| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | AAH05333 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-hFc |
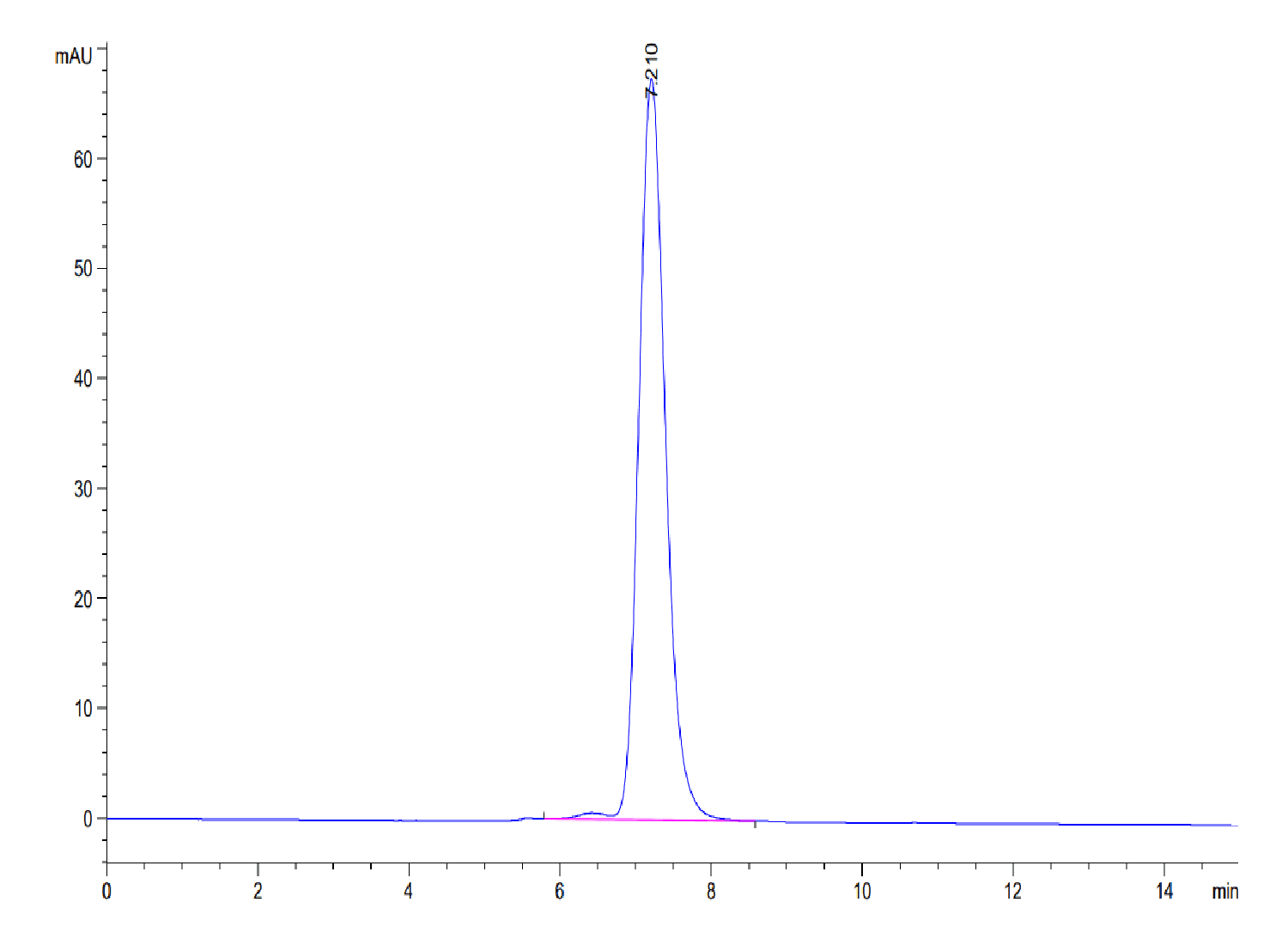
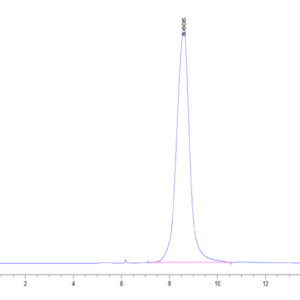
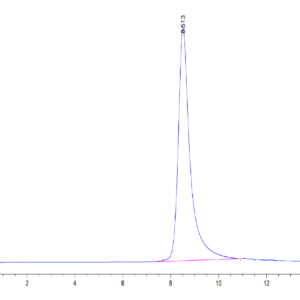
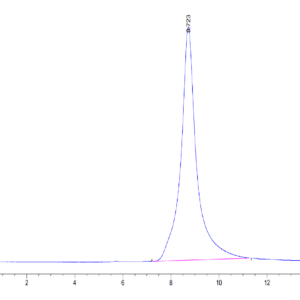
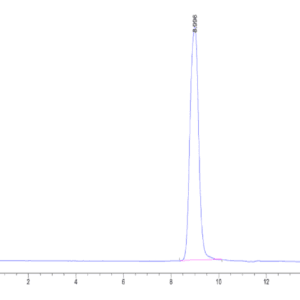
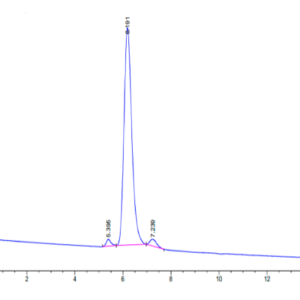
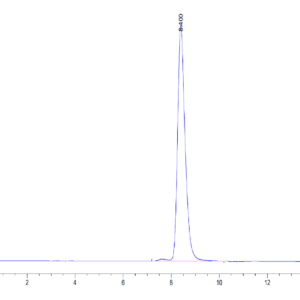
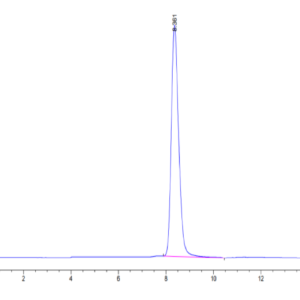
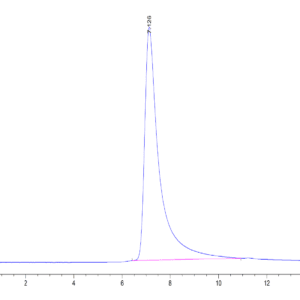
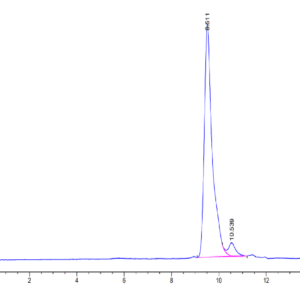
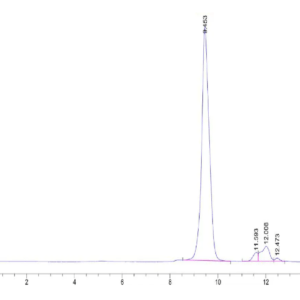
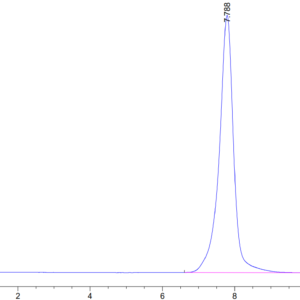
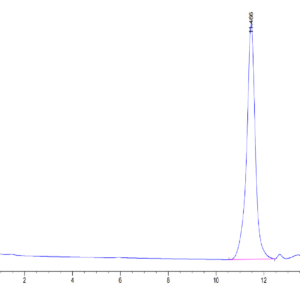
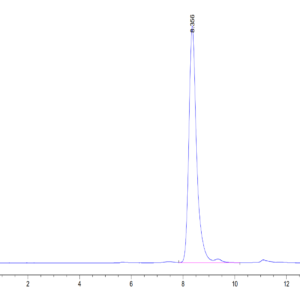
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | IFN-gamma and one of its receptor subunits, IFNGR1, are translocated to the nucleus, together with STAT1alpha as one macromolecular complex, via the classical importin-dependent pathway.Put IFN-gamma and its receptor subunit, IFNGR1, in direct contact with the promoter region of IFN-gamma-activated genes with associated increased activity, thus suggesting a transcriptional/cotranscriptional role for IFN-gamma/IFNGR1 as well as a possible role in determining the specificity of IFN-gamma action. |
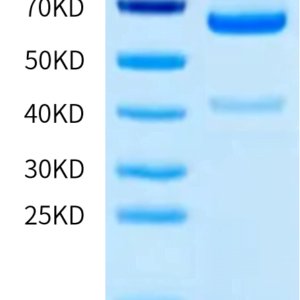
