| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His-Avi |
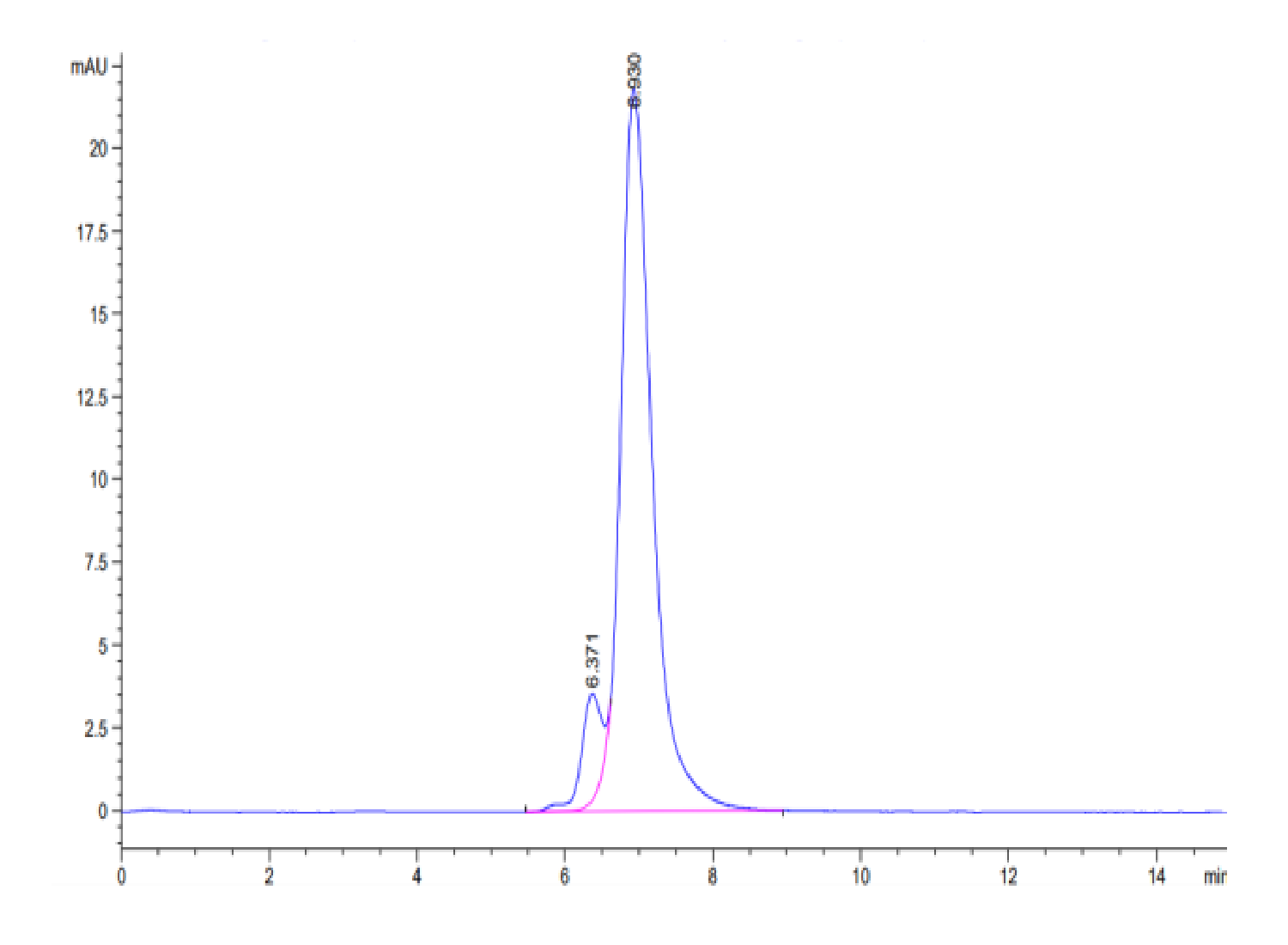
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 90% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Integrin alpha 5/ beta 1, also known as VLA-5, is a widely expressed non-covalent heterodimer of a 160 kDa alpha 5 and a 130 kDa beta 1 Integrin subunit.Alpha 5/ beta 1 is up‑regulated on tumor vasculature and promotes angiogenesis. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 111.8 kDa (ITGA5)&83.2 kDa (ITGB1). Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 110-140 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Biotinylated Human Integrin alpha 5 beta 1 (ITGA5&ITGB1) Heterodimer Protein 3064
$600.00 – $2,000.00
Summary
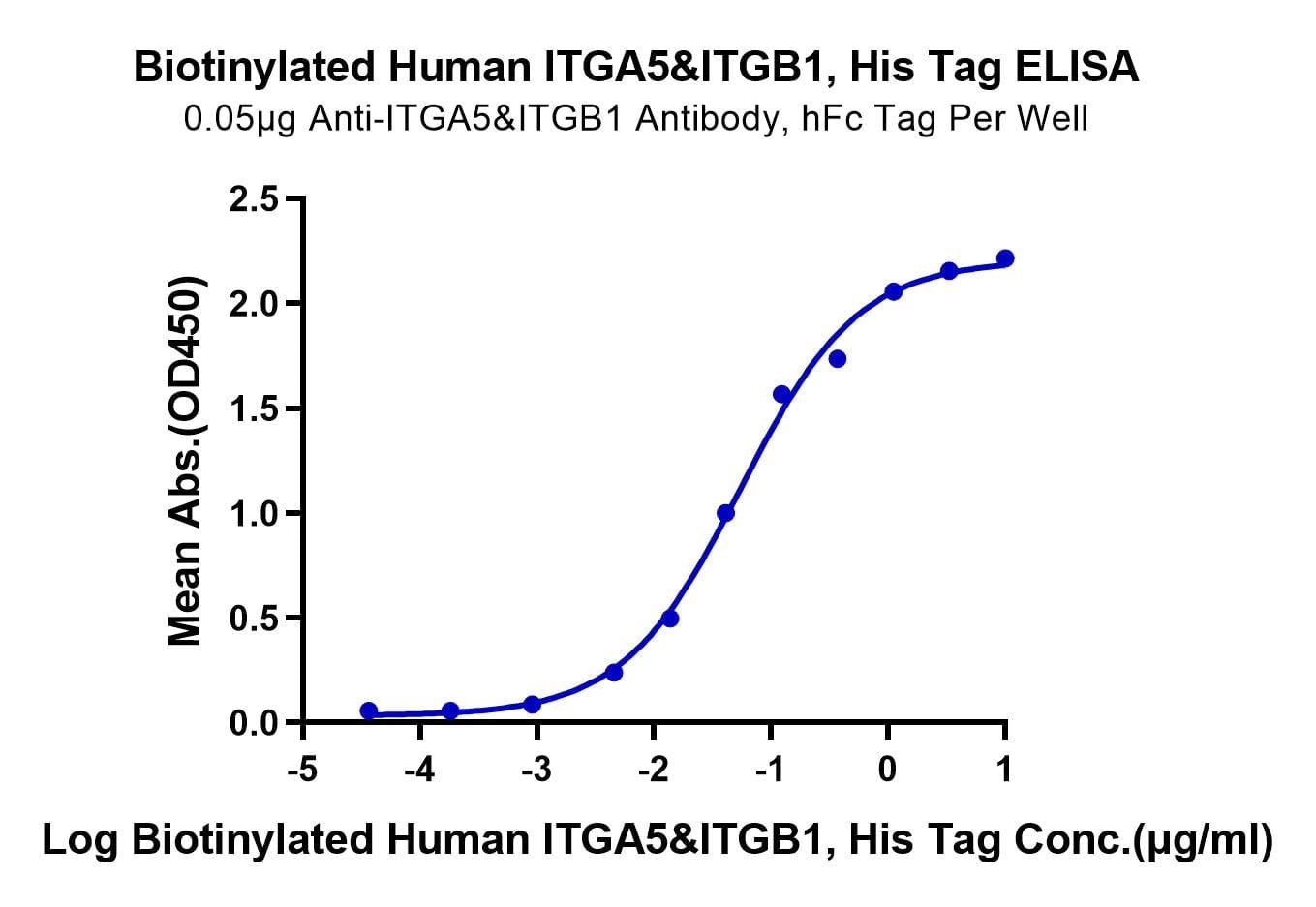
- Expression: HEK293
- Functional: Yes (ELISA)
- Amino Acid Range: Phe42-Tyr995(ITGA5)acidic tail & Gln21-Asp728(ITGB1)basic tail
Biotinylated Human Integrin alpha 5 beta 1 (ITGA5&ITGB1) Heterodimer Protein 3064
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Integrin alpha 5/ beta 1, also known as VLA-5, is a widely expressed non-covalent heterodimer of a 160 kDa alpha 5 and a 130 kDa beta 1 Integrin subunit.Alpha 5/ beta 1 is up-regulated on tumor vasculature and promotes angiogenesis. |
| Protein names Integrin alpha-5 (CD49 antigen-like family member E) (Fibronectin receptor subunit alpha) (Integrin alpha-F) (VLA-5) (CD antigen CD49e) [Cleaved into: Integrin alpha-5 heavy chain; Integrin alpha-5 light chain] |
| Gene names ITGA5,ITGA5 FNRA |
| Protein family Integrin alpha chain family |
| Mass 9606Da |
| Function Integrin alpha-5/beta-1 (ITGA5:ITGB1) is a receptor for fibronectin and fibrinogen. It recognizes the sequence R-G-D in its ligands. ITGA5:ITGB1 binds to PLA2G2A via a site (site 2) which is distinct from the classical ligand-binding site (site 1) and this induces integrin conformational changes and enhanced ligand binding to site 1 (PubMed:18635536, PubMed:25398877). ITGA5:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for fibrillin-1 (FBN1) and mediates R-G-D-dependent cell adhesion to FBN1 (PubMed:12807887, PubMed:17158881). ITGA5:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for fibronectin (FN1) and mediates R-G-D-dependent cell adhesion to FN1 (PubMed:33962943). ITGA5:ITGB1 is a receptor for IL1B and binding is