| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 9 × 5 × 2 in |
| target | Bordetella |
| species reactivity | For the detection of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis |
| applications | RT PCR |
| assay type | direct & qualitative |
| available sizes | 96 tests |
Bordetella RT-PCR test Mikrogen 830527
$487.00
Summary
- Mikrogen diagnostik RT PCR kit for research use (RUO)
- Direct Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis detection
- High sensitivity and specificity
- Internal control for monitoring nucleic acid extraction
(RNA/DNA) and real-time PCR inhibition in each reaction - Compatible with most common real-time PCR cyclers & RNA/DNA extraction methods
- 96 tests
Bordetella RT-PCR test Mikrogen 830527
| kit | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assay type RT PCR | |||||||||||||||
| Research area Infectious Disease | |||||||||||||||
| Sample type whole blood, serum, plasma, urine, tissue, stool, etc., food and environmental samples or from the carrier material | |||||||||||||||
Notes
| |||||||||||||||
Components
| |||||||||||||||
| Storage Store at -20°C. | |||||||||||||||
| Additional information Highly sensitive and specific direct detection of pathogens that can cause tick-borne infections
Applicable to human starting material as well as RNA/DNA from the tick |
| target relevance |
|---|
| Organism Bordetella pertussis |
| Protein names Bordetella pertussis |
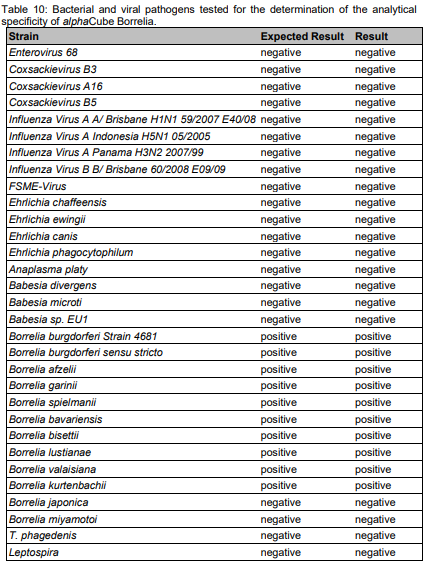
| Structure and strains Bordetella pertussis is a Gram-negative, aerobic, pathogenic, encapsulated coccobacillus of the genus Bordetella, and the causative agent of pertussis or whooping cough. Like B. bronchiseptica, B. pertussis can express a flagellum-like structure, even if it has been historically categorized as a nonmotile bacteria.[1] Its virulence factors include pertussis toxin, adenylate cyclase toxin, filamentous hemagglutinin, pertactin, fimbria, and tracheal cytotoxin. |
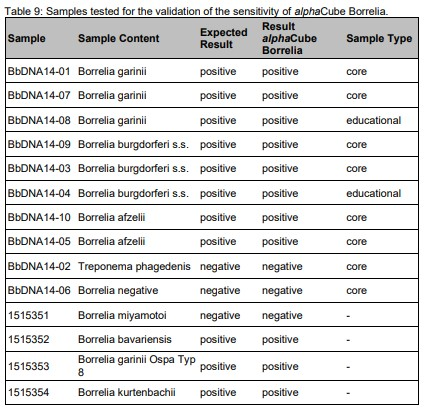
| Detection and diagnosis The ELISA technique is the most commonly chosen method for B. pertussis and B. parapertussis specific antibody determination in serodiagnosis and complements direct antigen detection. In over 90% of cases the IgG and IgA antibody responses are directed against the immunogens PT and FHA. Therefore, the SERION ELISA classic Bordetella pertussis IgG and IgA tests are based on antigen mixtures of PT and FHA. For the detection of IgM antibodies cellular bound lipopolysaccharid has outstanding diagnostic properties. Consequently, a whole-cell antigen preparation of B. pertussis is used in the SERION ELISA classic Bordetella pertussis IgM. |
Data
Publications
| pmid | title | authors | citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| We haven't added any publications to our database yet. | |||
Protocols
| relevant to this product |
|---|
| 830527 protocol |
Documents
| # | ||
|---|---|---|
| Please enter your product and batch number here to retrieve product datasheet, SDS, and QC information. | ||
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.