| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | P21802 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His |
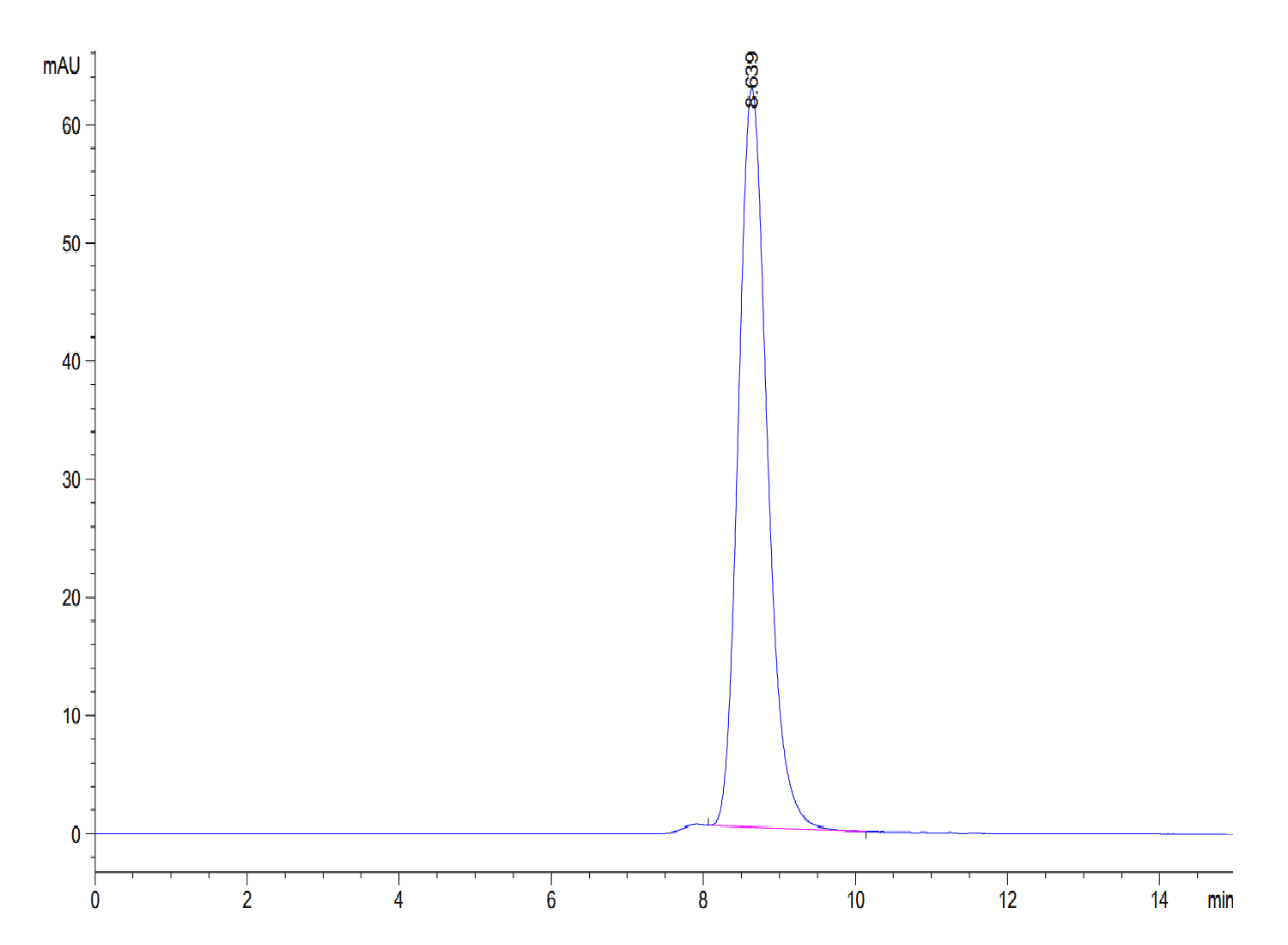
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Four distinct genes encoding closely related FGF receptors, FGF R1 – 4, are known. All four genes for FGF Rs encode proteins with an N-terminal signal peptide, three immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains, an acid-box region containing a run of acidic residues between the IgI and IgII domains, a transmembrane domain and the split tyrosine-kinase domain. Multiple forms of FGF R1 – 3 are generated by alternative splicing of the mRNAs. A frequent splicing event involving FGF R1 and 2 results in receptors containing all three Ig domains, referred to as the alpha isoform, or only IgII and IgIII, referred to as the beta isoform. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 24 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 50-70 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Human FGFR2 beta (IIIb) Protein 4858
$300.00 – $1,000.00
Summary
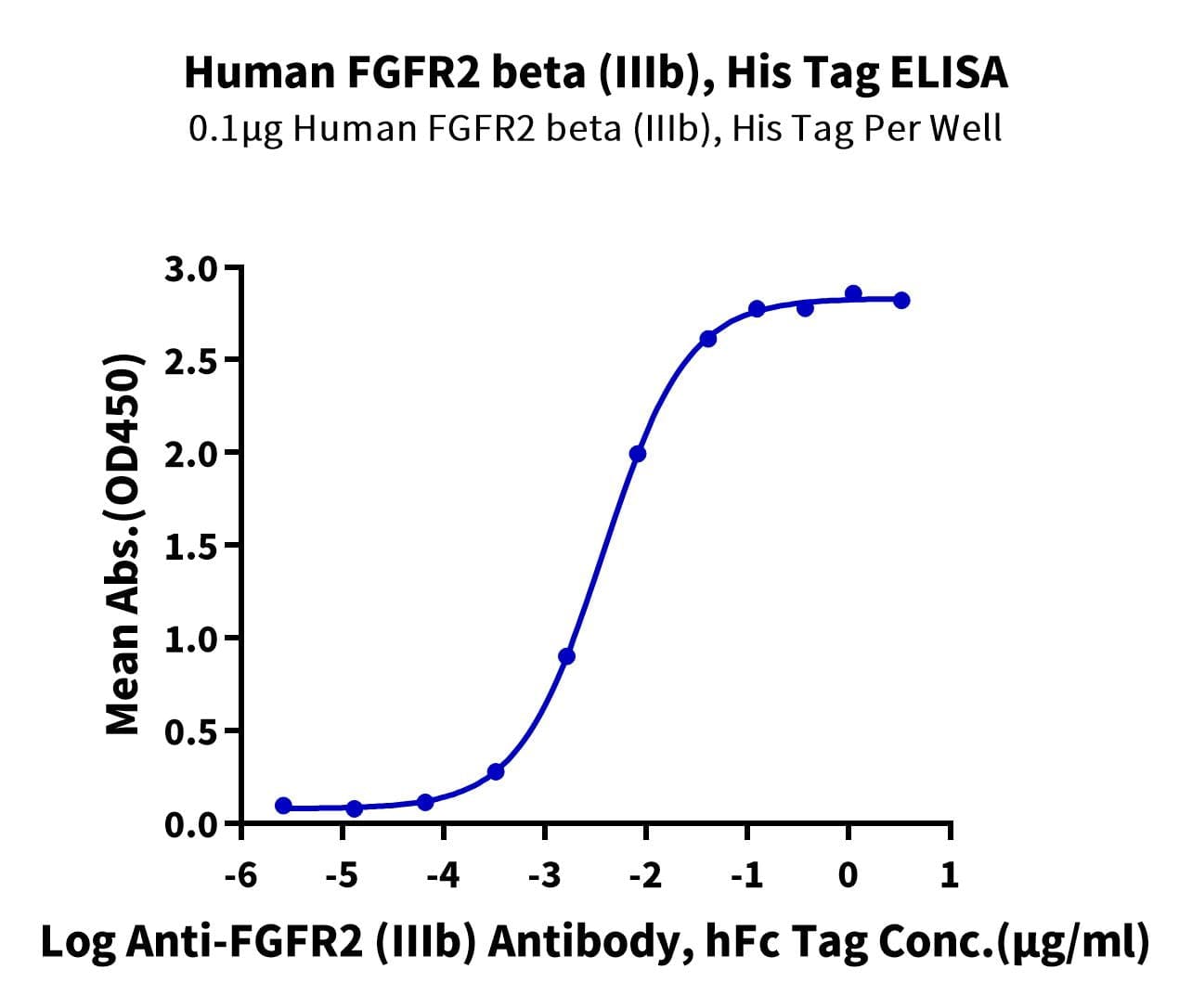
- Expression: HEK293
- Functional: Yes (ELISA)
- Amino Acid Range: Pro154-Leu358
Human FGFR2 beta (IIIb) Protein 4858
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Four distinct genes encoding closely related FGF receptors, FGF R1 - 4, are known. All four genes for FGF Rs encode proteins with an N-terminal signal peptide, three immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains, an acid-box region containing a run of acidic residues between the IgI and IgII domains, a transmembrane domain and the split tyrosine-kinase domain. Multiple forms of FGF R1 - 3 are generated by alternative splicing of the mRNAs. A frequent splicing event involving FGF R1 and 2 results in receptors containing all three Ig domains, referred to as the alpha isoform, or only IgII and IgIII, referred to as the beta isoform. |
