| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His-Avi |
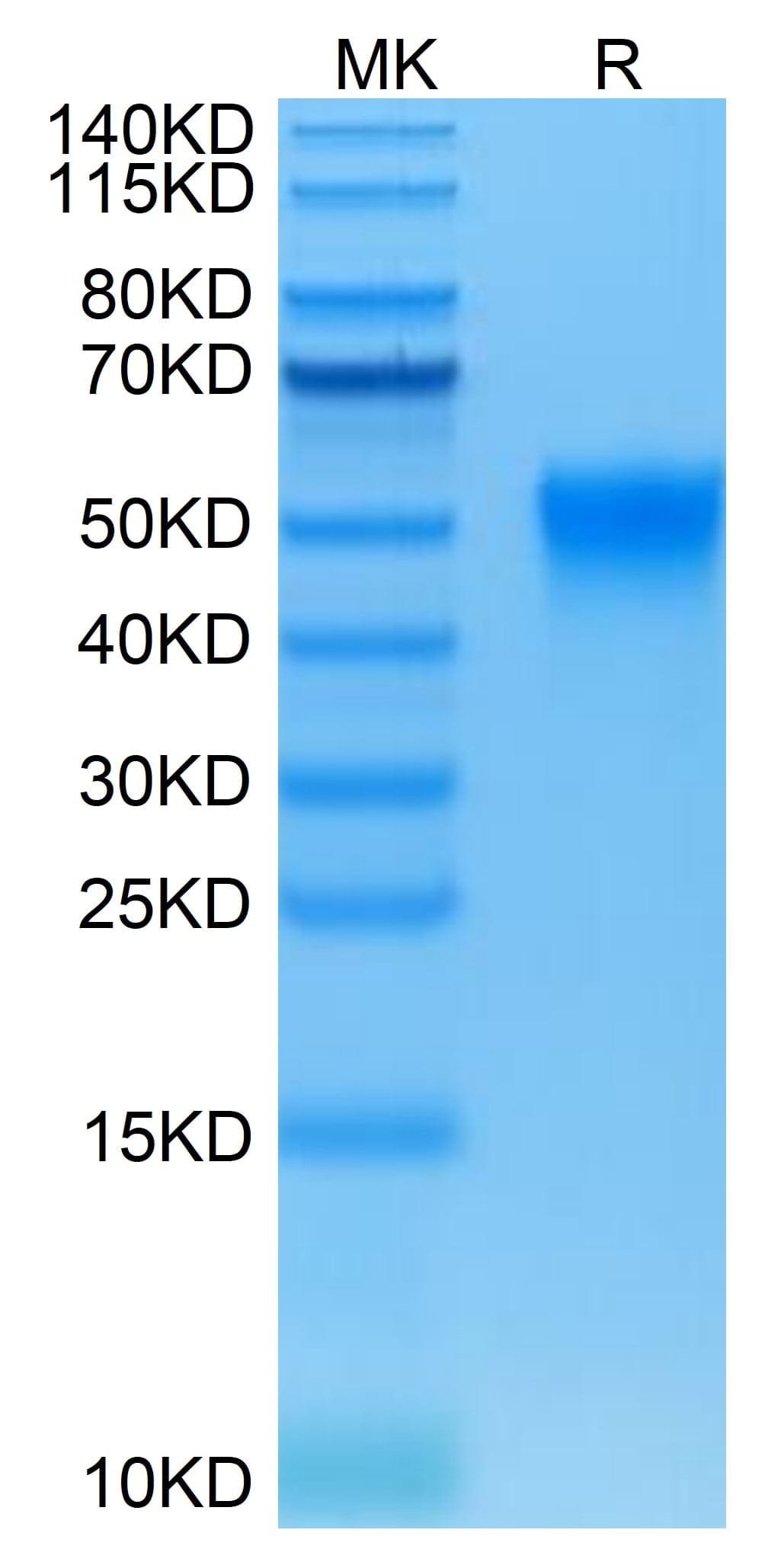
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Human Fc gamma RIIIA/CD16a Protein is a receptor for the Fc region of IgG. Binds complexed or aggregated IgG and also monomeric IgG. Mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and other antibody-dependent responses, such as phagocytosis. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 24.7 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 48-58 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIIA/CD16a (F176) Protein 4819
$525.00 – $1,750.00
Summary
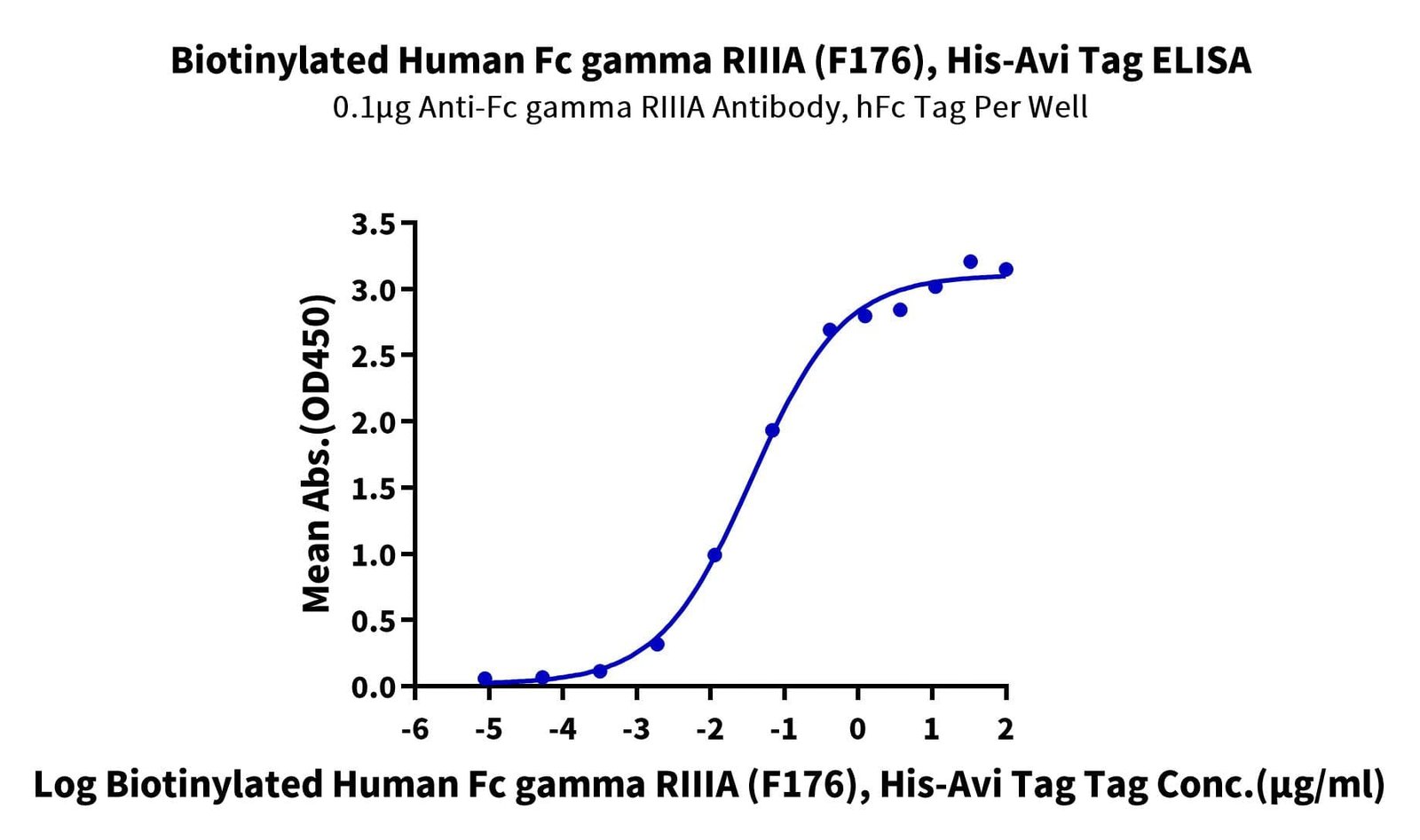
- Expression: HEK293
- Functional: Yes (ELISA)
- Amino Acid Range: Gly17-Gln208(F176)
Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIIA/CD16a (F176) Protein 4819
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Human Fc gamma RIIIA/CD16a Protein is a receptor for the Fc region of IgG. Binds complexed or aggregated IgG and also monomeric IgG. Mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and other antibody-dependent responses, such as phagocytosis. |
| Protein names Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-A (IgG Fc receptor III-A) (CD16-II) (CD16a antigen) (Fc-gamma RIII-alpha) (Fc-gamma RIII) (Fc-gamma RIIIa) (FcRIII) (FcRIIIa) (FcgammaRIIIA) (FcR-10) (IgG Fc receptor III-2) (CD antigen CD16a) |
| Protein family 413 |
| Function Receptor for the invariable Fc fragment of immunoglobulin gamma (IgG). Optimally activated upon binding of clustered antigen-IgG complexes displayed on cell surfaces, triggers lysis of antibody-coated cells, a process known as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Does not bind free monomeric IgG, thus avoiding inappropriate effector cell activation in the absence of antigenic trigger (PubMed:11711607, PubMed:21768335, PubMed:22023369, PubMed:24412922, PubMed:25786175, PubMed:25816339, PubMed:28652325, PubMed:8609432, PubMed:9242542). Mediates IgG effector functions on natural killer (NK) cells. Binds antigen-IgG complexes generated upon infection and triggers NK cell-dependent cytokine production and degranulation to limit viral load and propagation. Involved in the generation of memory-like adaptive NK cells capable to produce high amounts of IFNG and to efficiently eliminate virus-infected cells via ADCC (PubMed:24412922, PubMed:25786175). Regulates NK cell survival and proliferation, in particular by preventing NK cell progenitor apoptosis (PubMed:29967280, PubMed:9916693). Fc-binding subunit that associates with CD247 and/or FCER1G adapters to form functional signaling complexes. Following the engagement of antigen-IgG complexes, triggers phosphorylation of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-containing adapters with subsequent activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling and sustained elevation of intracellular calcium that ultimately drive NK cell activation. The ITAM-dependent signaling coupled to receptor phosphorylation by PKC mediates robust intracellular calcium flux that leads to production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, whereas in the absence of receptor phosphorylation it mainly activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling leading to cell degranulation (PubMed:1825220, PubMed:23024279, PubMed:2532305). Costimulates NK cells and trigger lysis of target cells independently of IgG binding (PubMed:10318937, PubMed:23006327). Mediates the antitumor activities of therapeutic antibodies. Upon ligation on monocytes triggers TNFA-dependent ADCC of IgG-coated tumor cells (PubMed:27670158). Mediates enhanced ADCC in response to afucosylated IgGs (PubMed:34485821).; (Microbial infection) Involved in Dengue virus pathogenesis via antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) mechanism. Secondary infection with Dengue virus triggers elevated levels of afucosylated non-neutralizing IgG1s with reactivity to viral envelope/E protein. Viral antigen-IgG1 complexes bind with high affinity to FCGR3A, facilitating virus entry in myeloid cells and subsequent viral replication. |
