| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | NP_001003032 |
| express system | E.coli |
| product tag | N-His |
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC |
| background | The cAMP-dependent protein kinase PKA is a well-characterized member of the serine-threonine protein AGC kinase family and is the effector kinase of cAMP signaling. As such, PKA is involved in the control of a wide variety of cellular processes including metabolism, cell growth, gene expression and apoptosis. cAMP-dependent PKA signaling pathways play important roles during infection and virulence of various pathogens. Since fluxes in cAMP are involved in multiple intracellular functions, a variety of different pathological infectious processes can be affected by PKA signaling pathways. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 41.51 kDa same as Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Canine PKA/PRKACA Protein 3099
$270.00 – $900.00
Summary
- Expression: E.coli
- Pure: Yes (HPLC)
- Amino Acid Range: Gly2-Phe350
Canine PKA/PRKACA Protein 3099
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and liquid |
| Form Liquid |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped with dry ice. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| The cAMP-dependent protein kinase PKA is a well-characterized member of the serine-threonine protein AGC kinase family and is the effector kinase of cAMP signaling. As such, PKA is involved in the control of a wide variety of cellular processes including metabolism, cell growth, gene expression and apoptosis. cAMP-dependent PKA signaling pathways play important roles during infection and virulence of various pathogens. Since fluxes in cAMP are involved in multiple intracellular functions, a variety of different pathological infectious processes can be affected by PKA signaling pathways. |
| Protein names cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PKA C-alpha) (EC 2.7.11.11) |
| Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, cAMP subfamily |
| Mass 40590Da |
| Function Phosphorylates a large number of substrates in the cytoplasm and the nucleus (PubMed:15642694, PubMed:15905176, PubMed:16387847, PubMed:17333334, PubMed:17565987, PubMed:17693412, PubMed:18836454, PubMed:19949837, PubMed:20356841, PubMed:21085490, PubMed:21514275, PubMed:21812984, PubMed:31112131). Phosphorylates CDC25B, ABL1, NFKB1, CLDN3, PSMC5/RPT6, PJA2, RYR2, RORA, SOX9 and VASP (PubMed:15642694, PubMed:15905176, PubMed:16387847, PubMed:17333334, PubMed:17565987, PubMed:17693412, PubMed:18836454, PubMed:19949837, PubMed:20356841, PubMed:21085490, PubMed:21514275, PubMed:21812984). Regulates the abundance of compartmentalized pools of its regulatory subunits through phosphorylation of PJA2 which binds and ubiquitinates these subunits, leading to their subsequent proteolysis (PubMed:21423175). RORA is activated by phosphorylation (PubMed:21514275). Required for glucose-mediated adipogenic differentiation increase and osteogenic differentiation inhibition from osteoblasts (PubMed:19949837). Involved in chondrogenesis by mediating phosphorylation of SOX9 (By similarity). Involved in the regulation of platelets in response to thrombin and collagen; maintains circulating platelets in a resting state by phosphorylating proteins in numerous platelet inhibitory pathways when in complex with NF-kappa-B (NFKB1 and NFKB2) and I-kappa-B-alpha (NFKBIA), but thrombin and collagen disrupt these complexes and free active PRKACA stimulates platelets and leads to platelet aggregation by phosphorylating VASP (PubMed:15642694, PubMed:20356841). Prevents the antiproliferative and anti-invasive effects of alpha-difluoromethylornithine in breast cancer cells when activated (PubMed:17333334). RYR2 channel activity is potentiated by phosphorylation in presence of luminal Ca(2+), leading to reduced amplitude and increased frequency of store overload-induced Ca(2+) release (SOICR) characterized by an increased rate of Ca(2+) release and propagation velocity of spontaneous Ca(2+) waves, despite reduced wave amplitude and resting cytosolic Ca(2+) (PubMed:17693412). PSMC5/RPT6 activation by phosphorylation stimulates proteasome (PubMed:17565987). Negatively regulates tight junctions (TJs) in ovarian cancer cells via CLDN3 phosphorylation (PubMed:15905176). NFKB1 