| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | Q60994 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-hFc |
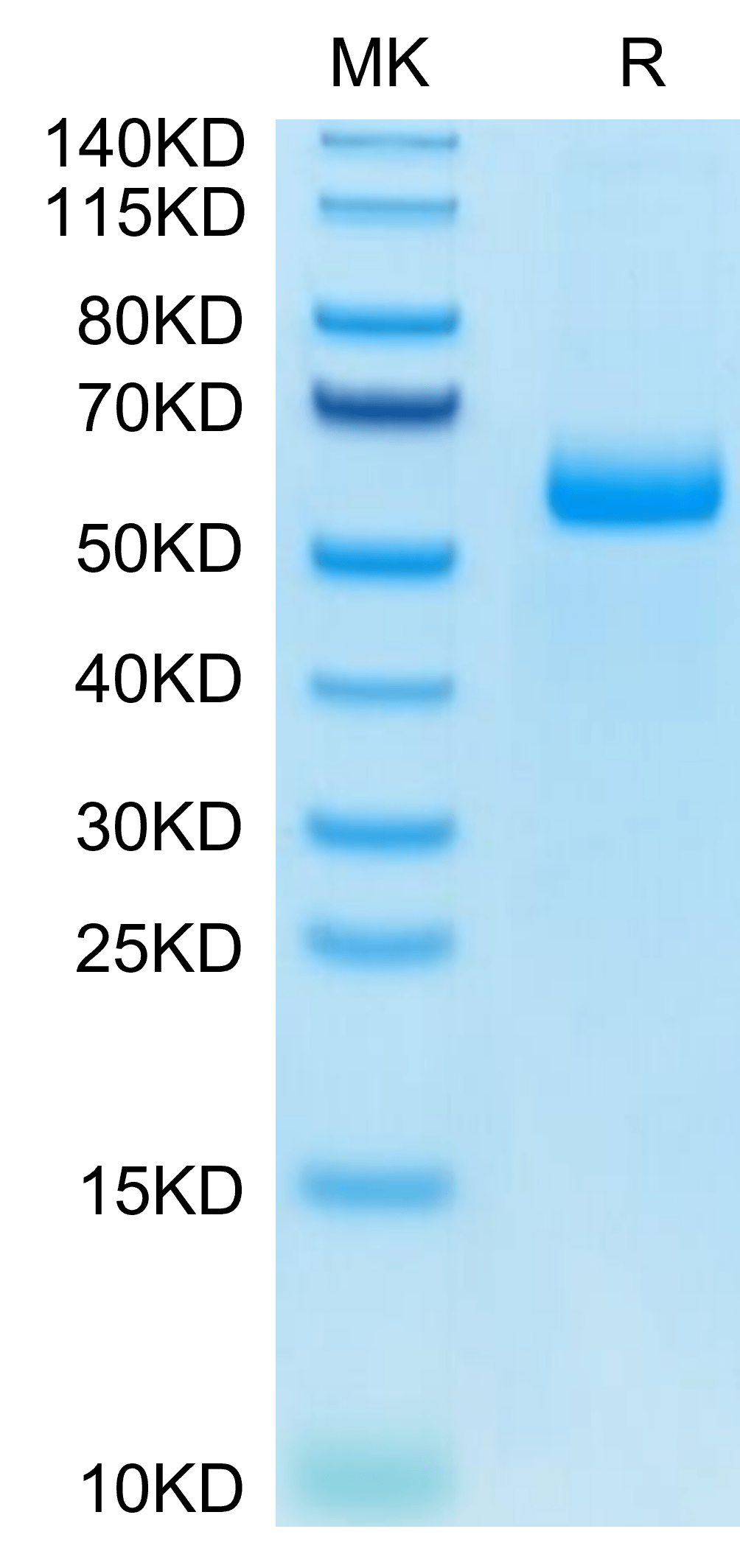
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| background | Adiponectin, also known as Acrp30, is an adipocyte-derived protein with wide ranging paracrine and endocrine effects on metabolism and inflammation.Important adipokine involved in the control of fat metabolism and insulin sensitivity, with direct anti-diabetic, anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory activities. Stimulates AMPK phosphorylation and activation in the liver and the skeletal muscle, enhancing glucose utilization and fatty-acid combustion. Antagonizes TNF-alpha by negatively regulating its expression in various tissues such as liver and macrophages, and also by counteracting its effects. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 51.3 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 52-70 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Mouse Adiponectin/Acrp30 Protein 3928
$225.00 – $750.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
- Pure: Yes (SDS-PAGE)
- Amino Acid Range: Glu18-Asn247
Mouse Adiponectin/Acrp30 Protein 3928
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Adiponectin, also known as Acrp30, is an adipocyte-derived protein with wide ranging paracrine and endocrine effects on metabolism and inflammation.Important adipokine involved in the control of fat metabolism and insulin sensitivity, with direct anti-diabetic, anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory activities. Stimulates AMPK phosphorylation and activation in the liver and the skeletal muscle, enhancing glucose utilization and fatty-acid combustion. Antagonizes TNF-alpha by negatively regulating its expression in various tissues such as liver and macrophages, and also by counteracting its effects. |
| Protein names Adiponectin (30 kDa adipocyte complement-related protein) (Adipocyte complement-related 30 kDa protein) (ACRP30) (Adipocyte, C1q and collagen domain-containing protein) (Adipocyte-specific protein AdipoQ) |
| Gene names Adipoq,Adipoq Acdc Acrp30 Apm1 |
| Mass 10090Da |
| Function Important adipokine involved in the control of fat metabolism and insulin sensitivity, with direct anti-diabetic, anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory activities. Stimulates AMPK phosphorylation and activation in the liver and the skeletal muscle, enhancing glucose utilization and fatty-acid combustion. Antagonizes TNF-alpha by negatively regulating its expression in various tissues such as liver and macrophages, and also by counteracting its effects. Inhibits endothelial NF-kappa-B signaling through a cAMP-dependent pathway. May play a role in cell growth, angiogenesis and tissue remodeling by binding and sequestering various growth factors with distinct binding affinities, depending on the type of complex, LMW, MMW or HMW. |
