| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | Q15465 |
| express system | E.coli |
| product tag | No Tag |
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | Sonic hedgehog (Shh) is a secreted protein with important roles in mammalian embryogenesis. During tooth development, Shh is primarily expressed in the dental epithelium, from initiation to the root formation stages. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 19.79 kDa kDa. The protein migrates to 23-25 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 0.05EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Human Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) Protein 2919
$270.00 – $900.00
Summary
- Expression: E.coli
- Pure: Yes (HPLC)
- Amino Acid Range: Cys24-Gly197
Human Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) Protein 2919
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Sonic hedgehog (Shh) is a secreted protein with important roles in mammalian embryogenesis. During tooth development, Shh is primarily expressed in the dental epithelium, from initiation to the root formation stages. |
| Protein names Sonic hedgehog protein (SHH) (EC 3.1.-.-) (HHG-1) (Shh unprocessed N-terminal signaling and C-terminal autoprocessing domains) (ShhNC) [Cleaved into: Sonic hedgehog protein N-product (ShhN) (Shh N-terminal processed signaling domains) (ShhNp)] |
| Gene names SHH,SHH |
| Protein family Hedgehog family |
| Mass 9606Da |
| Function [Sonic hedgehog protein]: The C-terminal part of the sonic hedgehog protein precursor displays an autoproteolysis and a cholesterol transferase activity (By similarity). Both activities result in the cleavage of the full-length protein into two parts (ShhN and ShhC) followed by the covalent attachment of a cholesterol moiety to the C-terminal of the newly generated ShhN (By similarity). Both activities occur in the reticulum endoplasmic (By similarity). Once cleaved, ShhC is degraded in the endoplasmic reticulum (By similarity).; [Sonic hedgehog protein N-product]: The dually lipidated sonic hedgehog protein N-product (ShhNp) is a morphogen which is essential for a variety of patterning events during development. Induces ventral cell fate in the neural tube and somites (PubMed:24863049). Involved in the patterning of the anterior-posterior axis of the developing limb bud (By similarity). Essential for axon guidance (By similarity). Binds to the patched (PTCH1) receptor, which functions in association with smoothened (SMO), to activate the transcription of target genes (PubMed:10753901). In the absence of SHH, PTCH1 represses the constitutive signaling activity of SMO (PubMed:10753901). |
