| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| accession | Q01279 |
| express system | HEK293 |
| product tag | C-His |
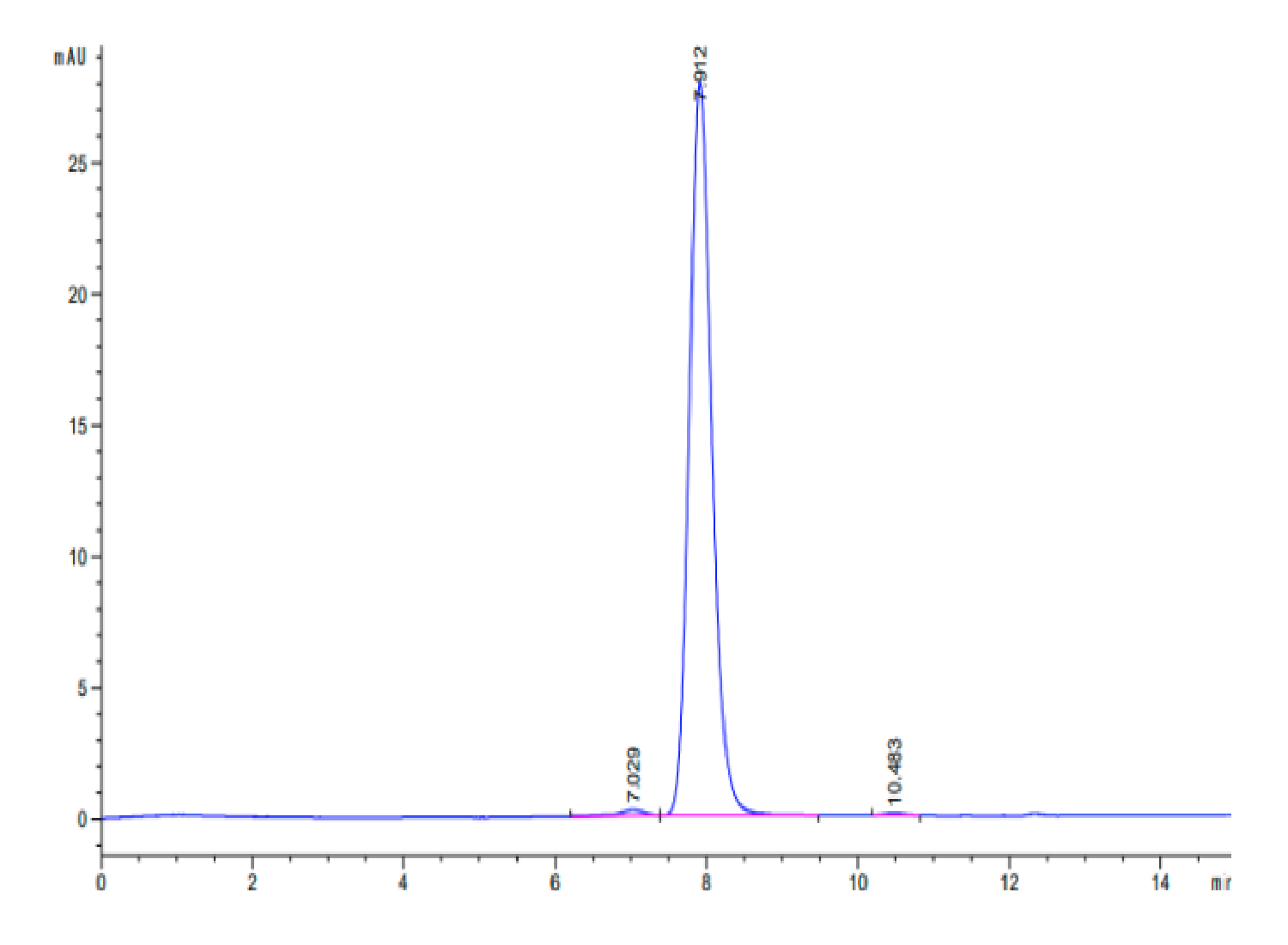
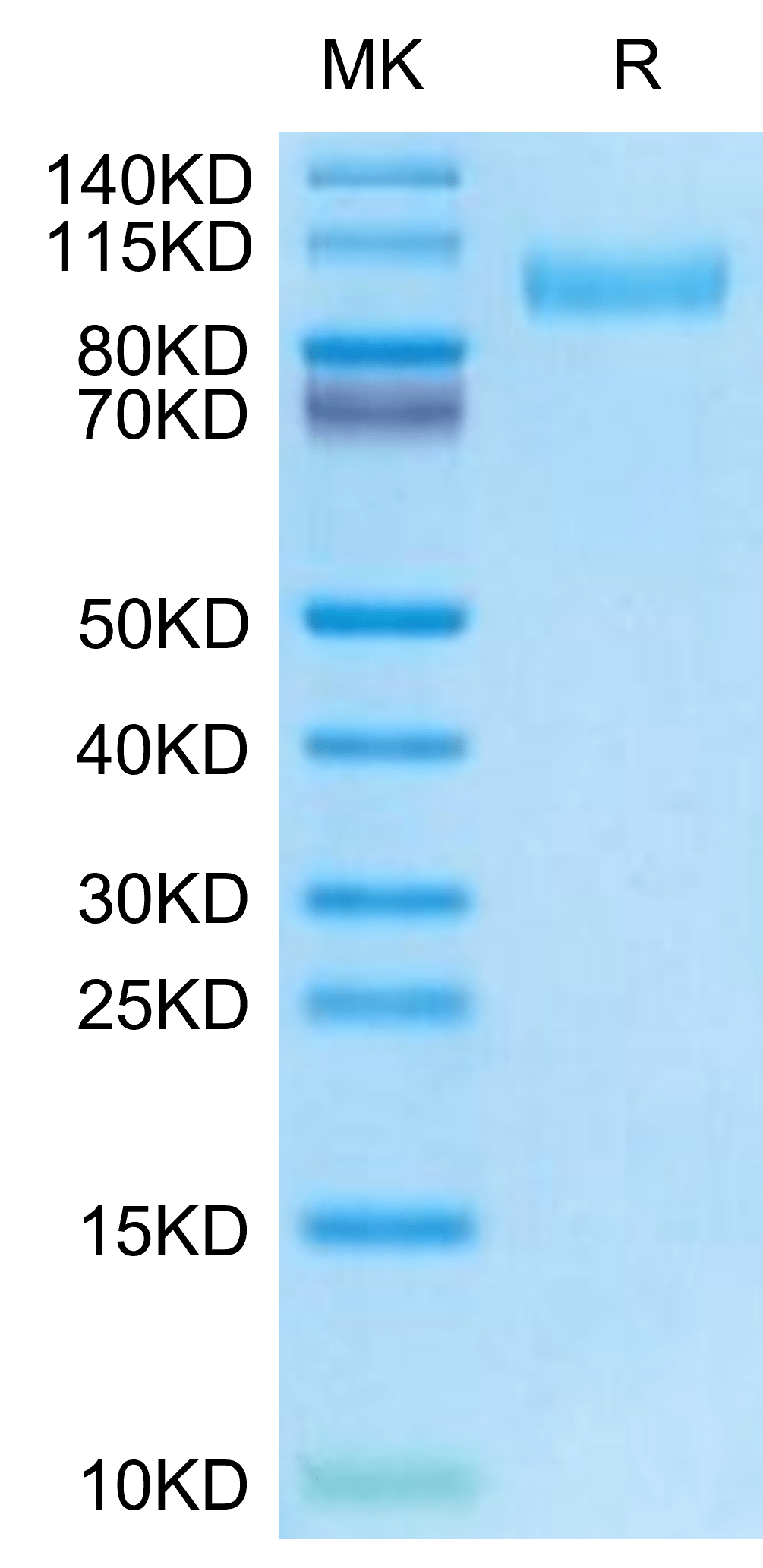
| purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE;> 95% as determined by HPLC |
| background | The epidermal growth factor receptor is a transmembrane protein that is a receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family of extracellular protein ligands. The epidermal growth factor receptor is a member of the ErbB family of receptors, a subfamily of four closely related receptor tyrosine kinases: EGFR, HER2/neu, Her 3 and Her 4. Receptor tyrosine kinase binding ligands of the EGF family and activating several signaling cascades to convert extracellular cues into appropriate cellular responses. |
| molecular weight | The protein has a predicted MW of 70.40 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 90-110 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| available size | 100 µg, 500 µg |
| endotoxin | Less than 1EU per μg by the LAL method. |
Mouse EGFR/HER1 Protein 2897
$270.00 – $900.00
Summary
- Expression: HEK293
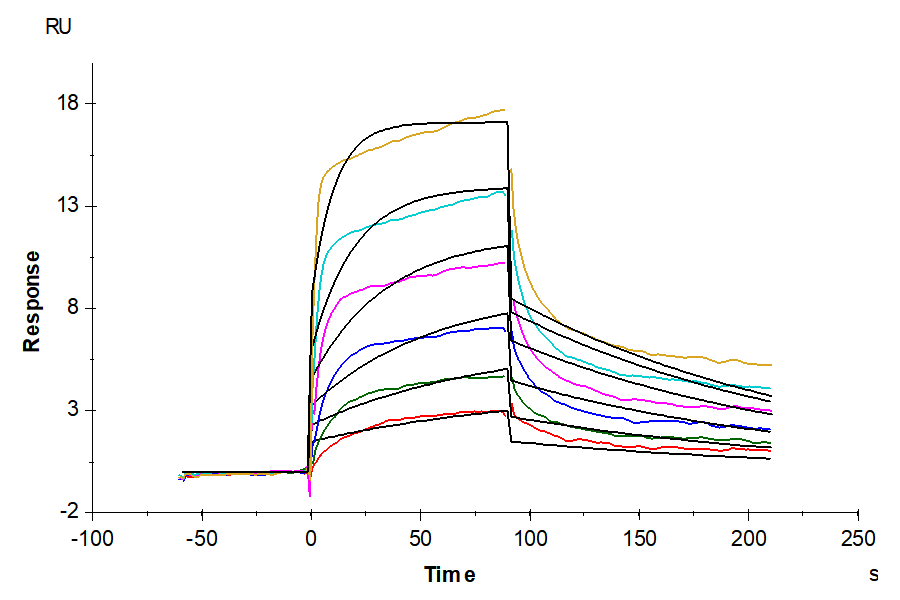
- Binding assay: Yes (SPR)
- Amino Acid Range: Leu25-Ser647
Mouse EGFR/HER1 Protein 2897
| protein |
|---|
| Size and concentration 100, 500µg and lyophilized |
| Form Lyophilized |
| Storage Instructions Valid for 12 months from date of receipt when stored at -80°C. Recommend to aliquot the protein into smaller quantities for optimal storage. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage buffer Shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Purity > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE |
| target relevance |
|---|
| The epidermal growth factor receptor is a transmembrane protein that is a receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family of extracellular protein ligands. The epidermal growth factor receptor is a member of the ErbB family of receptors, a subfamily of four closely related receptor tyrosine kinases: EGFR, HER2/neu, Her 3 and Her 4. Receptor tyrosine kinase binding ligands of the EGF family and activating several signaling cascades to convert extracellular cues into appropriate cellular responses. |
| Protein names Epidermal growth factor receptor (EC 2.7.10.1) |
| Gene names Egfr,Egfr |
| Protein family Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, EGF receptor subfamily |