| Subellular location Secreted . |
| Tissues Synthesized exclusively by adipocytes and secreted into plasma. |
| Structure Homomultimer (PubMed:23209641). Forms trimers, hexamers and 12- to 18-mers. The trimers (low molecular weight complexes / LMW) are assembled via non-covalent interactions of the collagen-like domains in a triple helix and hydrophobic interactions within the globular C1q domain. Several trimers can associate to form disulfide-linked hexamers (middle molecular weight complexes / MMW) and larger complexes (higher molecular weight / HMW) (PubMed:23209641). The HMW-complex assembly is also modulated by the degree of lysine hydroxylation and glycosylation (PubMed:23209641). LMW, MMW and HMW complexes bind to HBEGF, MMW and HMW complexes bind to PDGFB, and HMW complex binds to FGF2. Interacts with CTRP9 via the C1q domain (heterotrimeric complex) (PubMed:18787108). |
| Post-translational modification HMW complexes are more extensively glycosylated than smaller oligomers. Hydroxylation and glycosylation of the lysine residues within the collagen-like domain of adiponectin seem to be critically involved in regulating the formation and/or secretion of HMW complexes and consequently contribute to the insulin-sensitizing activity of adiponectin in hepatocytes.; O-glycosylated. Not N-glycosylated (By similarity) O-linked glycans on hydroxylysine residues consist of Glc-Gal disaccharides bound to the oxygen atom of post-translationally added hydroxyl groups (By similarity). O-linked glycosylation in the N-terminal is disialylated with the structure Neu5Acalpha2->8Neu5Acalpha2->3Gal. Sialylated by alpha 2,8-sialyltransferase III.; Succination of Cys-39 by the Krebs cycle intermediate fumarate, which leads to S-(2-succinyl)cysteine residues, inhibits polymerization and secretion of adiponectin. Adiponectin is a major target for succination in both adipocytes and adipose tissue of diabetic mice. It was proposed that succination of proteins is a biomarker of mitochondrial stress and accumulation of Krebs cycle intermediates in adipose tissue in diabetes and that succination of adiponectin may contribute to the decrease in plasma adiponectin in diabetes. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q60994 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||