| Catalytic activity BINDING 89; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW"; BINDING 90; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW"; BINDING 90; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW"; BINDING 95; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW"; BINDING 125; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW"; BINDING 126; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="1"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW"; BINDING 126; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW"; BINDING 129; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW"; BINDING 131; /ligand="Ca(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29108"; /ligand_label="2"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW"; BINDING 140; /ligand="Zn(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29105"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:10753901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3M1N, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW"; BINDING 147; /ligand="Zn(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29105"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:10753901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3M1N, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW"; BINDING 182; /ligand="Zn(2+)"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:29105"; /evidence="ECO:0000269|PubMed:10753901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504762, ECO:0007744|PDB:3M1N, ECO:0007744|PDB:3MXW" |
| Subellular location [Sonic hedgehog protein]: Endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Golgi apparatus membrane. Secreted. Note=Co-localizes with HHAT in the ER and Golgi membrane.; [Sonic hedgehog protein N-product]: Cell membrane ; Lipid-anchor. Note=The dual-lipidated sonic hedgehog protein N-product (ShhNp) is firmly tethered to the cell membrane where it forms multimers (PubMed:24522195). Further solubilization and release from the cell surface seem to be achieved through different mechanisms, including the interaction with DISP1 and SCUBE2, movement by lipoprotein particles, transport by cellular extensions called cytonemes or by the proteolytic removal of both terminal lipidated peptides (PubMed:24522195, PubMed:26875496). |
