| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | Q80W65 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His |
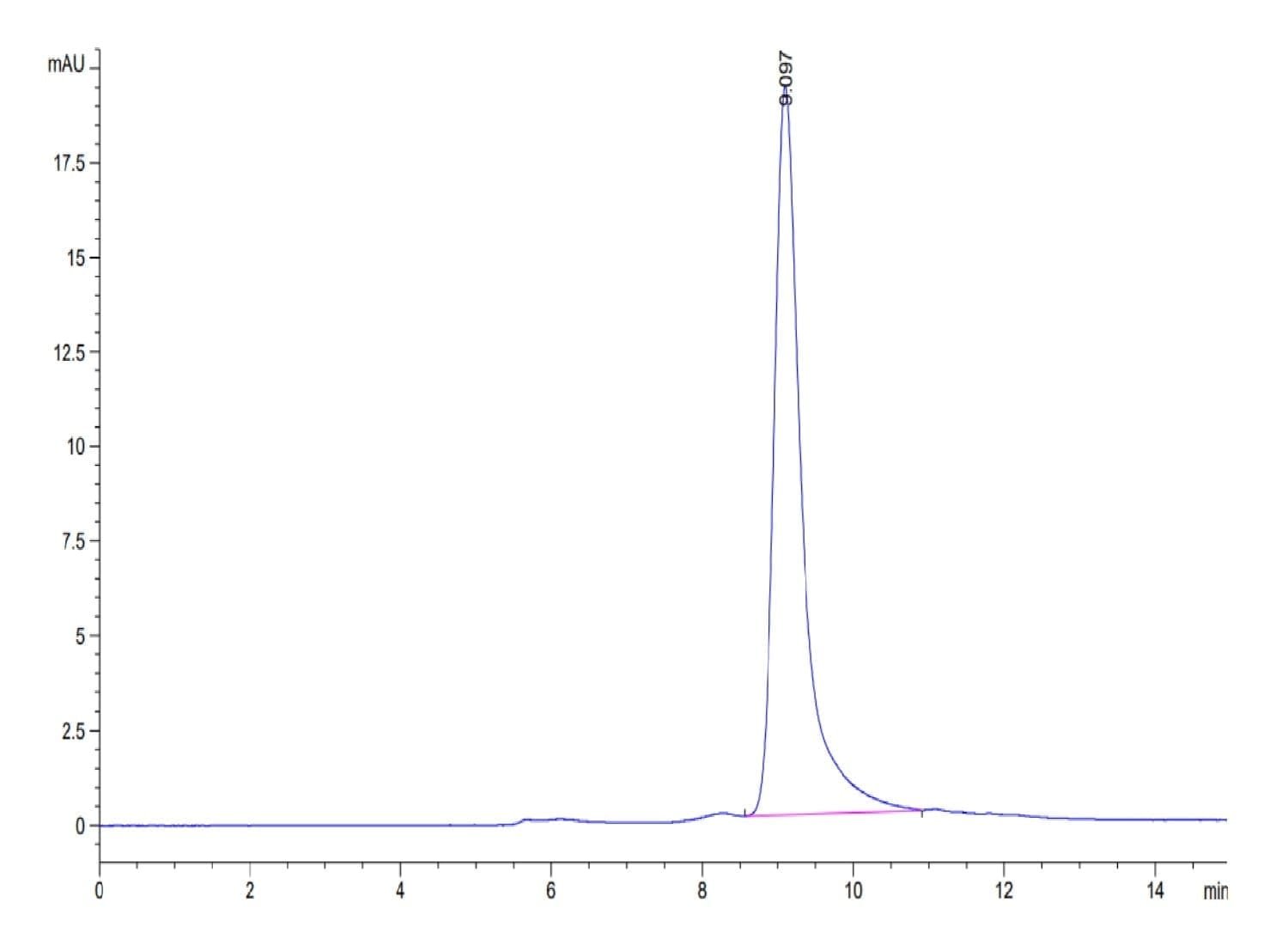
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is an enzyme encoded by the PCSK9 gene in humans on chromosome 1.The first two PCSK9 inhibitors, alirocumab and evolocumab, were approved as once every two week injections, by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2015 for lowering LDL-particle concentrations when statins and other drugs were not sufficiently effective or poorly tolerated. |
| molecular weight | Due to autocatalytic cleavage, the protein release the pro-form (59 kDa) and mature form (14 kDa). Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 65-68 kDa (pro-form) and 15kDa (mature form) based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Mouse PCSK9 Protein 5122
$270.00 – $900.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
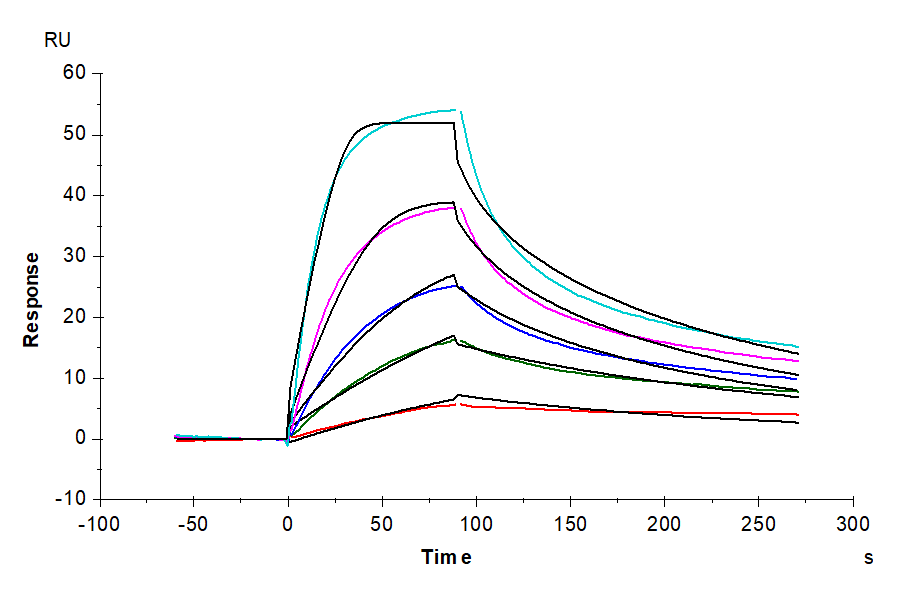
- Binding assay: Yes (SPR)
- Amino Acid Range: Gln35-Gln694
Mouse PCSK9 Protein 5122
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is an enzyme encoded by the PCSK9 gene in humans on chromosome 1.The first two PCSK9 inhibitors, alirocumab and evolocumab, were approved as once every two week injections, by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2015 for lowering LDL-particle concentrations when statins and other drugs were not sufficiently effective or poorly tolerated. |
| Protein names Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (EC 3.4.21.-) (Neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1) (NARC-1) (Proprotein convertase 9) (PC9) (Subtilisin/kexin-like protease PC9) |
| Gene names Pcsk9,Pcsk9 Narc1 |
| Protein family Peptidase S8 family |
| Mass 10090Da |
| Function Crucial player in the regulation of plasma cholesterol homeostasis. Binds to low-density lipid receptor family members: low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), very low density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR), apolipoprotein E receptor (LRP1/APOER) and apolipoprotein receptor 2 (LRP8/APOER2), and promotes their degradation in intracellular acidic compartments. Acts via a non-proteolytic mechanism to enhance the degradation of the hepatic LDLR through a clathrin LDLRAP1/ARH-mediated pathway. May prevent the recycling of LDLR from endosomes to the cell surface or direct it to lysosomes for degradation. Can induce ubiquitination of LDLR leading to its subsequent degradation. Inhibits