| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His-Avi |
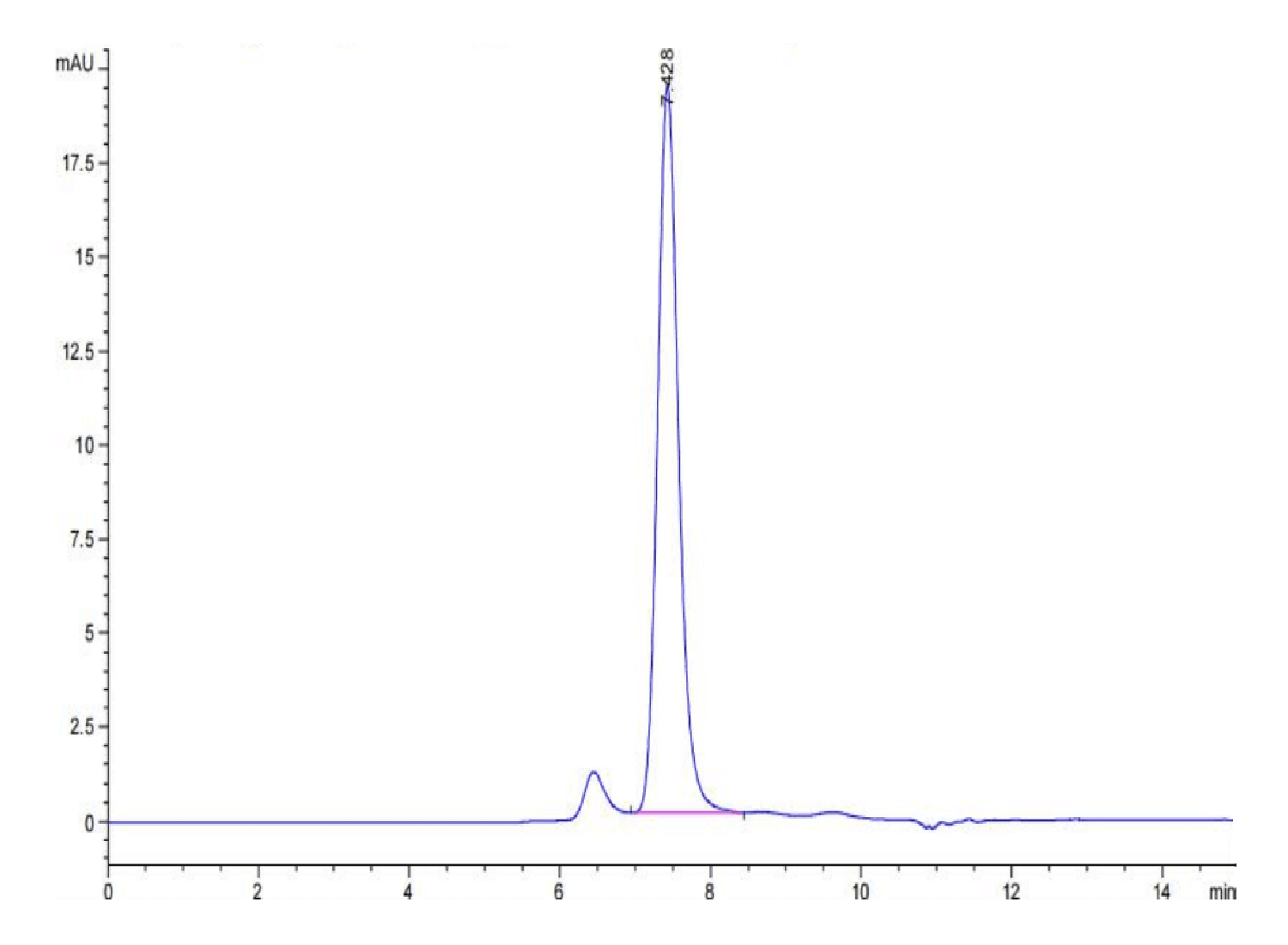
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | c-Met, also called tyrosine-protein kinase Met or hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGF R), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MET gene.The protein possesses tyrosine kinase activity. The primary single chain precursor protein is post-translationally cleaved to produce the alpha and beta subunits, which are disulfide linked to form the mature receptor. Following activation by ligand, interacts with the PI3-kinase subunit PIK3R1, PLCG1, SRC, GRB2, STAT3 or the adapter GAB1. |
| molecular weight | The mature form of HGF R is a heterodimer which can be cleaved into α and β chain. The protein has a predicted MW of 32.5 kDa (α chain) and 72.1 kDa (β chain). Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 45-50 kDa and 80-90 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Biotinylated Human HGF R/c-MET Protein 3798
$525.00 – $1,750.00
Summary
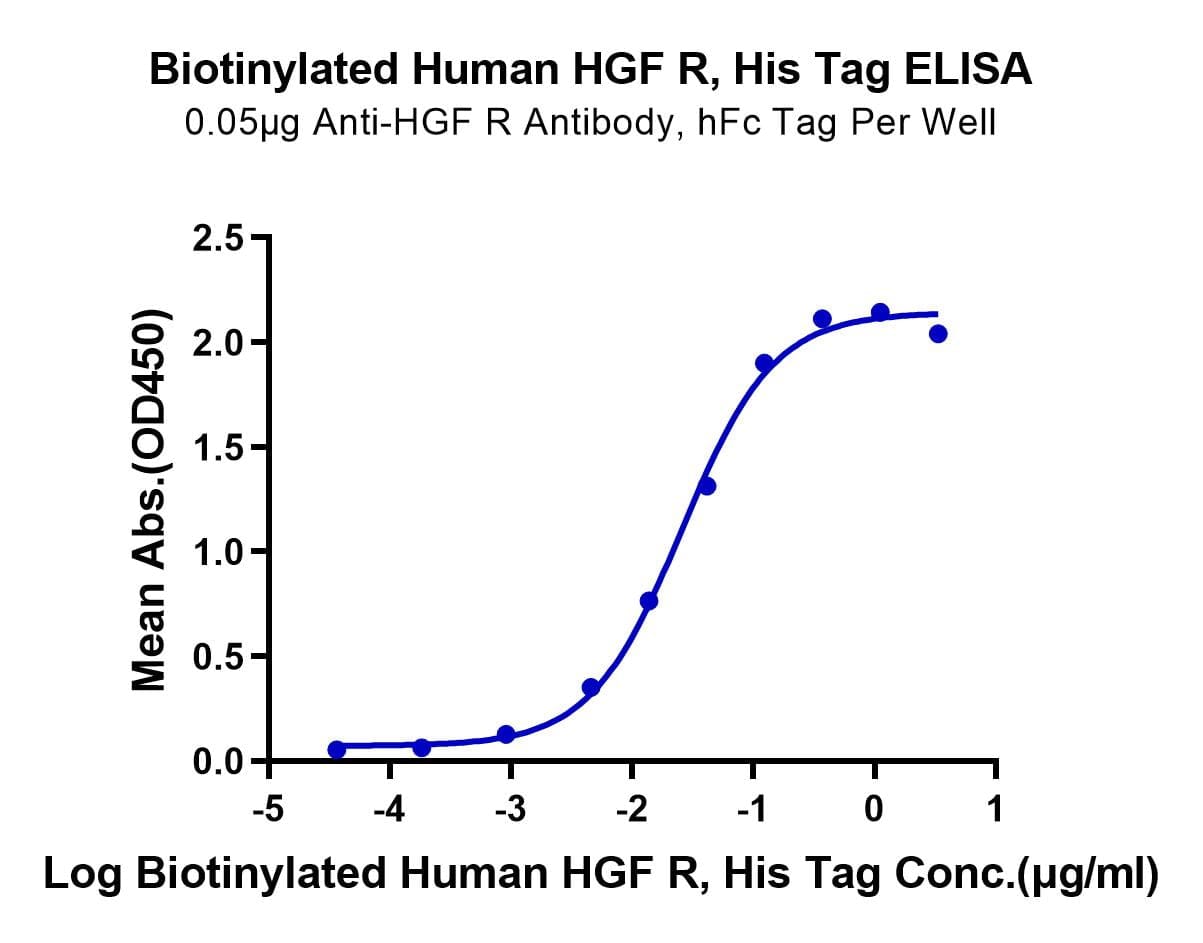
- Expression: HEK293
- Functional: Yes (ELISA)
- Amino Acid Range: Glu25-Thr932
Biotinylated Human HGF R/c-MET Protein 3798
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| c-Met, also called tyrosine-protein kinase Met or hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGF R), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MET gene.The protein possesses tyrosine kinase activity. The primary single chain precursor protein is post-translationally cleaved to produce the alpha and beta subunits, which are disulfide linked to form the mature receptor. Following activation by ligand, interacts with the PI3-kinase subunit PIK3R1, PLCG1, SRC, GRB2, STAT3 or the adapter GAB1. |
| Protein names Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGF receptor) (EC 2.7.10.1) (HGF/SF receptor) (Proto-oncogene c-Met) (Scatter factor receptor) (SF receptor) (Tyrosine-protein kinase Met) |
| Gene names MET,MET |
| Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family |
| Mass 9606Da |
