| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | P17181 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His-Avi |
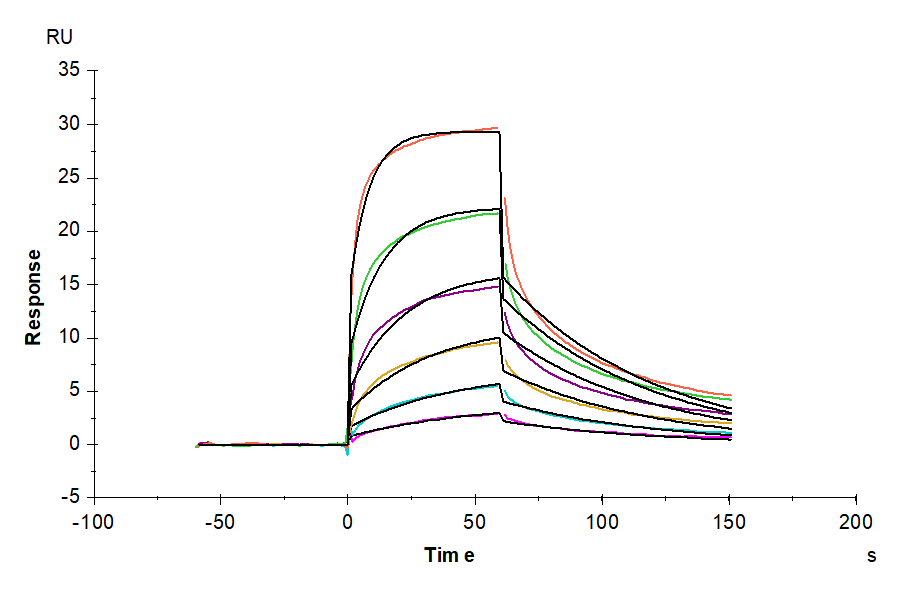
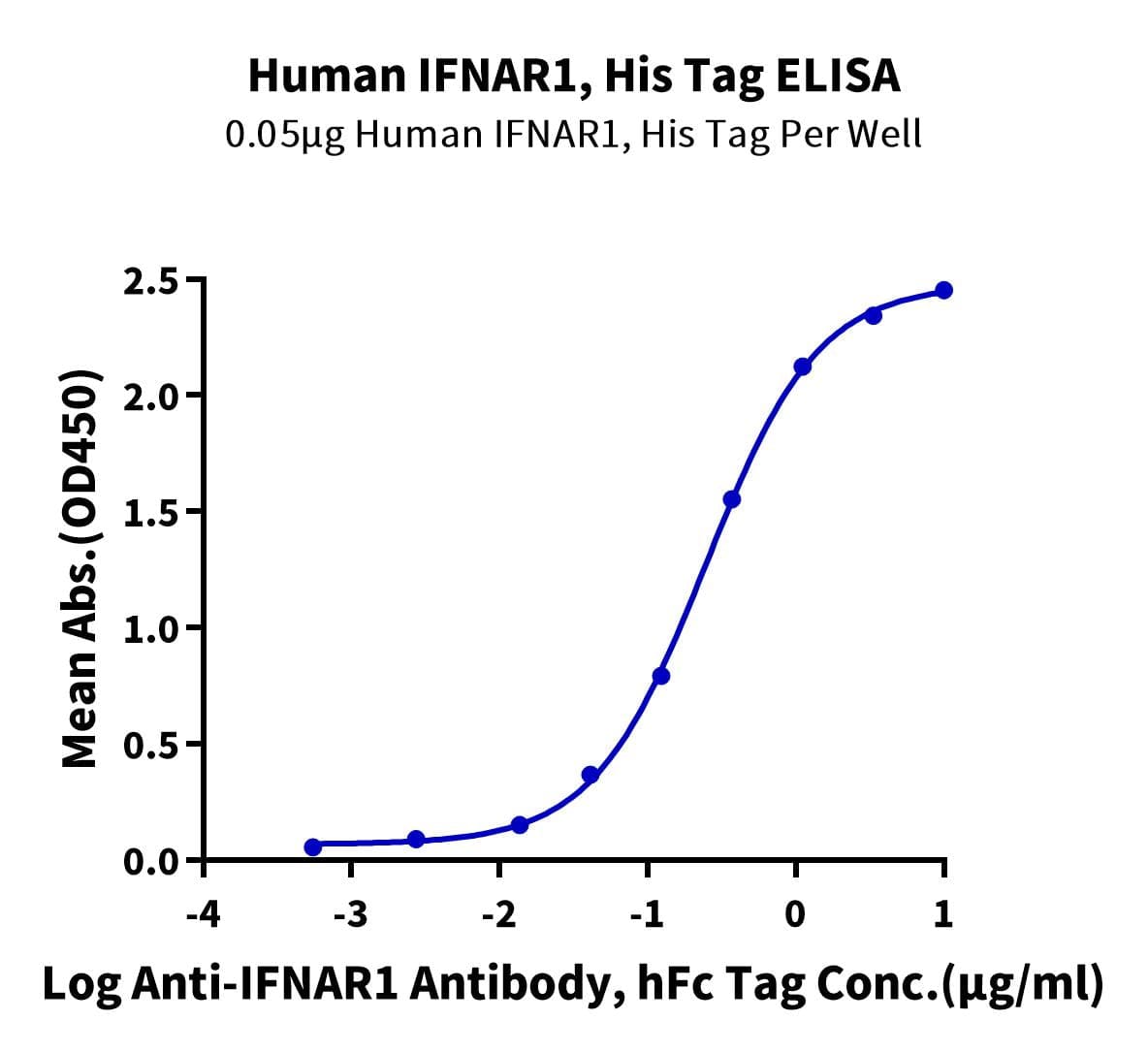
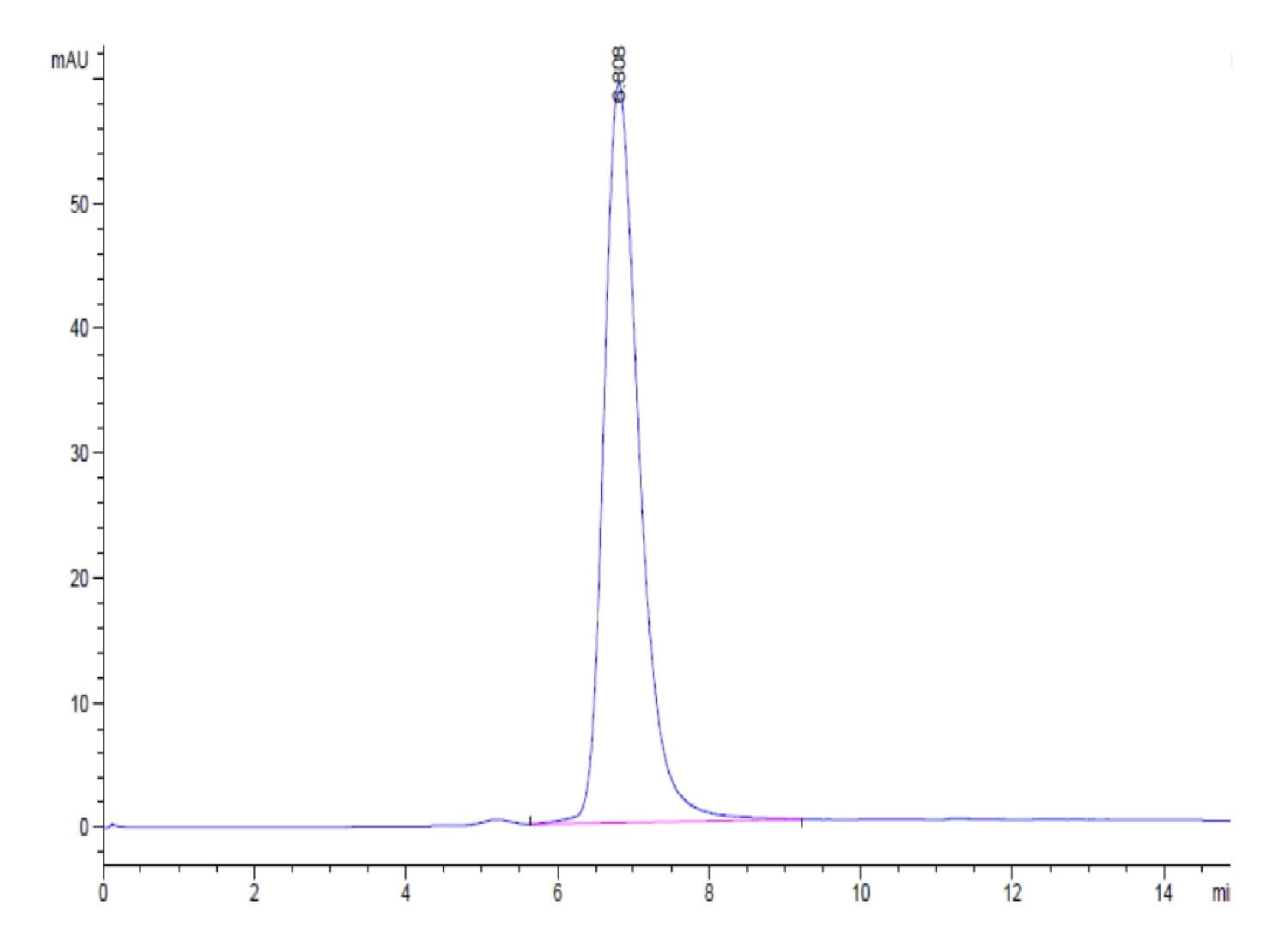
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | IFN-alpha / beta R1, also known as IFNAR1, belongs to the class II cytokine receptor family of proteins. Class II cytokine receptors form heterodimeric receptor complexes that mediate class II cytokine signals. Subunits of the different receptor complexes are shared and serve multiple functions.Functions in general as heterodimer with IFNAR2. Type I interferon binding activates the JAK-STAT signaling cascade, and triggers tyrosine phosphorylation of a number of proteins including JAKs, TYK2, STAT proteins and the IFNR alpha- and beta-subunits themselves. |
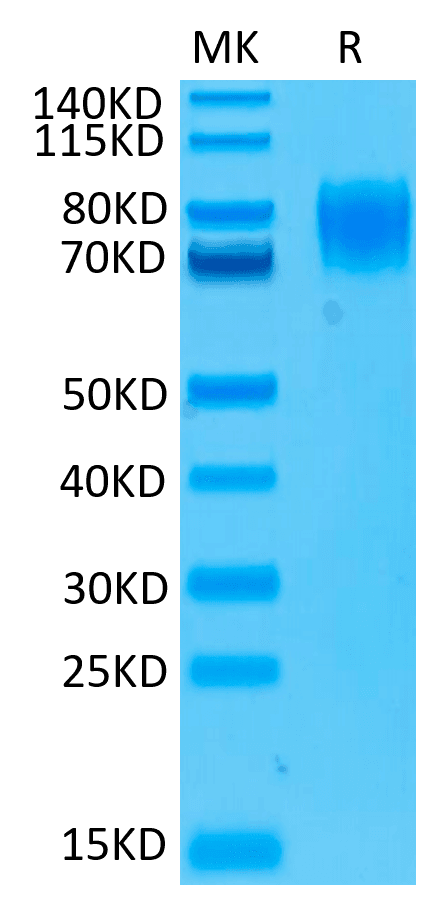
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 50.2 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 74-95 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Human IFN alpha/beta R1 Protein 4668
$300.00 – $1,000.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
- Functional: Yes (ELISA)
- Amino Acid Range: Lys28-Lys436
Human IFN alpha/beta R1 Protein 4668
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| IFN-alpha / beta R1, also known as IFNAR1, belongs to the class II cytokine receptor family of proteins. Class II cytokine receptors form heterodimeric receptor complexes that mediate class II cytokine signals. Subunits of the