| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | P04925 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-hFc |
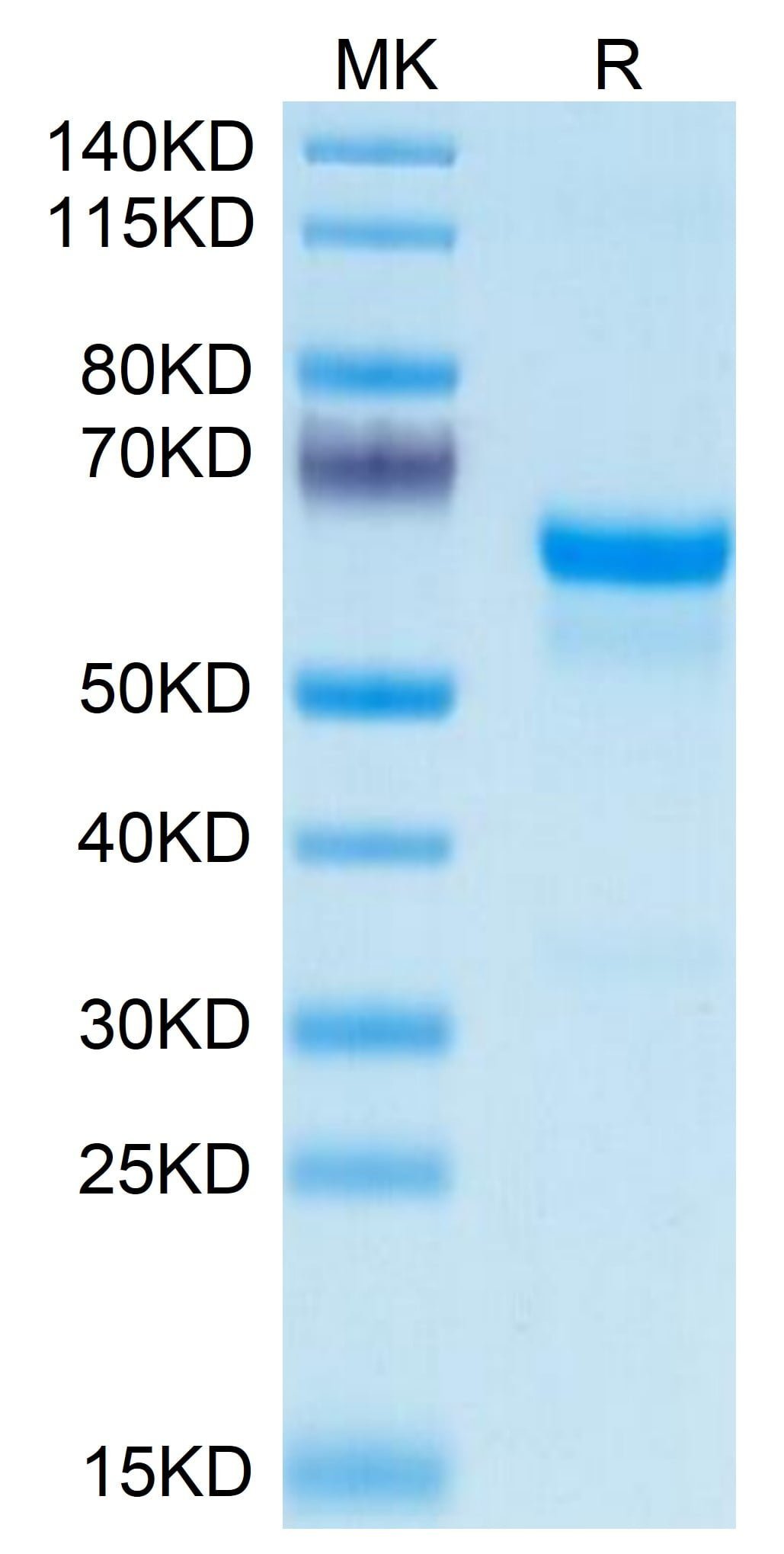
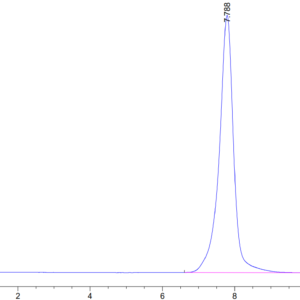
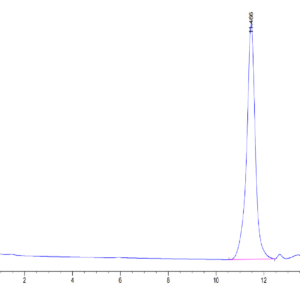
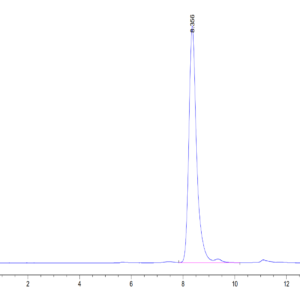
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| background | Prion protein gene (PRNP) variants determine the susceptibility of humans, sheep and mice to prion diseases, whereas polymorphisms in the open reading frame (ORF) of bovine PRNP seem to be unrelated to the incidence of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE). According to the latest reports, the genetic susceptibility of cattle to BSE is associated with polymorphisms ofthe regulatory region of the PRNP gene and the level ofits expression. |
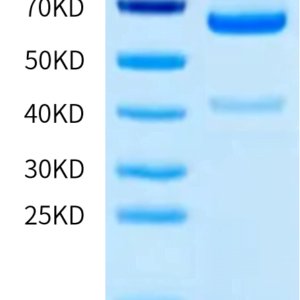
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 49.6 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 60-68 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Mouse PRNP Protein 3650
$270.00 – $900.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
- Pure: Yes (SDS-PAGE)
- Amino Acid Range: Lys23-Ser230
Mouse PRNP Protein 3650
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
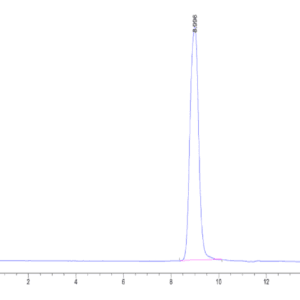
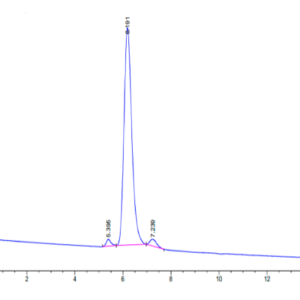
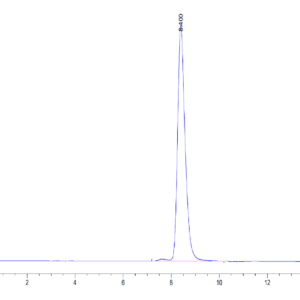
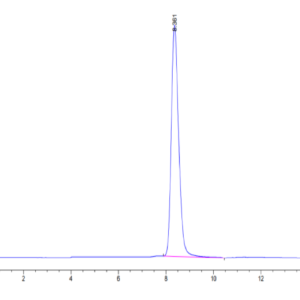
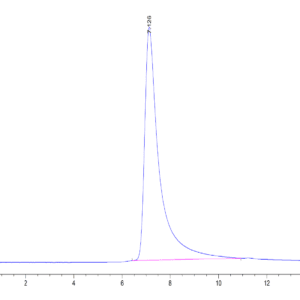
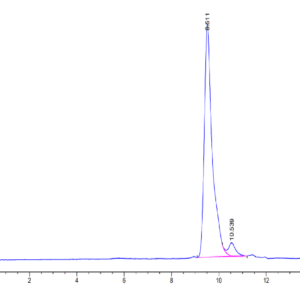
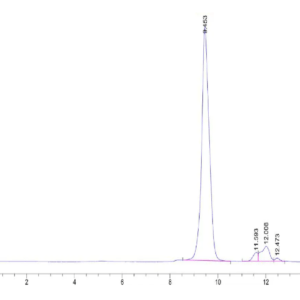
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Prion protein gene (PRNP) variants determine the susceptibility of humans, sheep and mice to prion diseases, whereas polymorphisms in the open reading frame (ORF) of bovine PRNP seem to be unrelated to the incidence of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE). According to the latest reports, the genetic susceptibility of cattle to BSE is associated with polymorphisms ofthe regulatory region of the PRNP gene and the level ofits expression. |
| Protein names Major prion protein (PrP) (PrP27-30) (PrP33-35C) (CD antigen CD230) |
| Gene names Prnp,Prnp Prn-p Prp |
| Protein family Prion family |
| Mass 10090Da |
| Function Its primary physiological function is unclear. May play a role in neuronal development and synaptic plasticity. May be required for neuronal myelin sheath maintenance. May promote myelin homeostasis through acting as an agonist for ADGRG6 receptor. May play a role in iron uptake and iron homeostasis. Soluble oligomers are toxic to cultured neuroblastoma cells and induce apoptosis (in vitro) (By similarity). Association with GPC1 (via its heparan sulfate chains) targets PRNP to lipid rafts. Also provides Cu(2+) or Zn(2+) for the ascorbate-mediated GPC1 deaminase degradation of its heparan sulfate side chains (PubMed:12732622, PubMed:16492732, PubMed:19242475, PubMed:19568430). |