phosphorylation promotes NF-kappa-B p50-p50 DNA binding (PubMed:15642694). Required for phosphorylation of GLI transcription factors which inhibits them and prevents transcriptional activation of Hedgehog signaling pathway target genes (By similarity). GLI transcription factor phosphorylation is inhibited by interaction of PRKACA with SMO which sequesters PRKACA at the cell membrane (By similarity). Involved in embryonic development by down-regulating the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway that determines embryo pattern formation and morphogenesis most probably through the regulation of OFD1 in ciliogenesis (PubMed:33934390). Prevents meiosis resumption in prophase-arrested oocytes via CDC25B inactivation by phosphorylation (By similarity). May also regulate rapid eye movement (REM) sleep in the pedunculopontine tegmental (PPT) (By similarity). Phosphorylates APOBEC3G and AICDA (PubMed:16387847, PubMed:18836454). Phosphorylates HSF1; this phosphorylation promotes HSF1 nuclear localization and transcriptional activity upon heat shock (PubMed:21085490). Acts as a negative regulator of mTORC1 by mediating phosphorylation of RPTOR (PubMed:31112131). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05132, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P27791, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15642694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15905176, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16387847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17333334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17565987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17693412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18836454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19949837, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20356841, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21085490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21423175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21514275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21812984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31112131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33934390}.; [Isoform 2]: Phosphorylates and activates ABL1 in sperm flagellum to promote spermatozoa capacitation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05132}. |
| Catalytic activity CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=ATP + L-seryl-[protein] = ADP + H(+) + O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein]; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:17989, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:9863, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11604, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:29999, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:83421, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.11.11; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:21812984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31112131}; CATALYTIC ACTIVITY: Reaction=ATP + L-threonyl-[protein] = ADP + H(+) + O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein]; Xref=Rhea:RHEA:46608, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11060, Rhea:RHEA-COMP:11605, ChEBI:CHEBI:15378, ChEBI:CHEBI:30013, ChEBI:CHEBI:30616, ChEBI:CHEBI:61977, ChEBI:CHEBI:456216; EC=2.7.11.11; Evidence={ECO:0000269|PubMed:21812984}; |
| Subellular location Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21085490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21423175}. Cell membrane {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19210988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21423175}. Membrane {ECO:0000305}; Lipid-anchor {ECO:0000305}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21085490}. Mitochondrion {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05132}. Note=Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (PubMed:21085490). Recruited to the cell membrane through interaction with SMO (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05132, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21085490}.; [Isoform 2]: Cell projection, cilium, flagellum {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10906071}. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, acrosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05132}. Note=Expressed in the midpiece region of the sperm flagellum (PubMed:10906071). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardless of the capacitation status of the sperm (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05132, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10906071}. |