essential for IL1B signaling (PubMed:29030430). ITGA5:ITGB3 is a receptor for soluble CD40LG and is required for CD40/CD40LG signaling (PubMed:31331973).; (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA5:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for Human metapneumovirus.; (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA2:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for Human parvovirus B19.; (Microbial infection) In case of HIV-1 infection, the interaction with extracellular viral Tat protein seems to enhance angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions. |
| Catalytic activity BINDING 262; /ligand="a protein"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:16541"; /ligand_part="L-arginine residue"; /ligand_part_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29965"; /ligand_part_note="Arg of R-G-D sequence recognized in fibronectin and fibrinogen"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:22451694"; BINDING 269; /ligand="a protein"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:16541"; /ligand_part="L-arginine residue"; /ligand_part_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29965"; /ligand_part_note="Arg of R-G-D sequence recognized in fibronectin and fibrinogen"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:22451694"; BINDING 280; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 282; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 284; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 286; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 288; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 334; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 336; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 338; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 340; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 342; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 401; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="3"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 403; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="3"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 405; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="3"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 407; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="3"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 409; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="3"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 465; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="4"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 467; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="4"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 469; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="4"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 471; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="4"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL"; BINDING 473; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="4"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:33962943, ECO:0000312|PDB:7NXD, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI3, ECO:0007744|PDB:3VI4, ECO:0007744|PDB:7NWL" |
| Subellular location Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell junction, focal adhesion . |
| Tissues Expressed in placenta (at protein level). |
| Structure Heterodimer of an alpha and a beta subunit. The alpha subunit is composed of a heavy and a light chain linked by a disulfide bond. ITGA5/Alpha-5 associates with ITGB1/beta-1 (PubMed:33962943). Interacts with NISCH (PubMed:11912194). Interacts with HPS5 (PubMed:10094488). Interacts with RAB21 and COMP. Interacts with CIB1. ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with CCN3. ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with FBN1 (PubMed:12807887, PubMed:17158881). ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with IL1B (PubMed:29030430). ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with ACE2 (PubMed:33102950). ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with SELP (PubMed:37184585). Interacts with ANGPT2 (PubMed:32908006).; (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with human metapneumovirus fusion protein.; (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with human parvovirus B19 capsid proteins.; (Microbial infection) Interacts with HIV-1 Tat.; (Microbial infection) ITGA5:ITGB1 interacts with SARS coronavirus-2/SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. |
| Post-translational modification Proteolytic cleavage by PCSK5 mediates activation of the precursor. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: P08648 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||