| Pathway 307 |
| Subellular location Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Secreted. Note=Exists also as a soluble receptor. |
| Tissues Expressed in natural killer cells (at protein level) (PubMed:2526846). Expressed in a subset of circulating monocytes (at protein level) (PubMed:27670158). |
| Structure Forms a heterooligomeric complex with ITAM-containing signaling subunits, either a homodimer of CD247, a homodimer of FCER1G or a heterodimer of CD247 and FCER1G (PubMed:1825220, PubMed:2532305, PubMed:28652325). Interacts (via transmembrane domain) with signaling subunits; this interaction is a prerequisite for receptor complex expression on the cell surface and intracellular signal transduction (PubMed:1825220, PubMed:2532305, PubMed:28652325). Binds the Fc region of antigen-complexed IgG with a preference for IgG1 and IgG3 isotypes (PubMed:11711607, PubMed:21768335, PubMed:22023369, PubMed:8609432, PubMed:9242542). Interacts with CD2; this interaction is involved in NK cell activation and cytotoxicity (PubMed:23006327). Interacts with S100A4; this interaction inhibits PKC-dependent phosphorylation of FCGR3A (PubMed:23024279). |
| Post-translational modification Glycosylated. Contains high mannose- and complex-type oligosaccharides. Glycosylation at Asn-180 is mandatory for high affinity binding to the Fc and for discrimination between fucosylated and afucosylated IgG glycoforms.; Undergoes rapid ectodomain shedding upon NK cell stimulation. The soluble form is produced by a proteolytic cleavage mediated by ADAM17. Repeated stimulation causes receptor shedding, a mechanism that allows for increased NK cell motility and detachment from opsonized target cells while avoiding activation-induced NK cell apoptosis.; Phosphorylated at RSSTR motif by PKC. The relevant physiological PKCs might be PRKCI, PRKCG, PRKCE, PRKCH and PRKCQ. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P08637 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||