:9209500). |
| Structure Homodimer (By similarity). Interacts (via extracellular domain) with CD6 (via extracellular domain) (PubMed:16914752, PubMed:9209500). Homodimerization and interaction with CD6 involve the same region and cannot occur simultaneously. The affinity for CD6 is much higher than the affinity for self-association. Interacts (via glycosylated extracellular domain) with LGALS1 and LGALS3. Interaction with LGALS1 or LGALS3 inhibits interaction with CD6. |
| Post-translational modification Glycosylated. |
| Domain Th |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q61490 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||