| Mass 10090Da |
| Function Receptor tyrosine kinase binding ligands of the EGF family and activating several signaling cascades to convert extracellular cues into appropriate cellular responses (PubMed:8404850). Known ligands include EGF, TGFA/TGF-alpha, AREG, epigen/EPGN, BTC/betacellulin, epiregulin/EREG and HBEGF/heparin-binding EGF. Ligand binding triggers receptor homo- and/or heterodimerization and autophosphorylation on key cytoplasmic residues. The phosphorylated receptor recruits adapter proteins like GRB2 which in turn activates complex downstream signaling cascades. Activates at least 4 major downstream signaling cascades including the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK, PI3 kinase-AKT, PLCgamma-PKC and STATs modules. May also activate the NF-kappa-B signaling cascade. Also directly phosphorylates other proteins like RGS16, activating its GTPase activity and probably coupling the EGF receptor signaling to the G protein-coupled receptor signaling. Also phosphorylates MUC1 and increases its interaction with SRC and CTNNB1/beta-catenin (By similarity). Positively regulates cell migration via interaction with CCDC88A/GIV which retains EGFR at the cell membrane following ligand stimulation, promoting EGFR signaling which triggers cell migration (By similarity). Plays a role in enhancing learning and memory performance (PubMed:20639532). Plays a role in mammalian pain signaling (long-lasting hypersensitivity) (PubMed:35131940). |
| Catalytic activity BINDING 720..728; /ligand="ATP"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:30616"; /evidence="ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00159"; BINDING 747; /ligand="ATP"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:30616"; /evidence="ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00159"; BINDING 792..793; /ligand="ATP"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:30616"; /evidence="ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00159"; BINDING 857; /ligand="ATP"; /ligand_id="ChEBI:CHEBI:30616"; /evidence="ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00159" |
| Subellular location Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Golgi apparatus membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Nucleus membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Endosome. Endosome membrane. Nucleus. Note=In response to EGF, translocated from the cell membrane to the nucleus via Golgi and ER. Endocytosed upon activation by ligand. Colocalized with GPER1 in the nucleus of estrogen agonist-induced cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF). |
