| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | Q9BY76 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | N-His |
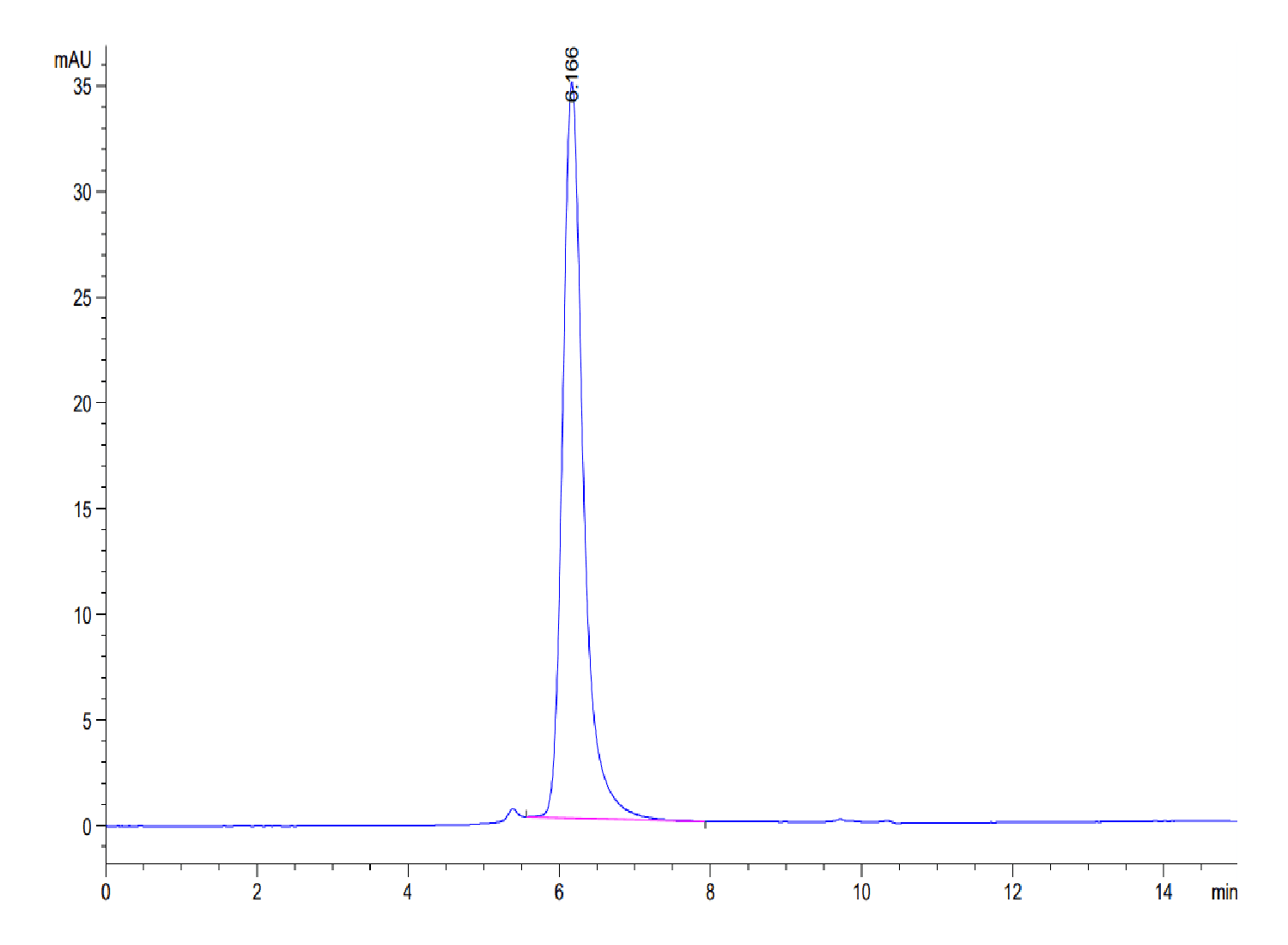
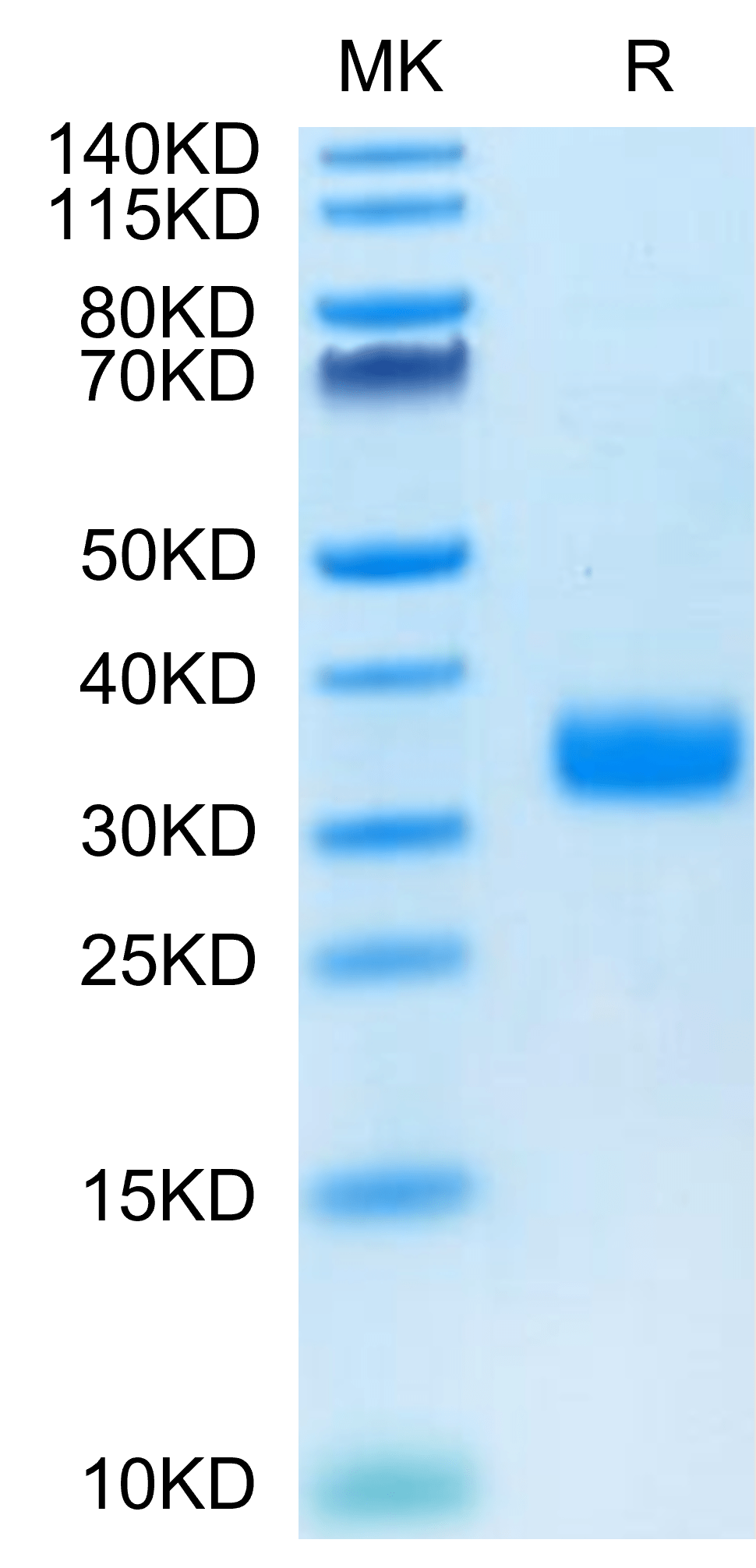
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Candidates for this common regulatory system include signals mediated by peroxisome proliferator-activated regulator and its response factor, angiopoietin-like 4. The expression and bioactivity of angiopoietin-like 4, an adipocytokine that was originally reported to have an angiogenic function, have been detected not only in the vascular system and adipose tissue but also in rheumatoid joints. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 28.2 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 30-40 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Human ANGPTL4/Angiopoietin-like 4 Protein 4316
$195.00 – $650.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
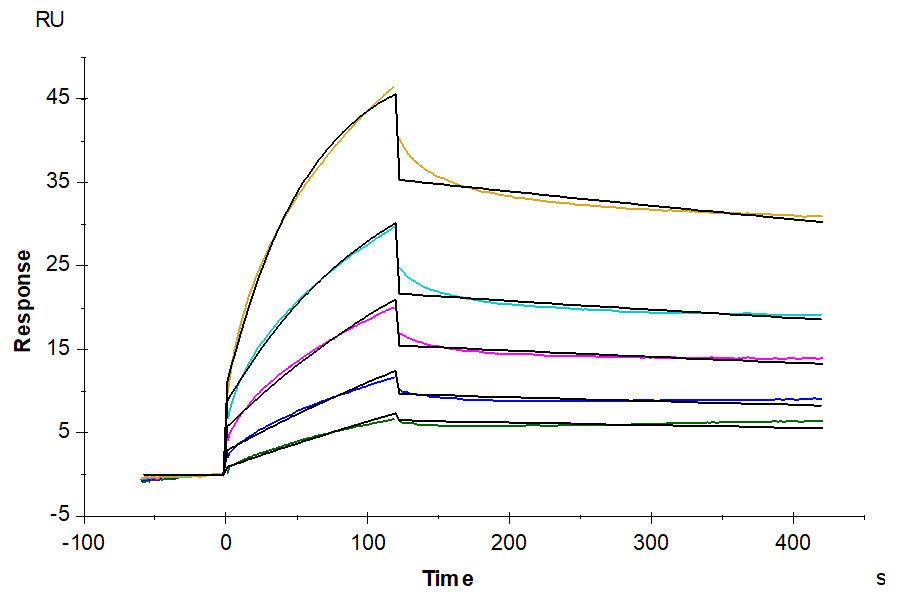
- Binding assay: Yes (SPR)
- Amino Acid Range: Pro166-Ser406
Human ANGPTL4/Angiopoietin-like 4 Protein 4316
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Candidates for this common regulatory system include signals mediated by peroxisome proliferator-activated regulator and its response factor, angiopoietin-like 4. The expression and bioactivity of angiopoietin-like 4, an adipocytokine that was originally reported to have an angiogenic function, have been detected not only in the vascular system and adipose tissue but also in rheumatoid joints. |