| Tissues Isoform 1 is ubiquitous. Isoform 2 is sperm-specific and is enriched in pachytene spermatocytes but is not detected in round spermatids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10906071, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21812984}. |
| Structure A number of inactive tetrameric holoenzymes are produced by the combination of homo- or heterodimers of the different regulatory subunits associated with two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. The cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit binds PJA2. Both isoforms 1 and 2 forms activate cAMP-sensitive PKAI and PKAII holoenzymes by interacting with regulatory subunit (R) of PKA, PRKAR1A/PKR1 and PRKAR2A/PKR2, respectively. Interacts with PRKAR1A and PRKAR2B (PubMed:33058759). Interacts with NFKB1, NFKB2 and NFKBIA in platelets; these interactions are disrupted by thrombin and collagen. Binds to ABL1 in spermatozoa and with CDC25B in oocytes. Interacts with APOBEC3G and AICDA. Interacts with RAB13; downstream effector of RAB13 involved in tight junction assembly. Found in a complex at least composed of MROH2B, PRKACA isoform 2 and TCP11 (By similarity). Interacts with MROH2B (By similarity). Isoform 2 interacts with TCP11 (By similarity). Interacts with HSF1 (PubMed:21085490). Interacts with TBC1D31; in regulation of OFD1 (PubMed:33934390). Interacts in free form with SMO (via C-terminus); the interaction leads to sequestration of PRKACA at the membrane, preventing PRKACA-mediated phosphorylation of GLI transcription factors (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05132, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15096524, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16387847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18836454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20356841, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20732331, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21085490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21774789, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21812984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33058759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33934390}. |
| Post-translational modification Autophosphorylated. Phosphorylation is enhanced by vitamin K(2) (PubMed:12372837, PubMed:17909264). Phosphorylated on threonine and serine residues. Phosphorylation on Thr-198 is required for full activity (PubMed:16765046, PubMed:20137943, PubMed:20481595, PubMed:20732331, PubMed:21774789, Ref.43). Phosphorylated at Tyr-331 by activated receptor tyrosine kinases EGFR and PDGFR; this increases catalytic efficiency (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05132, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12372837, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16765046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17909264, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20137943, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20481595, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20732331, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21774789, ECO:0000269|Ref.43}.; Asn-3 is partially deaminated to Asp-3 giving rise to 2 major isoelectric variants, called CB and CA respectively. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05132}.; When myristoylated, Ser-11 is autophosphorylated probably in conjunction with deamidation of Asn-3. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05132}. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P17612 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
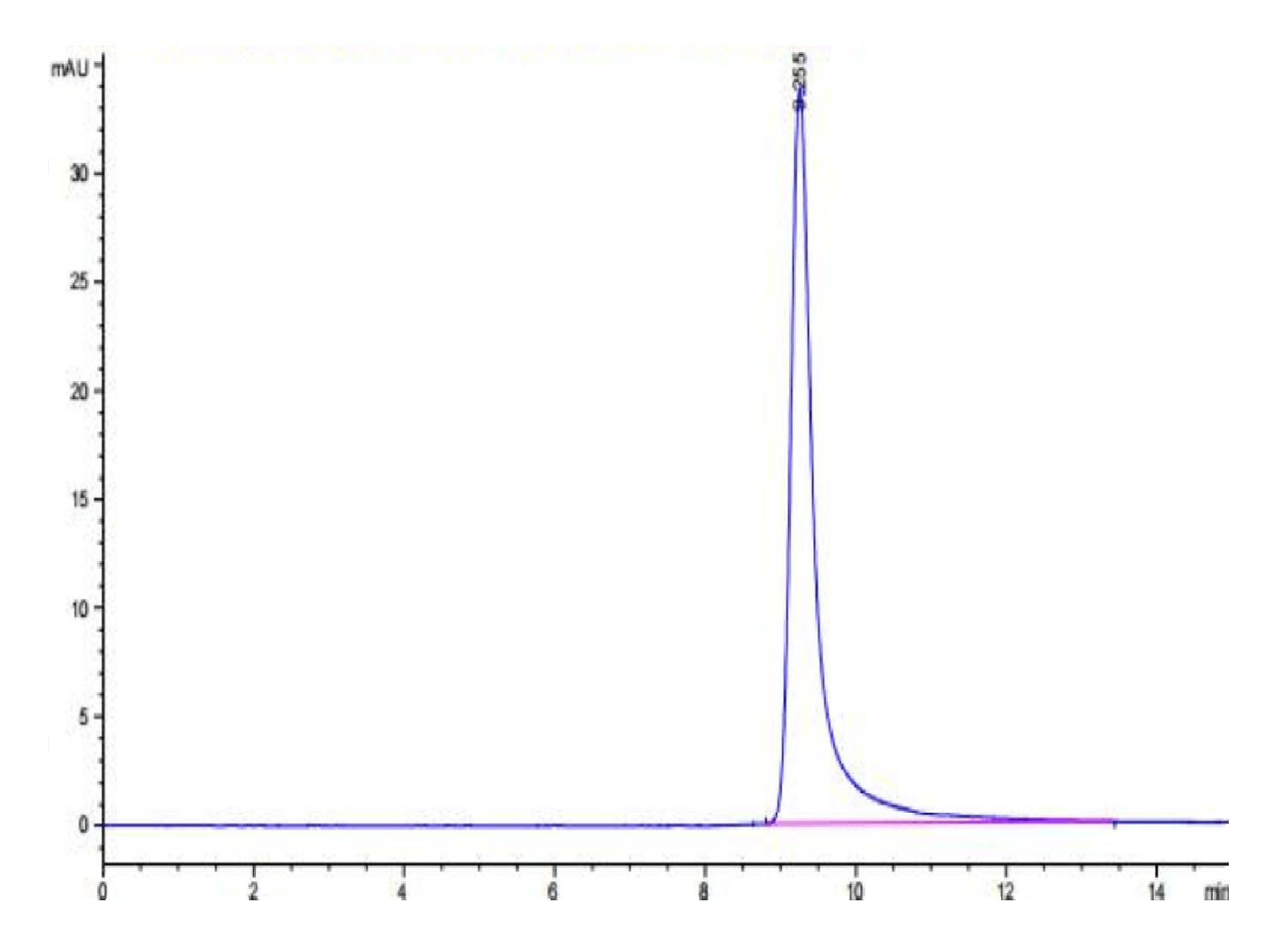 |
| The purity of Canine PKA is greater than 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC. |
 |
| Canine PKA on Tris-Bis PAGE under reduced condition. The purity is greater than 95%. |
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||