| Catalytic activity BINDING 60; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156"; BINDING 61; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156"; BINDING 62; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156"; BINDING 68; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156"; BINDING 69; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156"; BINDING 70; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156"; BINDING 76; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="3"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156"; BINDING 77; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="3"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156"; BINDING 78; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="3"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156"; BINDING 84; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="4"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156"; BINDING 85; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="4"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156"; BINDING 86; /ligand="Cu(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29036"; /ligand_label="4"; /evidence="ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04156" |
| Subellular location Cell membrane ; Lipid-anchor, GPI-anchor. Golgi apparatus. Note=Targeted to lipid rafts via association with the heparan sulfate chains of GPC1. Colocates, in the presence of Cu(2+), to. vesicles in para- and perinuclear regions, where both proteins undergo internalization. Heparin displaces PRNP from lipid rafts and promotes endocytosis. |
| Tissues Highly expressed in the brain, lung, kidney and heart. Expressed at low levels in the liver and spleen. |
| Structure Monomer and homodimer. Has a tendency to aggregate into amyloid fibrils containing a cross-beta spine, formed by a steric zipper of superposed beta-strands. Soluble oligomers may represent an intermediate stage on the path to fibril formation. Copper binding may promote oligomerization. Interacts with GRB2, APP, ERI3/PRNPIP and SYN1 (PubMed:11571277). Mislocalized cytosolically exposed PrP interacts with MGRN1; this interaction alters MGRN1 subcellular location and causes lysosomal enlargement (By similarity). Interacts with APP. Interacts with KIAA1191 (By similarity). Interacts with ADGRG6 (PubMed:27501152). |
| Post-translational modification N-glycosylated. |
| Domain Th |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P04925 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.