| Protein names Angiopoietin-related protein 4 (Angiopoietin-like protein 4) (Hepatic fibrinogen/angiopoietin-related protein) (HFARP) [Cleaved into: ANGPTL4 N-terminal chain; ANGPTL4 C-terminal chain] |
| Gene names ANGPTL4,ANGPTL4 ARP4 HFARP PGAR PP1158 PSEC0166 UNQ171/PRO197 |
| Mass 9606Da |
| Function Mediates inactivation of the lipoprotein lipase LPL, and thereby plays a role in the regulation of triglyceride clearance from the blood serum and in lipid metabolism (PubMed:19270337, PubMed:21398697, PubMed:27929370, PubMed:29899144). May also play a role in regulating glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity (Probable). Inhibits proliferation, migration, and tubule formation of endothelial cells and reduces vascular leakage (PubMed:14583458, PubMed:17068295). Upon heterologous expression, inhibits the adhesion of endothelial cell to the extracellular matrix (ECM), and inhibits the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions in endothelial cells that have adhered to ANGPTL4-containing ECM (in vitro) (PubMed:17068295). Depending on context, may modulate tumor-related angiogenesis (By similarity).; [ANGPTL4 N-terminal chain]: Mediates inactivation of the lipoprotein lipase LPL, and thereby plays an important role in the regulation of triglyceride clearance from the blood serum and in lipid metabolism (PubMed:19270337, PubMed:21398697, PubMed:27929370, PubMed:29899144). Has higher activity in LPL inactivation than the uncleaved protein (PubMed:19270337, PubMed:21398697). |