| Protein names Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR-2) (EC 2.7.10.1) (K-sam) (KGFR) (Keratinocyte growth factor receptor) (CD antigen CD332) |
| Gene names FGFR2,FGFR2 BEK KGFR KSAM |
| Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, Fibroblast growth factor rec |
| Mass 9606Da |
| Function Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors and plays an essential role in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and apoptosis, and in the regulation of embryonic development. Required for normal embryonic patterning, trophoblast function, limb bud development, lung morphogenesis, osteogenesis and skin development. Plays an essential role in the regulation of osteoblast differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis, and is required for normal skeleton development. Promotes cell proliferation in keratinocytes and immature osteoblasts, but promotes apoptosis in differentiated osteoblasts. Phosphorylates PLCG1, FRS2 and PAK4. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphorylation of FRS2 triggers recruitment of GRB2, GAB1, PIK3R1 and SOS1, and mediates activation of RAS, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. FGFR2 signaling is down-regulated by ubiquitination, internalization and degradation. Mutations that lead to constitutive kinase activation or impair normal FGFR2 maturation, internalization and degradation lead to aberrant signaling. Over-expressed FGFR2 promotes activation of STAT1. |
| Catalytic activity #N/A |
| Subellular location Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Golgi apparatus. Cytoplasmic vesicle. Note=Detected on osteoblast plasma membrane lipid rafts. After ligand binding, the activated receptor is rapidly internalized and degraded.; [Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Note=After ligand binding, the activated receptor is rapidly internalized and degraded.; [Isoform 3]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Note=After ligand binding, the activated receptor is rapidly internalized and degraded.; [Isoform 8]: Secreted.; [Isoform 13]: Secreted. |