| Structure Binding of the ligand triggers homo- and/or heterodimerization of the receptor triggering its autophosphorylation. Heterodimer with ERBB2. Forms a complex with CCDC88A/GIV (via SH2-like region) and GNAI3 which leads to enhanced EGFR signaling and triggering of cell migration; binding of CCDC88A requires autophosphorylation of the EGFR C-terminal region, and ligand stimulation is required for recruitment of GNAI3 to the complex (By similarity). Interacts with ERRFI1; inhibits dimerization of the kinase domain and autophosphorylation. Part of a complex with ERBB2 and either PIK3C2A or PIK3C2B. Interacts with GRB2; an adapter protein coupling the receptor to downstream signaling pathways. Interacts with GAB2; involved in signaling downstream of EGFR. Interacts with STAT3; mediates EGFR downstream signaling in cell proliferation. Interacts with RIPK1; involved in NF-kappa-B activation. Interacts (autophosphorylated) with CBL, CBLB and CBLC; involved in EGFR ubiquitination and regulation; interaction with CBL is reduced in the presence of tensin TNS4. Interacts with SOCS5; regulates EGFR degradation through ELOC- and ELOB-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Interacts with PRMT5; methylates EGFR and enhances interaction with PTPN6. Interacts (phosphorylated) with PTPN6; inhibits EGFR-dependent activation of MAPK/ERK. Interacts with COPG1; essential for regulation of EGF-dependent nuclear transport of EGFR by retrograde trafficking from the Golgi to the ER. Interacts with TNK2; this interaction is dependent on EGF stimulation and kinase activity of EGFR. Interacts with PCNA; positively regulates PCNA. Interacts with PELP1. Interacts with MUC1. Interacts with AP2M1. Interacts with FER. Interacts (via SH2 domains) with GRB2, NCK1 and NCK2. Interacts with EPS8; mediates EPS8 phosphorylation. Interacts with ATXN2. Interacts with GAREM1. Interacts (ubiquitinated) with ANKRD13A/B/D; the interaction is direct and may regulate EGFR internalization after EGF stimulation. Interacts with GPER1; the interaction occurs in an estrogen-dependent manner. Interacts (via C-terminal cytoplasmic kinase domain) with ZPR1 (via zinc fingers). Interacts with RNF115 and RNF126. Interacts with GPRC5A (via its transmembrane domain) (PubMed:25744720). Interacts