| Structure [Sonic hedgehog protein N-product]: Multimer.; Interacts with HHATL/GUP1 which negatively regulates HHAT-mediated palmitoylation of the SHH N-terminus (By similarity). Interacts with BOC and CDON (By similarity). Interacts with HHIP (PubMed:19561609). Interacts with DISP1 via its cholesterol anchor (PubMed:22677548, PubMed:22902404). Interacts with SCUBE2 (PubMed:22677548, PubMed:24522195). Interacts with glypican GPC3 (By similarity). |
| Post-translational modification [Sonic hedgehog protein]: The C-terminal domain displays an autoproteolysis activity and a cholesterol transferase activity (By similarity). Both activities result in the cleavage of the full-length protein and covalent attachment of a cholesterol moiety to the C-terminal of the newly generated N-terminal fragment (ShhN) (By similarity). Cholesterylation is required for the sonic hedgehog protein N-product targeting to lipid rafts and multimerization (PubMed:24522195, PubMed:26875496). ShhN is the active species in both local and long-range signaling, whereas the C-product (ShhC) is degraded in the reticulum endoplasmic (By similarity).; [Sonic hedgehog protein N-product]: N-palmitoylation by HHAT of ShhN is required for sonic hedgehog protein N-product multimerization and full activity (By similarity). It is a prerequisite for the membrane-proximal positioning and the subsequent shedding of this N-terminal peptide (PubMed:24522195).; [Sonic hedgehog protein N-product]: The lipidated N- and C-terminal peptides of ShhNp can be cleaved (shedding) (PubMed:24522195). The N-terminal palmitoylated peptide is cleaved at the Cardin-Weintraub (CW) motif site (PubMed:24522195). The cleavage reduced the interactions with heparan sulfate. The cleavage is enhanced by SCUBE2 (PubMed:23118222, PubMed:24522195). |
| Domain [S |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q15465 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
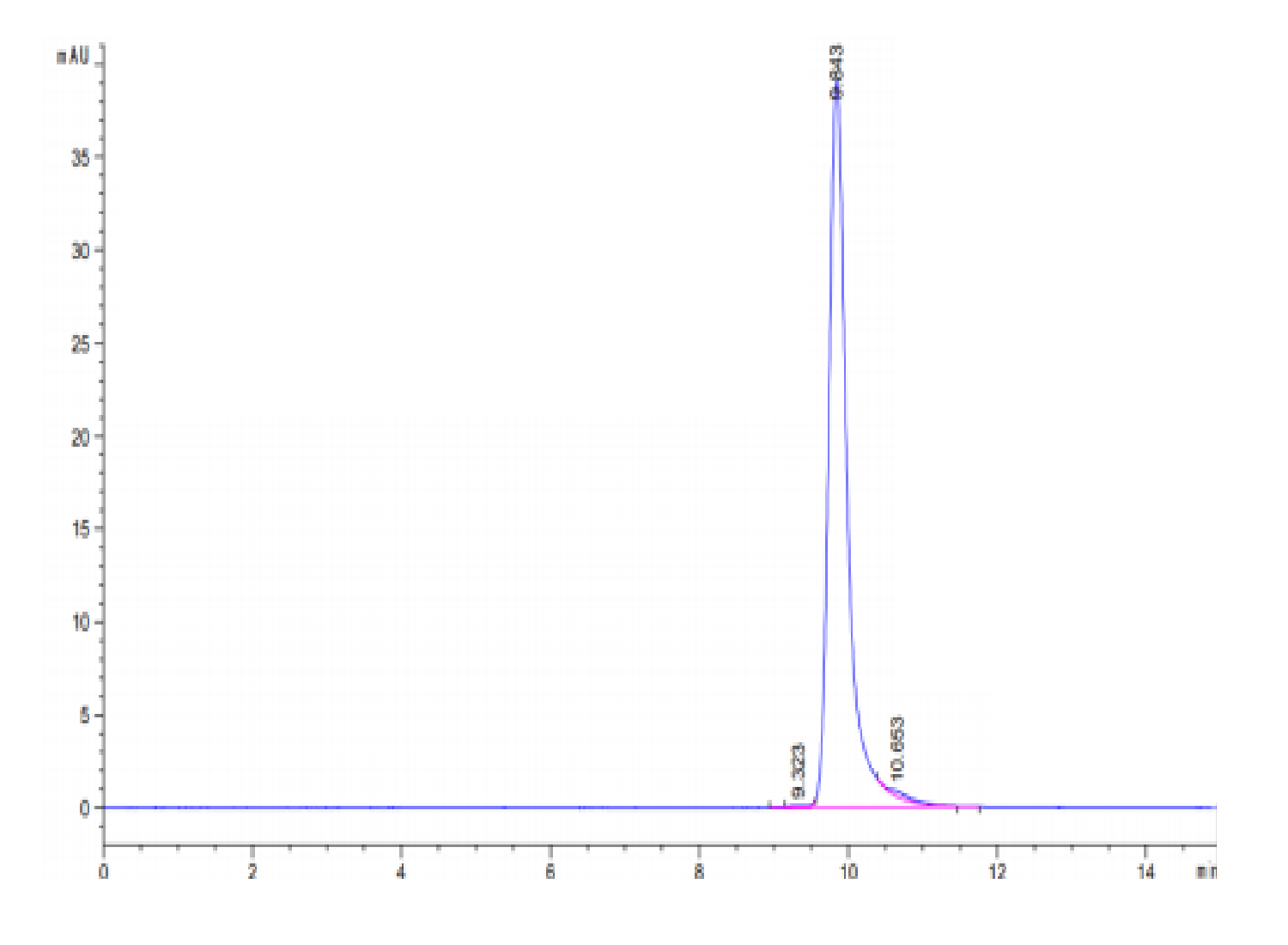 |
| The purity of Human Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) is greater than 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC. |
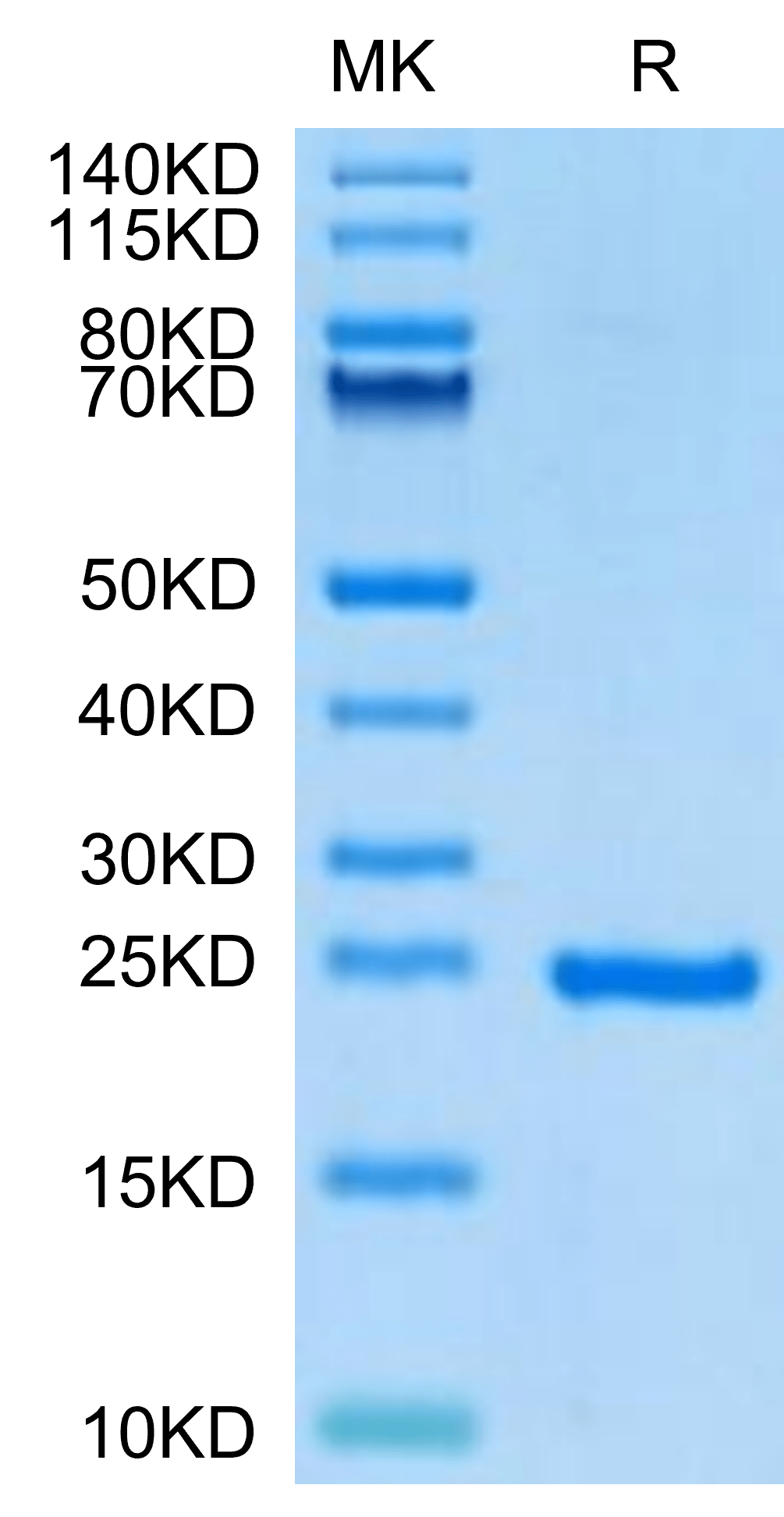 |
| Human Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) on Tris-Bis PAGE under reduced condition. The purity is greater than 95%. |
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||