| Function Receptor tyrosine kinase that transduces signals from the extracellular matrix into the cytoplasm by binding to hepatocyte growth factor/HGF ligand. Regulates many physiological processes including proliferation, scattering, morphogenesis and survival. Ligand binding at the cell surface induces autophosphorylation of MET on its intracellular domain that provides docking sites for downstream signaling molecules. Following activation by ligand, interacts with the PI3-kinase subunit PIK3R1, PLCG1, SRC, GRB2, STAT3 or the adapter GAB1. Recruitment of these downstream effectors by MET leads to the activation of several signaling cascades including the RAS-ERK, PI3 kinase-AKT, or PLCgamma-PKC. The RAS-ERK activation is associated with the morphogenetic effects while PI3K/AKT coordinates prosurvival effects. During embryonic development, MET signaling plays a role in gastrulation, development and migration of neuronal precursors, angiogenesis and kidney formation. During skeletal muscle development, it is crucial for the migration of muscle progenitor cells and for the proliferation of secondary myoblasts (By similarity). In adults, participates in wound healing as well as organ regeneration and tissue remodeling. Promotes also differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic cells. May regulate cortical bone osteogenesis (By similarity).; (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Listeria monocytogenes internalin InlB, mediating entry of the pathogen into cells. |
| Catalytic activity #N/A |
| Subellular location Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Isoform 3]: Secreted. |
| Tissues Expressed in normal hepatocytes as well as in epithelial cells lining the stomach, the small and the large intestine. Found also in basal keratinocytes of esophagus and skin. High levels are found in liver, gastrointestinal tract, thyroid and kidney. Also present in the brain. Expressed in metaphyseal bone (at protein level) (PubMed:26637977). |
| Structure Heterodimer made of an alpha chain (50 kDa) and a beta chain (145 kDa) which are disulfide linked. Binds PLXNB1. Interacts when phosphorylated with downstream effectors including STAT3, PIK3R1, SRC, PCLG1, GRB2 and GAB1. Interacts with SPSB1, SPSB2 and SPSB4 (By similarity). Interacts with INPP5D/SHIP1. When phosphorylated at Tyr-1356, interacts with INPPL1/SHIP2. Interacts with