different receptor complexes are shared and serve multiple functions.Functions in general as heterodimer with IFNAR2. Type I interferon binding activates the JAK-STAT signaling cascade, and triggers tyrosine phosphorylation of a number of proteins including JAKs, TYK2, STAT proteins and the IFNR alpha- and beta-subunits themselves. |
| Protein names Interferon alpha/beta receptor 1 (IFN-R-1) (IFN-alpha/beta receptor 1) (Cytokine receptor class-II member 1) (Cytokine receptor family 2 member 1) (CRF2-1) (Type I interferon receptor 1) |
| Gene names IFNAR1,IFNAR1 IFNAR |
| Protein family Type II cytokine receptor family |
| Mass 9606Da |
| Function Together with IFNAR2, forms the heterodimeric receptor for type I interferons (including interferons alpha, beta, epsilon, omega and kappa) (PubMed:10049744, PubMed:14532120, PubMed:15337770, PubMed:2153461, PubMed:21854986, PubMed:24075985, PubMed:31270247, PubMed:33252644, PubMed:35442418, PubMed:7813427). Type I interferon binding activates the JAK-STAT signaling cascade, resulting in transcriptional activation or repression of interferon-regulated genes that encode the effectors of the interferon response (PubMed:10049744, PubMed:21854986, PubMed:7665574). Mechanistically, type I interferon-binding brings the IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 subunits into close proximity with one another, driving their associated Janus kinases (JAKs) (TYK2 bound to IFNAR1 and JAK1 bound to IFNAR2) to cross-phosphorylate one another (PubMed:21854986, PubMed:32972995, PubMed:7665574, PubMed:7813427). The