with FAM83B; positively regulates EGFR inducing its autophosphorylation in absence of stimulation by EGF (By similarity). Interacts with LAPTM4B; positively correlates with EGFR activation (By similarity). Interacts with STX19 (PubMed:16420529). Interacts with CD44 (By similarity). Interacts with PGRMC1; the interaction requires PGRMC1 homodimerization (By similarity). Interacts with PIKFYVE (PubMed:17909029). Interacts with NEU3. Interacts with TRAF4. Interacts with the ant venom OMEGA-myrmeciitoxin(02)-Mg1a (PubMed:35131940). Interacts with CD82; this interaction facilitates ligand-induced endocytosis of the receptor and its subsequent desensitization (By similarity). |
| Post-translational modification Monoubiquitinated and polyubiquitinated upon EGF stimulation; which does not affect tyrosine kinase activity or signaling capacity but may play a role in lysosomal targeting. Polyubiquitin linkage is mainly through 'Lys-63', but linkage through 'Lys-48', 'Lys-11' and 'Lys-29' also occurs. Deubiquitinated by OTUD7B, preventing degradation (By similarity). Ubiquitinated by RNF115 and RNF126. Ubiquitinated by ZNRF1 or CBL at different lysines in response to EGF stimulation; leading to recruitment of the ESCRT machinery and subsequent degradation in the lysosomes (By similarity). Deubiquitinated by UCHL1 leading to the inhibition of its degradation (PubMed:32494592).; Phosphorylated on Tyr residues in response to EGF. Phosphorylation at Ser-697 is partial and occurs only if Thr-695 is phosphorylated. Phosphorylation at Thr-680 and Thr-695 by PRKD1 inhibits EGF-induced MAPK8/JNK1 activation. Dephosphorylation by PTPRJ prevents endocytosis and stabilizes the receptor at the plasma membrane. Autophosphorylation at Tyr-1199 is stimulated by methylation at Arg-1199 and enhances interaction with PTPN6. Autophosphorylation at Tyr-1092 and/or Tyr-1110 recruits STAT3. Dephosphorylated by PTPN1 and PTPN2.; Palmitoylated on Cys residues by ZDHHC20. Palmitoylation inhibits internalization after ligand binding, and increases the persistence of tyrosine-phosphorylated EGFR at the cell membrane. Palmitoylation increases the amplitude and duration of EGFR signaling.; Methylated. Methylation at Arg-1199 by PRMT5 stimulates phosphorylation at Tyr-1197. |
| Target Relevance information above includes information from UniProt accession: Q01279 |
| The UniProt Consortium |
Data
Publications
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||