| Structure Monomer. Homodimer after ligand binding. Interacts predominantly with FGF1 and FGF2, but can also interact with FGF3, FGF4, FGF6, FGF7, FGF8, FGF9, FGF10, FGF17, FGF18 and FGF22 (in vitro). Ligand specificity is determined by tissue-specific expression of isoforms, and differences in the third Ig-like domain are crucial for ligand specificity. Isoform 1 has high affinity for FGF1 and FGF2, but low affinity for FGF7. Isoform 3 has high affinity for FGF1 and FGF7, and has much higher affinity for FGF7 than isoform 1 (in vitro). Affinity for fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) is increased by heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans that function as coreceptors. Likewise, KLB increases the affinity for FGF19 and FGF21. Interacts with PLCG1, GRB2 and PAK4. Interacts with FLRT2 (By similarity). |
| Post-translational modification Autophosphorylated. Binding of FGF family members together with heparan sulfate proteoglycan or heparin promotes receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation on several tyrosine residues. Autophosphorylation occurs in trans between the two FGFR molecules present in the dimer. Phosphorylation at Tyr-769 is essential for interaction with PLCG1.; N-glycosylated in the endoplasmic reticulum. The N-glycan chains undergo further maturation to an Endo H-resistant form in the Golgi apparatus.; Ubiquitinated. FGFR2 is rapidly ubiquitinated after autophosphorylation, leading to internalization and degradation. Subject to degradation both in lysosomes and by the proteasome. |
| Domain Th |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P21802 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||