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 52.4 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 60-75 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Human IFN gamma R1/IFNGR1 Protein 4204
$150.00 – $500.00
Summary
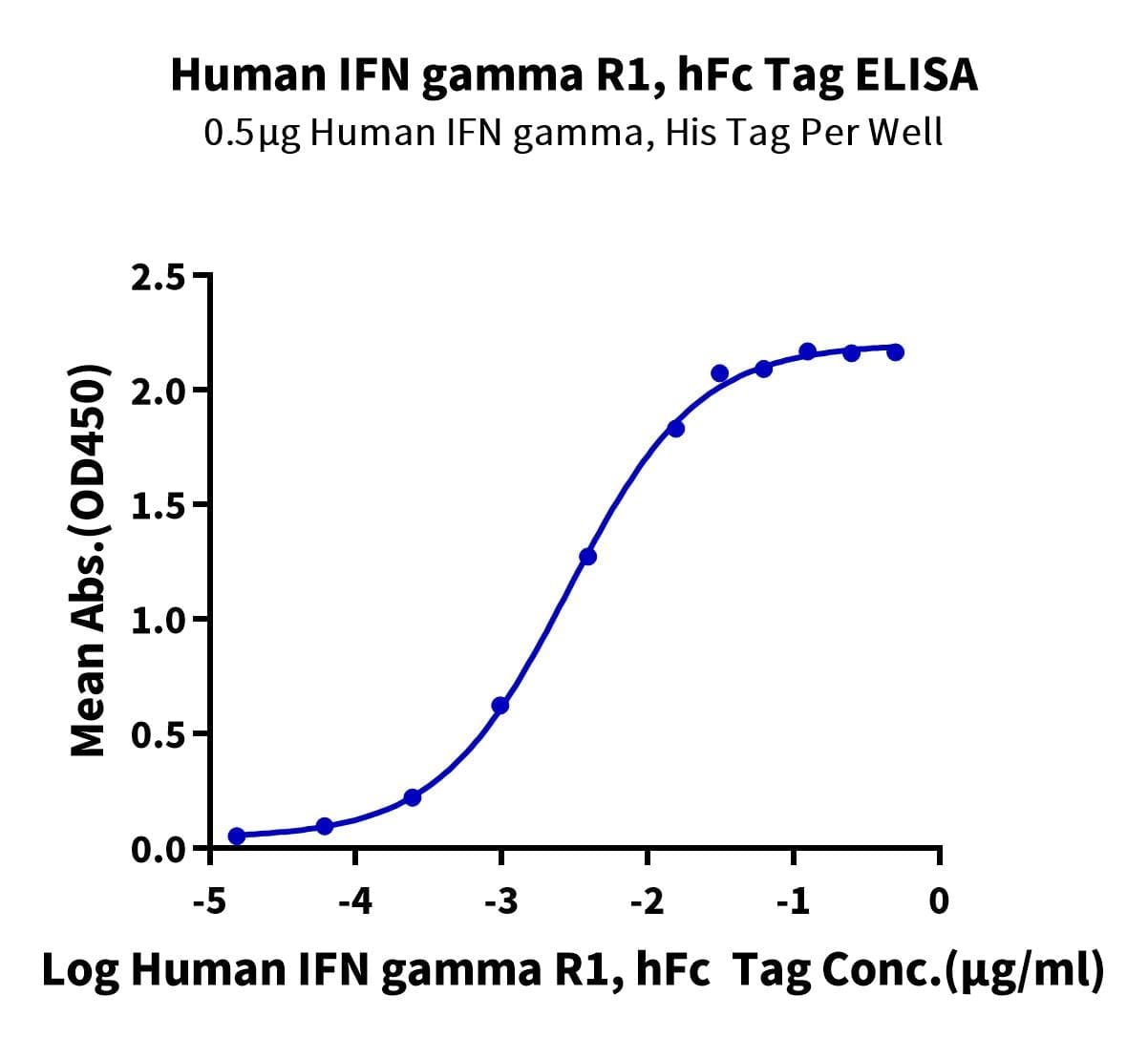
- Expression: HEK293
- Functional: Yes (ELISA)
- Amino Acid Range: Glu18-Gly245
Human IFN gamma R1/IFNGR1 Protein 4204
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| IFN-gamma and one of its receptor subunits, IFNGR1, are translocated to the nucleus, together with STAT1alpha as one macromolecular complex, via the classical importin-dependent pathway.Put IFN-gamma and its receptor subunit, IFNGR1, in direct contact with the promoter region of IFN-gamma-activated genes with associated increased activity, thus suggesting a transcriptional/cotranscriptional role for IFN-gamma/IFNGR1 as well as a possible role in determining the specificity of IFN-gamma action. |
| Protein names Interferon gamma receptor 1 (IFN-gamma receptor 1) (IFN-gamma-R1) (CDw119) (Interferon gamma receptor alpha-chain) (IFN-gamma-R-alpha) (CD antigen CD119) |
| Protein family Type II cytokine receptor family |
| Mass 54405Da |
| Function Receptor subunit for interferon gamma/INFG that plays crucial roles in antimicrobial, antiviral, and antitumor responses by activating effector immune cells and enhancing antigen presentation (PubMed:20015550). Associates with transmembrane accessory factor IFNGR2 to form a functional receptor (PubMed:10986460, PubMed:2971451, PubMed:7615558, PubMed:7617032, PubMed:7673114). Upon ligand binding, the intracellular domain of IFNGR1 opens out to allow association of downstream signaling components JAK1 and JAK2. In turn, activated JAK1 phosphorylates IFNGR1 to form a docking site for STAT1. Subsequent phosphorylation of STAT1 leads to dimerization, translocation to the nucleus, and stimulation of target gene transcription (PubMed:28883123). STAT3 can also be activated in a similar manner although activation seems weaker. IFNGR1 intracellular domain phosphorylation also provides a docking site for SOCS1 that regulates the JAK-STAT pathway by competing with STAT1 binding to IFNGR1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10986460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20015550, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28883123, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2971451, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7615558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7617032, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7673114}. |
| Subellular location Cell membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10811850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28883123}; Single-pass type I membrane protein {ECO:0000255}. |
| Structure Monomer (PubMed:9367779). Heterodimer with IFNGR2, to form the IFNG receptor complex (PubMed:7615558). Interacts with JAK1 (PubMed:7615558). Interacts (when phosphorylated) with STAT1 (PubMed:8156998). Interacts with SOCS1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7615558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8156998, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9367779}. |
| Post-translational modification Phosphorylated at Ser/Thr residues. Phosphorylation of Tyr-457 is required for IFNG receptor signal transduction (PubMed:8156998). Influenza virus infection leads to phosphorylation in a CSNK1A1-dependent manner (PubMed:29343571). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29343571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7615558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7673114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8156998}.; Ubiquitinated after phosphorylation in a CSNK1A1-dependent manner, leading to the lysosome-dependent degradation (PubMed:29343571). Proteasomally degraded through 'Lys-48'-mediated ubiquitination (PubMed:28883123). Ubiquitination is necessary for efficient IFNGR1 signaling (PubMed:28883123). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28883123, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29343571}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P15260 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.