RANBP9 and RANBP10, as well as SPSB1, SPSB2, SPSB3 and SPSB4. SPSB1 binding occurs in the presence and in the absence of HGF, however HGF treatment has a positive effect on this interaction. Interacts with MUC20; prevents interaction with GRB2 and suppresses hepatocyte growth factor-induced cell proliferation. Interacts with GRB10. Interacts with PTPN1 and PTPN2. Interacts with LECT2; this interaction may have an antagonistic effect on receptor activation (PubMed:27334921). Interacts with HSP90AA1 and HSP90AB1; the interaction suppresses MET kinase activity (PubMed:26517842). Interacts with tensin TNS3 (PubMed:24814316). Interacts (when phosphorylated) with tensin TNS4 (via SH2 domain); the interaction increases MET protein stability by inhibiting MET endocytosis and subsequent lysosomal degradation (PubMed:24814316).; (Microbial infection) Interacts via extracytoplasmic residues 25-656 with L.monocytogenes InlB; MET can bind HGF, its endogenous ligand, and InlB simultaneously (PubMed:11081636, PubMed:17662939). InlB probably dimerizes upon binding to MET, which encourages subsequent dimerization of MET (Probable). |
| Post-translational modification Autophosphorylated in response to ligand binding on Tyr-1234 and Tyr-1235 in the kinase domain leading to further phosphorylation of Tyr-1349 and Tyr-1356 in the C-terminal multifunctional docking site. Dephosphorylated by PTPRJ at Tyr-1349 and Tyr-1365. Dephosphorylated by PTPN1 and PTPN2.; Ubiquitinated. Ubiquitination by CBL regulates MET endocytosis, resulting in decreasing plasma membrane receptor abundance, and in endosomal degradation and/or recycling of internalized receptors.; O-mannosylation of IPT/TIG domains by TMEM260 is required for protein maturation (PubMed:37186866). O-mannosylated residues are composed of single mannose glycans that are not elongated or modified (PubMed:37186866).; (Microbial infection) Tyrosine phosphorylation is stimulated by L.monocytogenes InlB. Tyrosine phosphorylation is maximal 10-20 minutes after treatment with InlB and disappears by 60 minutes. The phosphorylated residues were not identified. |
| Domain Th |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P08581 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||