activated kinases phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues on the intracellular domains of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, forming docking sites for the STAT transcription factors (PubMed:21854986, PubMed:32972995, PubMed:7526154, PubMed:7665574, PubMed:7813427). STAT proteins are then phosphorylated by the JAKs, promoting their translocation into the nucleus to regulate expression of interferon-regulated genes (PubMed:19561067, PubMed:21854986, PubMed:32972995, PubMed:7665574, PubMed:7813427, PubMed:9121453). Can also act independently of IFNAR2: form an active IFNB1 receptor by itself and activate a signaling cascade that does not involve activation of the JAK-STAT pathway (By similarity). |
| Catalytic activity #N/A |
| Subellular location [Isoform 1]: Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Late endosome. Lysosome. Note=Interferon binding triggers internalization of the receptor from the cell membrane into endosomes and then into lysosomes. |
| Tissues IFN receptors are present in all tissues and even on the surface of most IFN-resistant cells. Isoform 1, isoform 2 and isoform 3 are expressed in the IFN-alpha sensitive myeloma cell line U266B1. Isoform 2 and isoform 3 are expressed in the IFN-alpha resistant myeloma cell line U266R. Isoform 1 is not expressed in IFN-alpha resistant myeloma cell line U266R. |
| Structure Heterodimer with IFNAR2; forming the receptor for type I interferon (PubMed:10049744, PubMed:21854986, PubMed:7665574). Interacts with TYK2 (PubMed:15337770, PubMed:24704786, PubMed:7526154). Interacts with STAT1 and STAT2; the interaction requires its phosphorylation at Tyr-466 (PubMed:9121453). Interacts (serine-phosphorylated form) with FBXW11, the substrate recognition component of a SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex (PubMed:14532120, PubMed:15337770, PubMed:18056411). Interacts with SHMT2; this promotes interaction with ABRAXAS2 and the BRISC complex (PubMed:24075985). Interacts with TRIM10; this interaction prevents association between IFNAR1 and TYK2 (PubMed:33811647). |
| Post-translational modification Ubiquitinated, leading to its internalization and degradation (PubMed:14532120, PubMed:15337770). Polyubiquitinated via 'Lys-48'-linked and 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin chains, leading to receptor internalization and lysosomal degradation (PubMed:18056411). The 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin chains are cleaved off by the BRISC complex (PubMed:24075985).; Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues in response to interferon-binding: phosphorylation by TYK2 tyrosine kinase creates docking sites for STAT proteins (PubMed:10049744, PubMed:7526154). Phosphorylated on serine residues in response to interferon binding; this promotes interaction with FBXW11 and ubiquitination (PubMed:14532120, PubMed:15337770, PubMed:24075985).; Palmitoylation at Cys-463 is required for the activation of STAT1 and STAT2. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P17181 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||