intracellular degradation of APOB via the autophagosome/lysosome pathway in a LDLR-independent manner. Involved in the disposal of non-acetylated intermediates of BACE1 in the early secretory pathway. Inhibits epithelial Na(+) channel (ENaC)-mediated Na(+) absorption by reducing ENaC surface expression primarily by increasing its proteasomal degradation. Regulates neuronal apoptosis via modulation of LRP8/APOER2 levels and related anti-apoptotic signaling pathways. |
| Subellular location Cytoplasm. Secreted. Endosome. Lysosome. Cell surface. Endoplasmic reticulum. Golgi apparatus. Note=Autocatalytic cleavage is required to transport it from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and for the secretion of the mature protein. Localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum in the absence of LDLR and co-localizes to the cell surface and to the endosomes/lysosomes in the presence of LDLR. The sorting to the cell surface and endosomes is required in order to fully promote LDLR degradation (By similarity). |
| Tissues Hepatocytes, kidney mesenchymal cells, intestinal ileum, colon epithelia and embryonic brain telencephalon neurons. |
| Structure Monomer. Can self-associate to form dimers and higher multimers which may have increased LDLR degrading activity. The precursor protein but not the mature protein may form multimers. Interacts with APOB, VLDLR, LRP8/APOER2 and BACE1. The full-length immature form (pro-PCSK9) interacts with SCNN1A, SCNN1B and SCNN1G. The pro-PCSK9 form (via C-terminal domain) interacts with LDLR. Interacts (via the C-terminal domain) with ANXA2 (via repeat Annexin 1); the interaction inhibits the degradation of LDLR. |
| Post-translational modification Cleavage by furin and PCSK5 generates a truncated inactive protein that is unable to induce LDLR degradation.; Undergoes autocatalytic cleavage in the endoplasmic reticulum to release the propeptide from the N-terminus and the cleavage of the propeptide is strictly required for its maturation and activation. The cleaved propeptide however remains associated with the catalytic domain through non-covalent interactions, preventing potential substrates from accessing its active site. As a result, it is secreted from cells as a propeptide-containing, enzymatically inactive protein (By similarity).; Phosphorylation protects the propeptide against proteolysis. |
| Domain Th |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q80W65 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||