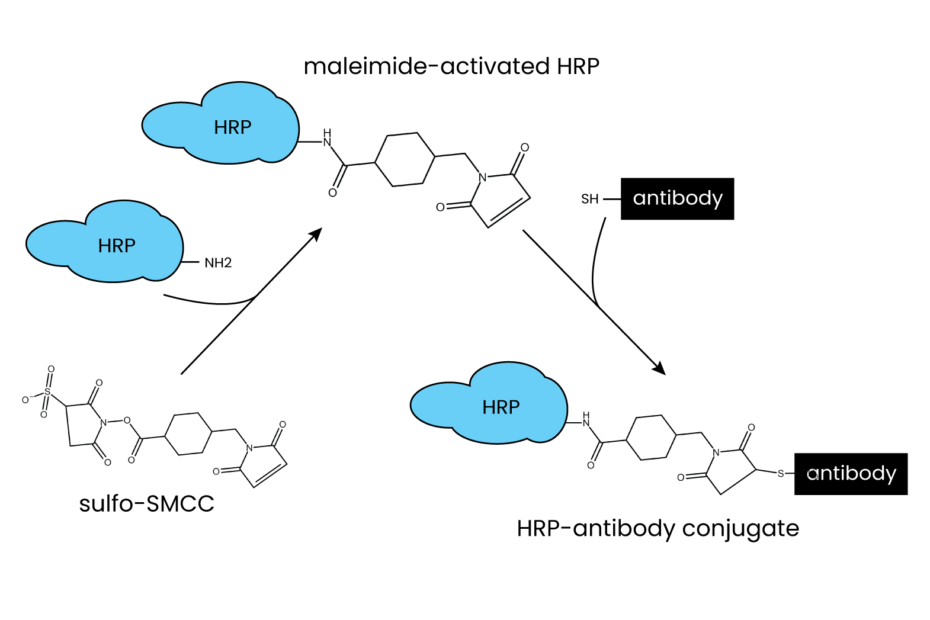
Scientists are continually seeking innovative methods to enhance the specificity and versatility of their reagents. One such technique involves the conjugation of antibodies with enzymes, peptides, or fluorophores, unlocking a plethora of possibilities for diagnostics, therapeutics, and fundamental research. In this blog post, we’ll explore how scientists achieve these conjugations using the Sulfo-SMCC heterobifunctional crosslinking reagent and discuss the remarkable applications enabled by this versatile approach.
The Magic of Sulfo-SMCC
Sulfo-SMCC (sulfosuccinimidyl 4-(N-maleimidomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylate) is a heterobifunctional crosslinking reagent that possesses two distinct reactive groups: a maleimide group and an NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide) ester. These groups play crucial roles in facilitating specific conjugations:
- Maleimide Group: This group reacts selectively with sulfhydryl (-SH) groups present in cysteine residues of proteins, peptides, or other molecules. This specific thiol-maleimide reaction ensures precise and controlled conjugation.
- NHS Ester Group: The NHS ester group readily reacts with primary amines (-NH2) found in the side chains of lysine residues or the N-terminus of proteins and peptides.
Conjugating Antibodies with Enzymes, Peptides, and Fluorophores
The process of conjugating antibodies with enzymes, peptides, or fluorophores using Sulfo-SMCC involves several key steps:
1. Activation: The first step is to activate the Sulfo-SMCC reagent by dissolving it in an appropriate solvent, such as dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), to create a stock solution. This activated reagent is then added to the antibody solution.
2. Reaction with Antibodies: The activated Sulfo-SMCC reacts with sulfhydryl (-SH) groups on the antibody’s cysteine residues. This forms a stable thioether bond, effectively attaching the maleimide group to the antibody.
3. Quenching Unreacted Sulfo-SMCC: Any unreacted Sulfo-SMCC can be quenched by adding a thiol-containing compound, such as DTT (dithiothreitol) or β-mercaptoethanol, which will react with the maleimide group, preventing further crosslinking.
4. Reaction with Target Molecule: The modified antibody with the maleimide group is now ready to react with the target molecule—whether it’s an enzyme, peptide, or fluorophore—containing a thiol or amine group. This reaction forms a stable covalent bond, resulting in the desired conjugate.
Applications of Antibody Conjugates
Antibody conjugates created through the Sulfo-SMCC crosslinking method find applications in various domains of biomedical research:
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): Enzyme-conjugated antibodies are fundamental in ELISA, enabling the detection and quantification of specific antigens with high sensitivity and specificity.
- Peptide Conjugates: Antibody-peptide conjugates can be employed to target specific cell signaling pathways or for drug delivery, providing a platform for precision medicine.
- Fluorescent Labeling: Fluorophore-conjugated antibodies are vital in fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, and immunofluorescence assays, allowing researchers to visualize and analyze cellular structures and processes.
The Sulfo-SMCC heterobifunctional crosslinking reagent has revolutionized the way scientists conjugate antibodies with enzymes, peptides, or fluorophores, enhancing the precision and versatility of their research. This versatile technique is a cornerstone of modern biomedical research, enabling the development of advanced diagnostic assays, targeted therapies, and a deeper understanding of biological processes.