Introduction
Within the intricate network of our immune system lies a crucial interplay between programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand, programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1). This nuanced partnership is fundamental in maintaining the delicate equilibrium between defense and tolerance. In this blog post, we will explore the molecular nuances of PD-1 and PD-L1, deciphering their interaction and the profound implications it holds for our understanding of health and disease.
The Molecular Dialogue
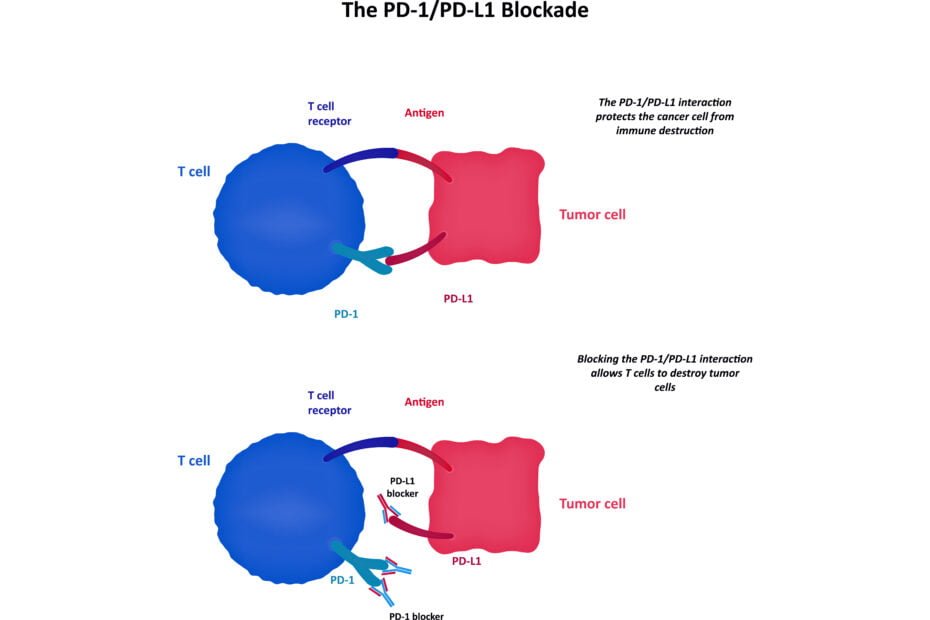
PD-1, situated on the surface of T cells, acts as a pivotal checkpoint in immune responses. Its counterpart, PD-L1, is found on various cells, including cancer and immune cells. The interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1 serves as a molecular conversation that regulates T cell activity. When PD-1 binds with PD-L1, inhibitory signals are transmitted to T cells, acting as a control mechanism to prevent overactive immune responses that might harm healthy tissues.
Implications in Cancer
Beyond its role in immune regulation, the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction is exploited by cancer cells as a means of evading the immune system. Some tumors increase the expression of PD-L1, effectively manipulating this immune checkpoint to evade T cell surveillance. Therapies that target this interaction, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, have revolutionized cancer treatment. By blocking PD-1 or PD-L1, these drugs unleash the immune system, enabling it to mount a robust anti-tumor response and offering a new frontier in cancer therapeutics.
Beyond Cancer: Emerging Roles in Autoimmunity
The influence of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis extends beyond cancer, contributing to autoimmune diseases. In conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, the balance between these molecules is disrupted, leading to uncontrolled immune responses against the body’s own tissues. This understanding opens avenues for developing targeted therapies that can restore balance and alleviate autoimmune symptoms.
Future Perspectives
As our comprehension of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction deepens, researchers are exploring innovative therapeutic approaches. Combination therapies, identification of biomarkers for patient stratification, and a deeper understanding of the molecular dynamics involved offer promise for more effective and personalized treatments. Ongoing research in this field not only advances our understanding of basic immunology but also holds significant potential for the development of novel therapies across a spectrum of diseases.
Conclusion
The interplay between PD-1 and PD-L1 represents a fascinating aspect of our immune system’s intricate tapestry. From the realm of cancer immunotherapy to autoimmune disease management, the multifaceted roles of these molecules continue to be unraveled through dedicated scientific inquiry. As we unveil the complexities of this molecular dialogue, we pave the way for innovative therapeutic interventions that have the potential to redefine the landscape of medicine, providing new avenues for treating a diverse range of conditions.