| Catalytic activity #N/A |
| Subellular location Secreted. Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix. Note=The unprocessed form interacts with the extracellular matrix (PubMed:17068295, PubMed:21398697). This may constitute a dynamic reservoir, a regulatory mechanism of the bioavailability of ANGPTL4 (Probable). |
| Tissues Detected in blood plasma (at protein level) (PubMed:29899519). Detected in liver (PubMed:10698685). Detected in white fat tissue and placenta (PubMed:10866690). Expressed at high levels in the placenta, heart, liver, muscle, pancreas and lung but expressed poorly in the brain and kidney. |
| Structure Homooligomer; disulfide-linked via Cys residues in the N-terminal part of the protein (PubMed:19270337). The homooligomer undergoes proteolytic processing to release the ANGPTL4 C-terminal chain, which circulates as a monomer (PubMed:19270337). The homooligomer unprocessed form is able to interact with the extracellular matrix (PubMed:21398697). |
| Post-translational modification N-glycosylated.; [ANGPTL4 N-terminal chain]: Forms disulfide-linked dimers and tetramers.; Cleaved into a smaller N-terminal chain and a larger chain that contains the fibrinogen C-terminal domain; both cleaved and uncleaved forms are detected in the extracellular space. The cleaved form is not present within the cell. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q9BY76 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||