| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| target | Entero |
| species reactivity | For the detection of enterovirus (Coxsackievirus A, Coxsackievirus B, Echovirus, Poliovirus). |
| applications | RT PCR |
| assay type | direct & qualitative |
| available sizes | 96 tests |
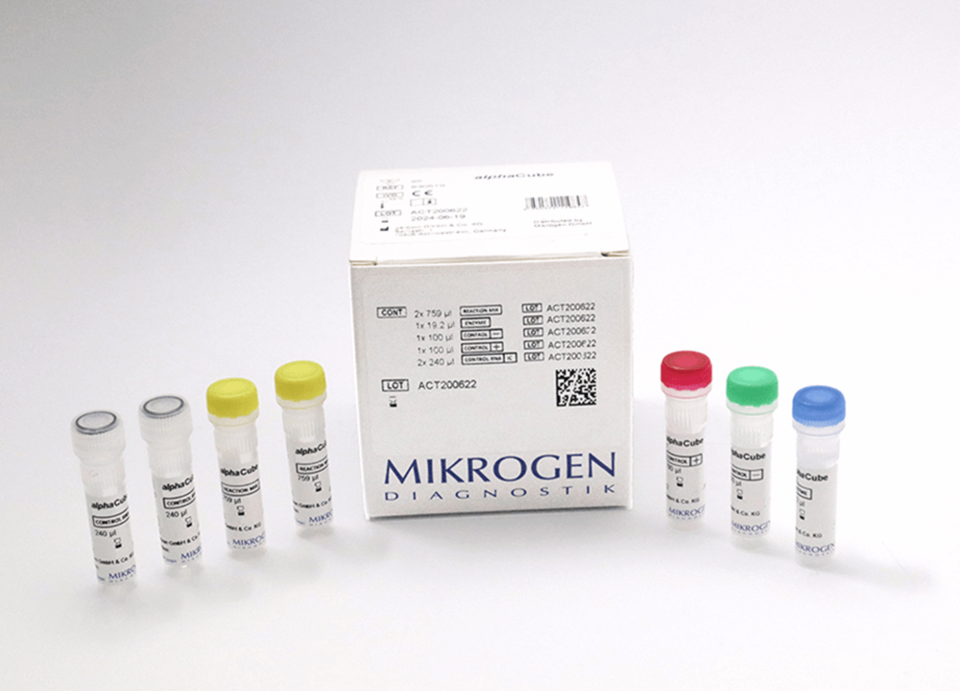
Entero RT-PCR test Mikrogen 830509
$487.00
Summary
- Mikrogen diagnostik RT PCR kit for research use (RUO)
- Direct Coxsackievirus, Echovirus, Poliovirus, Enterovirus detection
- High sensitivity and specificity
- Internal control for monitoring nucleic acid extraction
(RNA/DNA) and real-time PCR inhibition in each reaction - Compatible with most common real-time PCR cyclers & RNA/DNA extraction methods
- 96 tests
Entero RT-PCR test Mikrogen 830509
| kit | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assay type RT PCR | |||||||||||||||
| Research area Infectious Disease | |||||||||||||||
| Sample type whole blood, serum, plasma, urine, tissue, stool, etc., food and environmental samples or from the carrier material | |||||||||||||||
Notes
| |||||||||||||||
Components
| |||||||||||||||
| Storage Store at -20°C. | |||||||||||||||
| Additional information Highly sensitive and specific direct detection of pathogens that can cause tick-borne infections
Applicable to human starting material as well as RNA/DNA from the tick |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Organism Coxsackievirus |
| Protein names Coxsackievirus |
| Structure and strains Coxsackieviruses are a few related enteroviruses that belong to the Picornaviridae family of nonenveloped, linear, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, as well as its genus Enterovirus, which also includes poliovirus and echovirus. Enteroviruses are among the most common and important human pathogens, and ordinarily its members are transmitted by the fecal oral route. Coxsackieviruses share many characteristics with poliovirus. With control of poliovirus infections in much of the world, more attention has been focused on understanding the nonpolio enteroviruses such as coxsackievirus. Coxsackieviruses are among the leading causes of aseptic meningitis (the other usual suspects being echovirus and mumps virus). The entry of coxsackievirus into cells, especially endothelial cells, is mediated by coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor. |
| Detection and diagnosis The demonstration of infection by the detection of specific antibodies generally requires the analysis of serum pairs. A positive result for IgM or IgA combined with rising IgG activity serves as clear evidence of an acute or recent infection. Persisting IgM and IgA antibody levels are frequently observed in chronic infections. |
Data
| No results found |
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| 830509 protocol |
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here. | ||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.